
Pandemic Insurance Hidden Health Costs
Unexpected health insurance surprise possible when pandemic insurance programs expire sets the stage for a potentially costly transition. Many individuals relied on these programs during the pandemic, but as they wind down, unforeseen expenses may arise. This exploration dives deep into the expiration of these programs, examining the financial impacts on individuals, healthcare providers, and the system as a whole.
We’ll look at the different programs, their coverage, and the possible consequences of their end, equipping readers with the knowledge and strategies to navigate this evolving landscape.
This article will discuss the various types of pandemic insurance programs, their expiration dates, and the resulting financial implications for individuals, healthcare providers, and the overall healthcare system. We’ll explore the reasons behind program terminations, the potential increases in out-of-pocket costs, and the potential impact on healthcare premiums. We’ll also delve into potential strategies individuals can use to mitigate the impact of program expiration and find alternative healthcare options.
Understanding Pandemic Insurance Programs

Navigating the complexities of healthcare during a pandemic often necessitates specialized insurance programs. These programs, designed to address the unique challenges and financial burdens posed by outbreaks, offered a safety net for individuals and businesses. Understanding their structure, coverage, and limitations is crucial for anyone seeking to understand the landscape of healthcare insurance.
Types of Pandemic Insurance Programs
Various types of pandemic insurance programs emerged during the pandemic era. These included government-sponsored programs, employer-sponsored initiatives, and private insurance options. Each type had distinct characteristics and served a particular purpose.
Coverage Offered by Pandemic Programs
Pandemic insurance programs generally provided coverage for expenses related to the pandemic, such as medical costs, lost wages, and business interruption. Specific coverage varied by program. Some focused on direct medical expenses, while others extended to supplemental income support during periods of illness or quarantine. Essential elements of coverage typically included, but were not limited to, medical care, wage replacement, and financial assistance for businesses impacted by the pandemic.
Eligibility Criteria for Pandemic Programs
Eligibility criteria for pandemic insurance programs were determined by factors like location, employment status, and the nature of the claimed expenses. Government-backed programs often had specific income thresholds and geographic limitations. Employer-sponsored programs typically depended on the employer’s participation and employee eligibility based on their employment status and tenure. Private insurance coverage, if available, varied based on the individual policy and the specific circumstances of the insured.
Funding Mechanisms for Pandemic Programs
Funding for pandemic insurance programs stemmed from diverse sources. Government programs were often financed through tax revenue and dedicated funds. Employer-sponsored programs relied on employer contributions, often matched by employee contributions. Private insurance companies used premiums paid by policyholders to cover pandemic-related expenses. The interplay between these funding mechanisms varied significantly across different programs, impacting their sustainability and long-term viability.
Key Features of Pandemic Programs
The defining characteristics of these programs included their temporary nature, their responsiveness to the evolving pandemic, and their emphasis on financial support. Programs often included specific timelines for coverage and eligibility periods. Their structure aimed to address the immediate needs arising from the pandemic, while acknowledging the unpredictable nature of the crisis. Their effectiveness in meeting the demands of the public varied.
Comparison of Pandemic Insurance Programs
| Program Name | Coverage | Eligibility | Funding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Government-sponsored Covid-19 relief programs | Medical expenses, unemployment benefits, business grants | Based on income, location, and eligibility criteria | Tax revenue, dedicated funds |
| Employer-sponsored pandemic plans | Supplemental income, health benefits | Dependent on employer participation and employee status | Employer contributions, employee contributions (if applicable) |
| Private insurance pandemic riders/policies | Medical expenses, lost wages, depending on the policy | Dependent on policy specifics and eligibility requirements | Premiums paid by policyholders |
Expiration of Pandemic Insurance Programs
The expiration of pandemic insurance programs, designed to provide temporary financial relief during crises, raises critical questions about the future of coverage and the adequacy of existing systems. Understanding the reasons behind these expirations, the timelines involved, and the potential consequences is crucial for individuals and businesses navigating uncertain times.Expiration of these programs is often driven by a combination of factors, including budget constraints, shifting public health priorities, and the evolving economic landscape.
The desire to transition to more sustainable and permanent solutions, along with a recognition that temporary measures are not ideal long-term solutions, frequently leads to the phasing out of such programs.
Ugh, pandemic insurance programs expiring? That could mean a nasty health insurance surprise down the road. Thankfully, good news for breast health in the community! The Stevens Points Breast Care Center recently received redesignation, a great resource for local women , which is definitely a positive development. But don’t forget, those expiring pandemic programs could leave some people scrambling to find coverage, so be prepared for potential issues when the time comes.
Common Reasons for Expiration
Many pandemic insurance programs were initially designed as temporary measures. These programs aimed to provide crucial support during the acute phase of the pandemic, with the understanding that the need for such extensive financial assistance would eventually diminish. As the crisis subsided and the economy began to recover, the rationale for continued funding for these programs weakened. Furthermore, the initial funding allocated for these programs was often limited, which contributed to the necessity of their expiration.
Timeline of Expiration for Different Programs
Different pandemic insurance programs had varying timelines for expiration. Some programs ended abruptly after a few months, while others had a more gradual phasing-out process. The specific timeline for each program depended on factors like the program’s design, the severity and duration of the pandemic’s impact on the economy, and the availability of continued funding. A precise timeline cannot be universally stated without specifying the particular program.
Legal and Regulatory Aspects
The legal and regulatory framework surrounding the expiration of pandemic insurance programs often involved specific legislation and guidelines established during the pandemic. These guidelines Artikeld the conditions for program eligibility, the duration of coverage, and the mechanisms for the termination of the programs. The specifics of these legal aspects varied widely depending on the country and the specific program in question.
Reviewing relevant legislation is essential to fully understand the legal considerations.
Potential Consequences of Program Expiration
The expiration of pandemic insurance programs can have significant consequences for individuals and businesses who relied on them for support. For example, some individuals might face financial hardship as a result of losing access to crucial support programs. Businesses might experience difficulties in maintaining operations or facing reduced profitability due to a sudden withdrawal of support. These consequences can vary significantly based on the specific program and the individuals/businesses affected.
Ugh, the thought of pandemic health insurance expiring is a bit terrifying. We’re all hoping for a smooth transition, but there’s a potential for some serious surprises when those programs disappear. Thankfully, organizations like sustaining our waters the fox wolf watershed alliance are working hard to protect and restore our natural resources, and maybe that same dedication and planning can help us avoid those unexpected health insurance bills.
I’m crossing my fingers that we can navigate this potential crisis without too much trouble.
The impact often depends on the availability of alternative support systems and the resilience of the affected sectors.
Timeline of Expiration of Key Programs (Illustrative Example)
| Program Name | Initial Start Date | Expiration Date |
|---|---|---|
| Pandemic Unemployment Assistance (PUA) | March 2020 | September 2021 |
| Emergency Rental Assistance (ERA) | April 2020 | December 2022 |
| Small Business Administration (SBA) Loans | March 2020 | Various Dates |
Note: This table provides a general illustration and is not exhaustive. Specific dates and programs will vary depending on the jurisdiction.
Unexpected Health Insurance Surprises
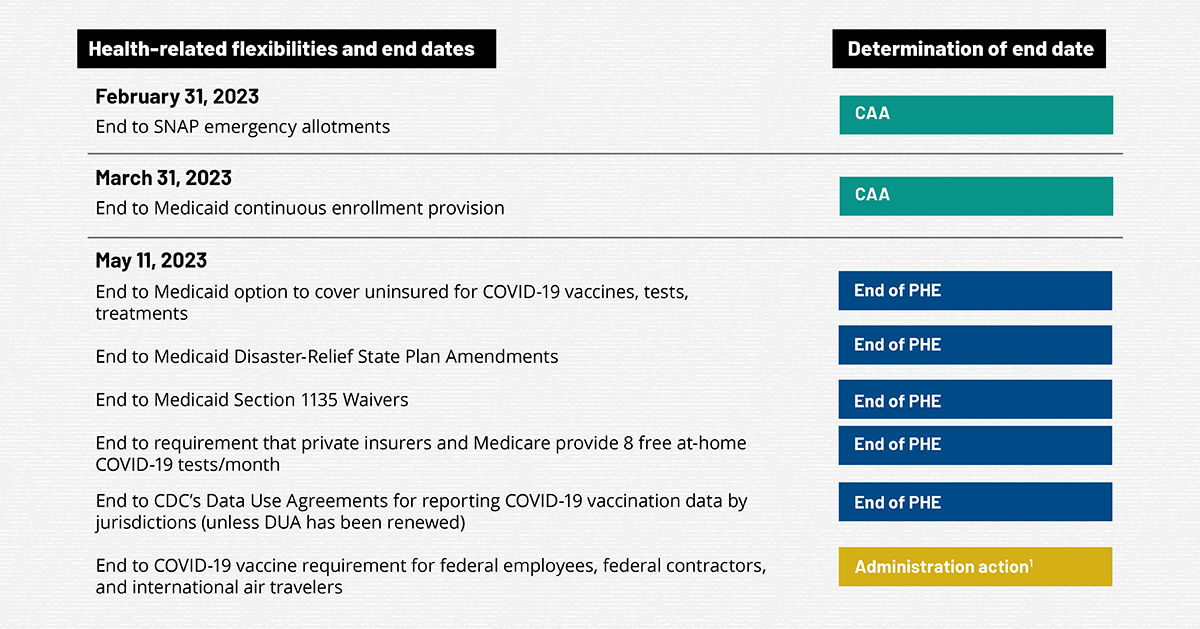
The expiration of pandemic-era health insurance programs presents a significant financial challenge for many individuals. These programs, designed to offer temporary relief during a period of extraordinary health needs, are now vanishing, leaving a void in coverage that could lead to substantial out-of-pocket expenses. Understanding the potential impacts is crucial for proactive planning and financial preparedness.The expiration of pandemic insurance programs is poised to have a considerable impact on individuals’ financial stability.
The temporary subsidies and expanded benefits offered during the pandemic are now gone, and the responsibility for healthcare costs shifts back to individual consumers. This transition can create unforeseen expenses and financial strain for those who relied on these programs.
Financial Impact of Program Expiration
The absence of pandemic-era insurance programs will likely result in increased out-of-pocket costs for healthcare services. Individuals who previously had coverage or lower premiums due to these programs may now face significantly higher costs for doctor visits, hospital stays, and other medical needs. This shift can be particularly challenging for those with pre-existing conditions or those who require ongoing medical care.
So, pandemic insurance programs are expiring, and that could leave you facing a nasty health insurance surprise. Thinking about selling your business? Consider these five tips for a smooth transition: five tips for selling a business. You might be able to use some of those strategies to prepare for the unexpected cost increases you might see as these programs vanish.
It’s a good idea to plan ahead and potentially factor in those unexpected expenses.
Potential Increase in Out-of-Pocket Costs
The elimination of pandemic-era health insurance provisions will likely lead to higher out-of-pocket costs for various healthcare services. Individuals may encounter higher deductibles, co-pays, and co-insurance amounts, which will translate to direct financial burdens. The cessation of these programs could significantly impact individuals who rely on them for their essential medical expenses.
Potential Changes in Health Insurance Premiums
The expiration of these programs may trigger adjustments in health insurance premiums for individuals. Insurers may raise premiums to account for the increased risk and demand, potentially leading to higher monthly payments for health insurance. This adjustment may affect individuals who are already struggling with rising healthcare costs.
Scenarios of Unexpected Healthcare Costs
Individuals could experience unexpected healthcare costs due to program expiration in several scenarios. For example, someone with a pre-existing condition who had a temporary reduction in out-of-pocket costs under the pandemic programs might now face a significant increase in medical expenses. Similarly, a sudden illness requiring hospitalization could lead to substantial bills for those without adequate coverage.
Common Misconceptions
A common misconception is that the expiration of these programs won’t affect individuals with existing health insurance plans. In reality, the expiration of pandemic-era insurance programs can affect the cost of healthcare, regardless of whether someone has a standard health insurance plan. These programs could have been acting as a supplementary or temporary relief mechanism, and their disappearance could lead to unexpected costs.
Another misconception is that the increased costs will only affect those with low incomes. This isn’t necessarily true; increased costs can affect people from all income levels.
Preparing for Potential Surprises
Individuals can prepare for potential unexpected healthcare costs by evaluating their current health insurance coverage and understanding their out-of-pocket responsibilities. This includes reviewing their deductibles, co-pays, and co-insurance amounts. Budgeting for potential increases in healthcare expenses is also important, and exploring options for supplemental coverage can help mitigate financial risks.
Potential Financial Impacts
| Coverage Type | Impact on Out-of-Pocket Costs | Impact on Premiums |
|---|---|---|
| Individuals with pre-existing conditions | Potentially significant increase in out-of-pocket costs for medical treatments. | Premiums may increase to reflect the higher risk associated with these conditions. |
| Individuals requiring ongoing medical care | Higher costs for treatments and medication. | Potential for increased premiums as insurers account for the continuous care needs. |
| Individuals without adequate health insurance | Significant increase in out-of-pocket expenses for basic medical needs. | Premiums will likely rise for the uninsured as demand for coverage increases. |
Alternatives and Strategies for Individuals: Unexpected Health Insurance Surprise Possible When Pandemic Insurance Programs Expire
The expiration of pandemic-era health insurance programs presents a significant challenge for many individuals. Navigating the transition to new coverage options and healthcare systems requires careful planning and understanding of available resources. This section details strategies to mitigate the impact of program expiration and effectively manage healthcare costs.
Potential Strategies for Mitigation
Several strategies can help individuals prepare for the shift in healthcare coverage. Prioritize building an emergency fund to cover unexpected medical expenses. Research and compare different healthcare options to find the most suitable and affordable plan. Investigate potential financial assistance programs, including those offered by state and local governments.
Healthcare System Navigation, Unexpected health insurance surprise possible when pandemic insurance programs expire
Understanding the healthcare system is crucial. Learn about your rights and responsibilities as a patient, including how to access care, understand bills, and resolve disputes. Familiarize yourself with the different types of healthcare providers and their specialties. This knowledge empowers you to make informed decisions and effectively navigate the healthcare system.
Comparison of Healthcare Options
Different healthcare options offer varying levels of coverage and cost. This comparison provides a framework for evaluating your needs.
| Option | Cost | Coverage | Accessibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| Health Insurance Marketplace Plans | Variable, depending on plan and individual factors | Varying levels of coverage, from basic to comprehensive | Accessible through online portals and insurance agents |
| Short-Term Health Insurance Plans | Generally lower premiums than traditional plans | Limited coverage period and types of conditions | Accessible through insurance brokers and online platforms |
| Catastrophic Health Plans | Low monthly premiums | Minimal coverage for catastrophic illnesses or injuries | Accessible through the marketplace |
| Uninsured Options | High out-of-pocket costs | No coverage for most medical services | May require accessing public health clinics or emergency rooms |
| Healthcare Sharing Ministries | Variable | Based on religious principles, often with limited medical coverage | Varying accessibility depending on the ministry’s policies |
Financial Assistance Programs
Financial assistance programs are available to help individuals with healthcare costs. These programs can provide subsidies, grants, or other forms of financial support. Contact your state’s health department, local social services agencies, or non-profit organizations to explore available resources. Also, investigate employer-sponsored healthcare options, if applicable.
Budgeting for Healthcare Expenses
Creating a healthcare budget is essential. Track all medical expenses, including premiums, co-pays, and out-of-pocket costs. Develop a plan for managing unexpected expenses and prioritize preventive care to reduce the likelihood of costly treatments. Set aside a portion of your income for healthcare costs each month. Example: Allocate 10% of your monthly income to a dedicated healthcare savings account.
Impact on Healthcare Providers and Systems
The expiration of pandemic insurance programs will likely trigger significant shifts in the healthcare landscape, impacting providers, systems, and ultimately, patient access. These changes will ripple through the entire healthcare ecosystem, demanding careful consideration and proactive strategies from all stakeholders.The transition away from these programs necessitates a comprehensive understanding of the potential consequences for healthcare providers and systems. Analyzing the implications on reimbursement, service utilization, and capacity is crucial for mitigating negative impacts and ensuring continued access to care.
This examination also sheds light on the broader economic implications for the sector, highlighting the need for robust adaptation and support.
Potential Impact on Healthcare Providers
The expiration of pandemic insurance programs will directly affect healthcare providers’ revenue streams. Providers who heavily relied on the expanded coverage for services like telehealth and COVID-19 testing will likely experience a substantial decrease in reimbursement. This change will necessitate adjustments in service offerings and pricing strategies to compensate for the reduced revenue.
Revenue Changes Faced by Providers
- Reduced reimbursements for telehealth services: Telehealth, which became more prevalent during the pandemic, may see a significant drop in reimbursement as the programs expire. This could force providers to adjust their telehealth offerings or potentially increase their fees to maintain profitability. For example, a primary care physician who heavily relied on telehealth for preventative care might see a decline in patient volume and a reduction in revenue if patients are no longer covered.
- Decreased demand for certain specialized services: Demand for services directly related to the pandemic, such as COVID-19 testing and treatment, is likely to decrease significantly. Providers offering these services will need to adapt their practices or seek alternative revenue streams.
- Shift in patient demographics: The expiration of pandemic insurance programs might lead to a shift in the patient demographics that providers serve. This could affect the mix of patients with various insurance plans, which may require providers to adjust their pricing strategies and service offerings to remain financially viable.
Service Adjustments by Providers
- Potential reduction in telehealth services: Providers might reduce the availability or scope of telehealth services, potentially impacting access to care, especially in rural or underserved areas.
- Adjustment in pricing strategies: Providers will likely adjust their pricing structures to compensate for the reduced reimbursements and potential decreases in patient volume. This could lead to increased out-of-pocket costs for patients.
- Re-evaluation of service portfolios: Providers will need to re-evaluate their service portfolios, potentially focusing on areas where reimbursement remains stable or where demand is anticipated to remain high.
Impact on Healthcare System Capacity
The expiration of these programs could strain healthcare system capacity. Reduced reimbursements could lead to decreased staffing and a reduction in resources allocated to areas impacted by the decreased demand. This could result in delays in service delivery and reduced access to care, particularly for vulnerable populations.
Consequences for Healthcare Access and Equity
The changes in provider reimbursement and service utilization could disproportionately affect vulnerable populations. Those without alternative coverage options may face significant barriers to accessing essential healthcare services. This could exacerbate existing health disparities and negatively impact health outcomes.
Broader Economic Impact on the Healthcare Sector
The expiration of pandemic insurance programs could lead to a broader economic impact on the healthcare sector. Decreased demand for services, reduced reimbursements, and potential staff reductions could result in decreased economic activity within hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare organizations.
Framework for Understanding Impact on Healthcare Providers
| Provider Type | Revenue Changes | Service Adjustments |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Care Physician | Potential decrease in telehealth reimbursement, possible shift in patient demographics. | Reduction in telehealth offerings, potential adjustment in office visit fees. |
| Specialized Clinics (COVID-19 testing) | Significant decrease in revenue due to reduced demand. | Re-evaluation of services, exploration of alternative revenue streams (e.g., non-COVID-19 testing). |
| Rural Hospitals | Potential decrease in revenue from pandemic-related services, shift in patient mix. | Possible reduction in staff, reassessment of service offerings to cater to new patient mix. |
Government and Regulatory Responses

The expiration of pandemic-era health insurance programs presents a complex challenge, demanding swift and effective government and regulatory responses. These responses will directly impact individuals’ access to healthcare, the financial stability of healthcare providers, and the overall functioning of the healthcare system. Navigating this transition requires careful consideration of the potential consequences for all stakeholders.The regulatory environment surrounding healthcare access and costs is crucial in mitigating the impact of program expiration.
A well-defined regulatory framework can ensure a smooth transition, minimizing disruption and protecting vulnerable populations. Government interventions, including policy adjustments and potential financial support, will play a significant role in this process.
Government Actions and Proposed Actions
The expiration of pandemic-era insurance programs will likely trigger a variety of government actions, both at the federal and state levels. These actions will vary in scope and approach, reflecting the diverse needs and priorities of different communities. Some possible actions include expanding existing healthcare programs or developing new ones, providing financial assistance to individuals and healthcare providers, and revising regulations to better address the potential increases in healthcare costs.
Regulatory Environment Concerning Healthcare Access and Costs
The regulatory environment surrounding healthcare access and costs plays a pivotal role in shaping the impact of pandemic insurance program expiration. Current regulations, including those governing insurance premiums, provider reimbursement rates, and consumer protections, will need to be examined and potentially adjusted to ensure continued access to affordable healthcare. This requires careful consideration of the evolving healthcare landscape and the unique challenges faced by different segments of the population.
Role of Regulatory Bodies in Managing the Transition
Regulatory bodies, such as the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) and state insurance departments, will play a crucial role in managing the transition. These bodies are responsible for overseeing the implementation of policies and regulations related to healthcare access and costs. Their actions will determine how smoothly the transition unfolds and how effectively the needs of individuals and healthcare providers are addressed.
This includes ensuring compliance with new regulations and providing guidance to stakeholders.
Potential for Policy Changes in Response to Challenges
The expiration of pandemic insurance programs may prompt significant policy changes. Policymakers may introduce new regulations or revise existing ones to address the challenges arising from the transition. These changes may focus on affordability, access to care, and the sustainability of the healthcare system. For example, a possible policy change could involve expanding eligibility criteria for existing programs or implementing new financial assistance programs to help individuals manage increased healthcare costs.
Potential Impact on Individuals and Healthcare Providers
The government and regulatory responses to the expiration of pandemic insurance programs will have a direct impact on individuals and healthcare providers. Individuals may experience increased healthcare costs, reduced access to care, or difficulties in maintaining health insurance coverage. Healthcare providers may face financial strain due to reduced reimbursement rates or increased administrative burdens. These potential impacts highlight the importance of proactive and well-coordinated government responses to ensure a smooth transition.
Illustrative Case Studies
The expiration of pandemic-era health insurance programs has created a ripple effect, impacting individuals, healthcare providers, and communities. Understanding the potential consequences requires examining real-world scenarios. These case studies highlight the diverse challenges and potential solutions related to the transition.
A Fictional Case Study of Unexpected Health Costs
Maria, a 35-year-old single mother, relied on the pandemic-era expanded health insurance coverage. Her pre-existing condition, requiring ongoing medication and specialist visits, was covered under the expanded plan. When the program ended, her premiums skyrocketed, exceeding her affordable budget. She lost her job shortly after, exacerbating her financial situation. Seeking alternative coverage, she explored various options, but her pre-existing condition made it difficult to find affordable plans.
Maria’s case illustrates the sudden financial burden and healthcare access challenges faced by many individuals when pandemic-era programs expire.
Impact on a Healthcare Provider
A small, rural clinic in the Appalachian Mountains primarily serves a population with high rates of chronic diseases. The clinic relied on the pandemic-era programs for a substantial portion of its patient base. When these programs ended, the clinic experienced a significant drop in patient volume and revenue. This led to decreased staffing levels, limited access to specialists, and reduced services, ultimately impacting the overall health of the community.
The clinic’s situation demonstrates the interconnectedness of healthcare access and financial sustainability.
Impact on a Specific Geographic Area
The state of Nevada experienced a substantial increase in uninsured individuals following the expiration of the pandemic-era health insurance programs. Areas with lower incomes and higher rates of pre-existing conditions faced the greatest burden. The increased demand on emergency rooms and clinics, coupled with a reduction in preventative care, created a significant strain on the healthcare system in those areas.
The long-term implications included a decrease in overall health outcomes and a rise in healthcare costs.
Impact on Vulnerable Populations
The expiration of pandemic-era programs disproportionately affected vulnerable populations, including low-income families, individuals with pre-existing conditions, and those in rural areas. These groups often lack the resources to navigate complex insurance markets and secure affordable coverage. Limited access to healthcare services and increased financial burdens could lead to worsening health outcomes and exacerbate existing health disparities. This illustrates the critical role of government interventions in supporting these vulnerable populations.
Potential Impact of Different Government Responses
Different government responses to the expiration of pandemic-era programs would have varying impacts. A proactive government response, offering subsidies or tax credits for individuals, could mitigate the negative effects and maintain coverage for vulnerable populations. A less proactive approach could result in a significant increase in the uninsured population, impacting healthcare access and costs.
Effect of Proactive Planning by Individuals
Individuals who proactively researched alternative coverage options before the expiration date were better positioned to navigate the transition. By comparing various plans and understanding their individual needs, they could secure affordable and suitable coverage. Individuals with pre-existing conditions should have proactively investigated plans that specifically accommodate those conditions. This demonstrates the importance of preparedness and understanding one’s healthcare needs.
Last Point
The expiration of pandemic insurance programs presents a complex web of challenges and opportunities. Individuals need to understand the potential financial surprises and proactively plan to avoid unexpected healthcare costs. Healthcare providers and systems will also need to adapt to the changing landscape. This article has highlighted the importance of understanding these changes, exploring alternative options, and engaging with policymakers to ensure a smooth and equitable transition.
The government’s response will be crucial in mitigating potential hardships and ensuring continued access to quality healthcare for all.

