
The Who What Where When and Why of SVB Failure
The who what where when and why of SVB failure. Silicon Valley Bank’s sudden collapse sent shockwaves through the financial world, prompting intense scrutiny of its practices and the broader banking sector. This in-depth look delves into the bank’s history, the events leading to its downfall, and the wider implications for the economy and financial institutions.
From its origins as a regional bank catering to tech startups to its sudden demise, the narrative reveals the intricate interplay of financial pressures, market fluctuations, and regulatory responses. We’ll examine the key players, the timeline of events, and the critical decisions that ultimately led to SVB’s failure, exploring the systemic factors at play.
Background of SVB

Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) was a regional bank specializing in serving the needs of technology companies and startups in the San Francisco Bay Area. Founded in 1983, SVB built a reputation for understanding and catering to the unique financial requirements of this dynamic sector. Its success was largely tied to its ability to provide specialized financial services to a rapidly growing and evolving market.The bank’s history is intertwined with the rise of Silicon Valley’s tech industry.
It played a critical role in financing innovation and expansion within this ecosystem. However, the bank’s sudden collapse in March 2023 highlighted vulnerabilities in the financial system and the importance of careful risk management.
Key Services and Products
SVB offered a range of financial products and services tailored to the specific needs of its customer base. These included deposit accounts, lending, investment products, and wealth management solutions. The bank’s core strength was its ability to understand and meet the specific financial demands of technology companies at various stages of growth. For example, SVB provided tailored lending options for startups, venture capital firms, and established tech companies, ensuring their needs were met effectively.
Target Market and Customer Base
SVB’s primary target market comprised technology companies, venture capital firms, and entrepreneurs in the Silicon Valley area. Its customer base included startups, established tech companies, and high-net-worth individuals involved in the tech sector. The bank recognized the unique financial challenges faced by these businesses and provided tailored services to address them effectively. The bank actively catered to the specific needs of each segment, from early-stage startups to established enterprises.
Financial Performance
SVB’s financial performance was marked by consistent growth over the years. The bank’s success was driven by its focus on the tech sector and its ability to understand and meet the specific financial needs of its customers. However, the bank’s financial health was significantly impacted by the changing economic conditions and market dynamics.
| Year | Revenue (USD Millions) | Assets (USD Billions) | Key Events |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 1,500 | 100 | Continued growth in deposits and loans; expansion of services |
| 2021 | 1,800 | 150 | Further expansion; acquisition of smaller institutions |
| 2022 | 2,200 | 200 | Increased market share; interest rate adjustments |
| 2023 (pre-failure) | 2,500 | 220 | Growing concern about bond portfolio and rising interest rates |
The table above illustrates a trend of increasing revenue and assets for SVB, but it is important to note that these figures are not definitive and should be verified from official sources.
Triggers of the Failure
Silicon Valley Bank’s (SVB) rapid collapse was a stark reminder of the interconnectedness and fragility within the financial system. The bank, a cornerstone of the tech industry, crumbled under a confluence of factors, highlighting vulnerabilities that had been present, though perhaps underestimated, for some time. Understanding these triggers is crucial for learning from this incident and preventing similar events in the future.The primary triggers of SVB’s failure revolved around a rapid shift in interest rates and the bank’s unique business model, particularly its heavy reliance on deposits from technology companies.
This model, while seemingly lucrative, proved to be exceptionally vulnerable when confronted with unforeseen market changes.
Key Events Leading to the Decline, The who what where when and why of svb failure
SVB’s predicament stemmed from a combination of events that progressively eroded its financial stability. The significant rise in interest rates, coupled with the subsequent shift in market expectations, proved to be the final straw.
The recent Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) failure highlighted the fragility of the financial system, especially when considering the “who,” “what,” “where,” “when,” and “why” behind it. Understanding the intricate web of interconnected institutions and their risky lending practices is crucial. Ultimately, a lack of transparency and genuine commitment to sound financial principles—a key aspect of authenticity is essential to brand building —can have devastating consequences, as seen in the fallout from SVB.
This failure serves as a stark reminder of the importance of robust regulations and ethical practices in the financial sector.
- Federal Reserve Interest Rate Hikes (2022): The Federal Reserve’s aggressive campaign to combat inflation resulted in a substantial increase in interest rates. This directly impacted SVB’s profitability, as its loan portfolio’s returns were not keeping pace with the higher borrowing costs. The bank’s considerable holdings of long-term securities, typically carrying lower yields, further exacerbated the situation.
- Market Volatility and Investor Concerns (Q1 2023): Uncertainty in the market, fueled by rising interest rates and economic concerns, led to increased investor anxiety. This, in turn, triggered a wave of withdrawals from SVB, as depositors sought safer alternatives. The domino effect was amplified by the bank’s reliance on attracting deposits from a relatively concentrated segment of the market. The initial withdrawals, though seemingly small, created a cascading effect that proved difficult to contain.
- Bank Run and Liquidity Crisis (March 2023): The loss of confidence in SVB’s ability to meet its obligations led to a substantial outflow of funds. This phenomenon, known as a bank run, quickly escalated, leaving the bank with insufficient liquidity to meet its withdrawal demands. The situation mirrored previous financial crises, demonstrating the rapid and potentially devastating nature of a loss of trust in a financial institution.
Financial Pressures on SVB
SVB’s business model, which prioritized deposits from technology startups, proved to be a double-edged sword. The rapid growth of the tech sector was initially beneficial but made the institution highly sensitive to changes in the market.
- Reliance on Tech Sector Deposits: SVB’s heavy reliance on deposits from technology companies exposed the institution to the cyclical nature of the sector. Economic downturns or shifts in market sentiment can significantly impact these deposits, as seen in the case of SVB.
- Low-Yielding Securities Portfolio: The bank’s significant holdings of long-term, low-yielding securities proved insufficient to offset the higher interest rates and decreased market valuations. This misalignment between the interest rates and the bank’s asset portfolio contributed significantly to the bank’s liquidity issues.
- Valuation Mismatch: The perceived value of SVB’s assets didn’t accurately reflect the changing market conditions. The bank’s balance sheet, with its heavy emphasis on illiquid assets, proved vulnerable to sudden shifts in investor confidence.
Comparison with Other Institutions
The failure of SVB highlighted similarities and differences with other institutions experiencing financial difficulties. While each case has its unique characteristics, the underlying themes of liquidity issues and market volatility often emerge as common denominators.
- Other Banks Experiencing Similar Issues: Other financial institutions have faced similar pressures related to interest rate hikes and market volatility, though the magnitude of the impact has varied. Analyzing these cases can provide valuable insights into the systemic vulnerabilities that can lead to failures.
- The Role of Market Volatility: Market volatility plays a crucial role in creating the conditions for bank runs. Fluctuations in interest rates, economic anxieties, and broader market uncertainties can quickly escalate into crises, as seen in the SVB case.
Role of Interest Rate Hikes
The Federal Reserve’s aggressive interest rate hikes played a critical role in SVB’s downfall. The mismatch between the bank’s asset portfolio and the rapidly rising interest rates created significant financial pressures.
- Impact on Asset Values: The significant increase in interest rates impacted the value of SVB’s holdings, leading to potential losses that were not adequately accounted for.
- Higher Borrowing Costs: The higher interest rates increased the cost of borrowing for SVB, putting further strain on its financial position.
Timeline of Events
| Date | Event | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 2022 | Federal Reserve begins raising interest rates | Increased borrowing costs, reduced returns on existing securities |
| Q1 2023 | Market volatility and investor concerns increase | Increased withdrawals, erosion of confidence |
| March 2023 | Significant deposit outflows trigger a bank run | Insufficient liquidity to meet withdrawal demands |
| March 2023 | SVB is taken over by the FDIC | Significant financial loss for depositors |
The “What” of the Failure
Silicon Valley Bank’s (SVB) collapse was a catastrophic event, highlighting the intricate interplay of factors that can lead to the downfall of even seemingly stable financial institutions. The failure exposed vulnerabilities in the banking system and raised concerns about the adequacy of regulatory oversight. Understanding the “what” requires dissecting the mechanisms that triggered the collapse, analyzing the bank’s financial position, and evaluating the impact on depositors.
Mechanisms of Collapse
SVB’s downfall was precipitated by a confluence of events, primarily related to its substantial exposure to technology company debt and the rapid shift in interest rates. The bank’s investment portfolio, heavily weighted toward long-term securities, was significantly impacted by rising interest rates. This resulted in substantial unrealized losses as the market value of these assets declined. Furthermore, the substantial outflows of deposits from SVB’s customers, driven by concerns regarding the bank’s stability, accelerated the bank’s liquidity crisis.
Breakdown of Assets and Liabilities
SVB’s balance sheet, prior to its collapse, displayed a significant concentration of assets in government bonds and mortgage-backed securities. A substantial portion of its liabilities were comprised of deposits from technology companies and startups. The rapid erosion of the value of its assets, coupled with the significant withdrawal of deposits, created a liquidity crisis that the bank was unable to overcome.
The significant portion of its assets held in long-term bonds made it vulnerable to rising interest rates. These bonds, when held for a longer duration, experienced a decline in their market value. This significant decline was not fully accounted for in the bank’s reported assets, leading to substantial unrealized losses.
Nature of Losses Incurred
The losses incurred by SVB were multifaceted. The bank experienced significant unrealized losses due to the decline in the market value of its assets, particularly long-term government bonds and mortgage-backed securities. These unrealized losses, coupled with the substantial outflows of deposits, created a liquidity crisis that ultimately led to the bank’s insolvency. The losses were not only financial but also reputational, impacting the confidence in the entire banking system.
Impact on Depositors
The failure of SVB had a devastating impact on its depositors. Many depositors, particularly those from the technology sector, lost a substantial portion of their savings. The FDIC’s intervention, while providing some protection, did not fully compensate depositors for their losses. The swiftness and scale of the crisis underscore the vulnerability of depositors when a bank experiences a sudden liquidity crisis.
Many depositors faced significant financial hardship, impacting their personal and business operations.
Comparison of SVB’s Assets
| Asset Category | Description | Approximate Value (Illustrative, in billions USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Government Bonds | Long-term government bonds, typically considered low-risk | ~10 |
| Mortgage-Backed Securities | Securities backed by mortgages, potentially carrying higher risk | ~15 |
| Loans to Technology Companies | Loans to technology firms, potentially with higher risk and longer repayment periods | ~5 |
| Cash and Cash Equivalents | Liquid assets, readily available for meeting immediate obligations | ~2 |
Note: The values in the table are illustrative and not actual figures. The specific proportions of each asset category varied.
The “Where” of the Failure: The Who What Where When And Why Of Svb Failure
The Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) collapse reverberated far beyond the tech industry, impacting a diverse range of businesses and individuals. Understanding the geographical footprint of SVB’s operations and the cascading effects on various regions is crucial to grasping the full extent of the crisis. This analysis will delve into the locations of SVB’s branches and offices, highlight the specific regions and industries affected, and demonstrate the interconnectedness of financial markets in the context of this failure.The geographical impact of SVB’s collapse wasn’t confined to a single region or industry.
The failure triggered a ripple effect, impacting financial institutions and businesses relying on SVB for services, showcasing the interconnected nature of global finance.
Geographical Reach of SVB
SVB maintained a significant presence across the United States, particularly in California, where its headquarters were located. This concentrated presence within the Silicon Valley area had a direct and profound impact on tech startups and venture capital firms. However, the failure’s effects extended beyond the immediate area. SVB’s branches and offices were strategically placed to serve a wide range of clients.
Impact on Specific Regions and Industries
The tech industry, particularly startups and venture capital firms heavily reliant on SVB for funding, suffered the most direct impact. These firms often utilized SVB’s services for deposit accounts, loans, and other financial needs. The collapse resulted in significant disruptions to their operations, potentially hindering innovation and job creation. Beyond the tech sector, the collapse also had consequences for other businesses and individuals who held deposits with SVB.
Interconnectedness of Financial Markets
The SVB failure underscored the interconnectedness of financial markets. SVB’s significant role in the financial ecosystem meant that its collapse had cascading effects on other financial institutions, particularly those holding SVB securities. The uncertainty and fear created by this event led to a wider tightening of credit markets, impacting lending activities across the board. The contagion effect demonstrated the vulnerability of the financial system when a major player experiences failure.
Affected Regions and Industries
- California: SVB’s headquarters and many of its branches were located in California, leading to significant disruption within the state’s tech ecosystem. The collapse directly impacted thousands of startups, venture capital firms, and other businesses dependent on SVB’s services.
- Other States: SVB maintained a presence across other states, although less extensive than in California. The impact on these states, while less dramatic, was still felt by individuals and businesses with accounts and loans. The interconnectedness of the financial system meant that the repercussions were felt even in regions not directly served by SVB.
- Global Impact: The fallout from SVB’s collapse was not limited to the United States. The crisis highlighted the vulnerability of global financial systems to shocks originating in specific regions. This event demonstrated the necessity of robust risk management and regulatory frameworks to prevent similar crises from occurring in the future. The fear and uncertainty generated by SVB’s collapse led to increased volatility in international financial markets.
Illustrative Map
A map depicting the geographic distribution of SVB’s branches and offices would highlight the concentration of impact in California and the broader regional effects. The map could also visually represent the interconnectedness of financial markets by showing how the failure spread to other institutions and regions. The visualization would clearly demonstrate the cascading impact of the crisis.
The “When” of the Failure
The collapse of Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) wasn’t a sudden event, but rather a cascading series of events triggered by a confluence of factors. Understanding the timeline of these events is crucial to comprehending the speed and severity of the crisis. The rapid deterioration of SVB’s financial health highlights the importance of vigilance in the financial sector and the potential for unforeseen shocks.
Timeline of Events Leading to SVB’s Collapse
This timeline illustrates the crucial dates and events that ultimately led to SVB’s failure. Each event had cascading consequences, accelerating the bank’s descent into crisis.
| Date | Event | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Early 2022 | Rising interest rates and the shift to a higher interest rate environment significantly impacted SVB’s portfolio of highly liquid assets. | Increased pressure on the bank’s profitability and solvency. |
| March 2023 | Significant outflows from SVB’s deposits, particularly from tech startups, due to fears about the bank’s health. | A notable loss of confidence in the bank’s financial stability. |
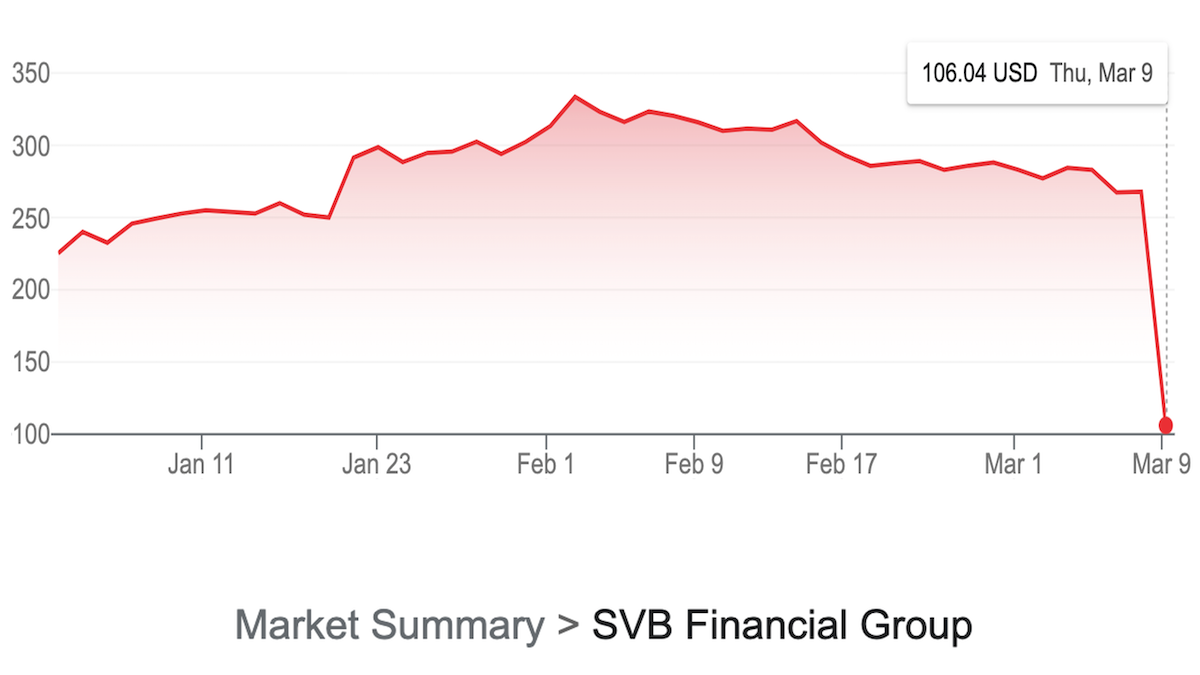
| March 9, 2023 | SVB announced a massive loss on its holdings of U.S. Treasury bonds and other securities, resulting in a negative net asset value. | Caused a significant drop in confidence and triggered a wave of withdrawals from customers. |
| March 10, 2023 | Federal Reserve, and other regulators, initiated emergency measures to address the liquidity crisis and to maintain stability in the financial system. | A significant effort to prevent a broader financial crisis. |
| March 10, 2023 | The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) took over SVB, a historic event and a significant intervention. | A major government intervention, intended to prevent a contagion effect, and to protect depositors. |
| March 13, 2023 | The FDIC announced that deposits would be fully covered, and SVB was officially declared insolvent. | Brought a degree of relief to depositors and prevented widespread panic. |
Comparison to Other Financial Crises
Comparing SVB’s failure to other financial crises reveals both similarities and unique characteristics. While past crises often involved complex financial instruments, SVB’s collapse was driven primarily by a rapid loss of confidence in its solvency, amplified by the outflows and the changing interest rate environment.
Timeframes of Regulatory Responses and Interventions
The speed of the regulatory response to SVB’s failure was notable. The FDIC’s swift action prevented a potentially catastrophic chain reaction, highlighting the importance of quick and decisive interventions in crisis situations. The timeframe for the intervention was crucial in mitigating the contagion risk.
The “Why” of the Failure
Silicon Valley Bank’s (SVB) collapse was a stark reminder of the interconnectedness and fragility of the financial system. Beyond the immediate triggers, a complex interplay of factors, including poor risk management, unsustainable lending practices, and the impact of rapidly changing interest rates, ultimately led to the bank’s demise. Understanding these underlying causes is crucial for preventing similar failures in the future.
Underlying Causes of the Collapse
SVB’s downfall wasn’t a single event but a culmination of several interconnected issues. The bank’s reliance on highly concentrated deposits from technology companies, coupled with aggressive lending strategies, proved unsustainable. This concentration of risk made the institution vulnerable to sudden shifts in market sentiment and liquidity pressures. Furthermore, SVB’s exposure to long-term, low-interest-rate investments proved to be a fatal flaw.
The bank’s assets were heavily invested in long-term US Treasury bonds, which depreciated in value as interest rates rose. This mismatch between asset and liability duration, combined with the need to meet deposit outflows, made the bank’s financial position untenable.
Role of Poor Risk Management and Lending Practices
SVB’s lending practices, particularly its focus on high-growth technology companies, were a significant contributor to its downfall. These companies often held substantial deposits in SVB, making the bank vulnerable to mass withdrawals. This reliance on a single sector created significant concentration risk. Furthermore, the bank’s risk management procedures were insufficient to address the evolving needs of its clientele and the market.
Poorly diversified loan portfolios and inadequate provisions for potential losses further exacerbated the situation. This resulted in substantial losses when market conditions shifted. SVB’s lending practices were insufficiently robust to withstand the impact of a rapid change in interest rates.
Effects of Rapid Interest Rate Changes
The rapid increase in interest rates, driven by the Federal Reserve’s efforts to combat inflation, played a crucial role in SVB’s failure. The rise in rates negatively impacted the value of the bank’s bond portfolio. As interest rates climbed, the value of the bank’s long-term, fixed-income securities decreased. This loss of value had a cascading effect on the bank’s capital reserves, making it more vulnerable to potential liquidity crises.
A significant mismatch between the duration of assets and liabilities proved to be a critical factor in the bank’s collapse.
The recent Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) failure, a who-what-where-when-and-why that’s still being debated, highlights the inherent risks in the current financial system. But the future of sustainable energy looks to alternative materials, like those explored in this insightful piece on the future of sustainable energy looks to alternative materials. While these innovative materials might offer a pathway to cleaner energy solutions, understanding the underlying factors behind SVB’s collapse is crucial for building a more resilient financial landscape.
Ultimately, the fragility of the banking sector, and the related implications of such events, remain a significant concern.
Impact of Technological Advancements on the Banking Industry
The rapid pace of technological advancements has fundamentally reshaped the financial landscape. The rise of fintech companies and the digitalization of financial services have introduced new challenges and opportunities for traditional banks. SVB’s reliance on a traditional banking model, coupled with its inability to adapt to the evolving needs of its customers, proved to be a significant weakness.
The rise of digital banking and alternative financial services presents a dynamic and competitive landscape.
Causal Chain of Events
| Event | Explanation |
|---|---|
| High Concentration of Deposits from Tech Companies | High concentration of deposits from technology companies increased vulnerability to mass withdrawals. |
| Aggressive Lending Strategies | Aggressive lending strategies towards high-growth technology companies increased concentration risk. |
| Rising Interest Rates | Rising interest rates depreciated the value of long-term fixed-income securities held by SVB. |
| Mismatch of Asset and Liability Duration | The mismatch between the duration of assets and liabilities left SVB vulnerable to rapid changes in interest rates. |
| Run on the Bank | Fears of insolvency triggered a run on the bank, leading to a liquidity crisis. |
| Bank Failure | Inability to meet deposit demands resulted in the bank’s failure. |
Impact of the Failure
The collapse of Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) sent shockwaves through the global financial system, highlighting vulnerabilities in the banking sector and triggering a cascade of events with far-reaching consequences. The failure exposed systemic risks and prompted significant regulatory responses aimed at preventing similar catastrophes. The fallout from SVB’s collapse reverberated beyond the banking industry, impacting investor confidence and the broader economy.The SVB implosion was not merely a localized event; it triggered a chain reaction, demonstrating the interconnectedness of financial institutions and the fragility of the global financial system.
The ripple effects were felt across various sectors, from tech startups to traditional banks, and the consequences extended far beyond the immediate stakeholders.
Understanding the factors behind Silicon Valley Bank’s collapse is crucial, and it’s a complex story. Beyond the immediate who, what, where, and when, the “why” is still being debated. However, looking at initiatives like sustaining our waters the fox wolf watershed alliance , we see a similar need for careful consideration and proactive measures to ensure financial stability and resilience in all sectors.
Ultimately, the deeper understanding of the SVB failure hinges on learning from these types of scenarios and the systems that failed.
Wider Implications on the Financial System
The failure of SVB highlighted the interconnectedness of financial institutions and the potential for a systemic crisis. Deposit runs at SVB triggered a similar phenomenon at other banks, particularly those with significant exposure to the tech sector. This demonstrated the vulnerability of the financial system to contagion effects, where the failure of one institution can rapidly spread to others.
The contagion risk highlighted the need for robust regulatory frameworks and improved crisis management protocols.
Ripple Effects on Other Financial Institutions
Numerous financial institutions felt the impact of SVB’s collapse. Banks with significant exposure to SVB faced potential losses and had to reassess their portfolios. This ripple effect extended to other financial markets, causing uncertainty and volatility. The uncertainty surrounding the future stability of the financial system created a challenging environment for investment and economic growth. The crisis forced banks to re-evaluate their risk management strategies and the safety of their assets.
Impact on Investor Confidence and the Economy
SVB’s failure severely damaged investor confidence. The sudden and unexpected nature of the collapse led to widespread anxiety about the stability of the financial system. This decline in confidence translated into reduced investment, hindering economic growth. Uncertainty about the future direction of the economy dampened consumer spending and business expansion. The fear of further bank failures further eroded confidence, creating a self-reinforcing cycle of economic contraction.
Regulatory Responses to the Crisis
The SVB failure spurred immediate regulatory responses aimed at bolstering the stability of the financial system. Governments worldwide implemented measures to improve bank supervision, strengthen capital requirements, and enhance crisis management procedures. These actions aimed to prevent similar events from occurring in the future. Regulatory agencies increased scrutiny of banks’ risk management practices and investment strategies.
Lessons Learned for Financial Institutions and Regulators
The SVB collapse underscored the importance of robust risk management practices for financial institutions. It highlighted the need for diversification of assets and a thorough understanding of the risks associated with specific investment strategies. Regulators learned the importance of proactive supervision and the need for more stringent capital requirements. The crisis highlighted the need for a more comprehensive understanding of systemic risks and the need for enhanced regulatory oversight.
The failure emphasized the need for continuous monitoring and evaluation of financial institutions’ resilience.
Regulatory Responses and Interventions

The collapse of Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) sent shockwaves through the financial world, highlighting vulnerabilities in the regulatory framework. Swift and decisive action from governmental bodies was crucial to mitigating the fallout and restoring investor confidence. This section details the regulatory responses, assesses their effectiveness, and compares them to past financial crises.
Regulatory Actions Taken
The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) played a pivotal role in the SVB resolution. They rapidly implemented the process of a government takeover, ensuring the continuity of customer deposits and preventing a wider financial contagion. This swift action, while unprecedented in scale, was deemed necessary to prevent a systemic crisis. Other regulatory bodies, such as the Federal Reserve, also took measures to stabilize the financial markets.
These included emergency lending programs and communication efforts aimed at reassuring the public.
Government Mitigation Efforts
The government’s intervention in SVB’s failure involved more than just the FDIC. The Federal Reserve acted as a lender of last resort, offering support to banks facing liquidity challenges. This support aimed to maintain the stability of the broader financial system. The Treasury Department also played a critical role in coordinating these efforts, ensuring a coordinated and effective response.
These measures were intended to prevent a domino effect, preventing similar bank failures.
Effectiveness of the Regulatory Response
The regulatory response to SVB’s failure was, by many accounts, deemed successful in preventing a wider crisis. The swift resolution of SVB prevented a run on other banks, limiting the systemic risk. However, the response was not without its critics, who argued that the underlying regulatory framework was insufficient to prevent such a failure. The experience highlighted the need for ongoing assessment and adaptation in financial regulations.
Further examination of the factors contributing to the failure and a review of the regulatory oversight were crucial to improve future resilience.
Comparison to Other Financial Crises
Comparing the response to SVB’s failure with those of previous financial crises reveals both similarities and differences. The 2008 financial crisis, for instance, involved a much larger scale of intervention and government bailouts. The swiftness of the SVB resolution was a key difference, highlighting the evolution of regulatory practices. However, the underlying issues of risk management and regulatory oversight, as seen in both crises, remain central concerns.
Each event underscored the ongoing need for a robust regulatory framework to ensure stability in the financial system.
Regulatory Actions Table
| Action | Agency | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| FDIC assumed control of SVB | FDIC | Protected customer deposits, prevented a run on other banks. |
| Federal Reserve offered emergency lending programs | Federal Reserve | Maintained liquidity in the financial system, stabilized market confidence. |
| Treasury Department coordinated efforts | Treasury Department | Ensured a coordinated response, minimizing potential systemic risk. |
Summary
In conclusion, the SVB failure serves as a potent reminder of the interconnectedness of financial markets and the importance of sound risk management. The rapid response from regulators, while necessary, highlighted the vulnerability of the system and the need for ongoing adaptation to evolving economic landscapes. The lessons learned from this crisis will shape the future of banking regulations and practices for years to come.

