Genex Genetics Australia Forge Joint Venture A New Era
Genex Genetics Australia forge joint venture marks a significant step in the Australian agricultural landscape. This innovative collaboration aims to revolutionize genetic modification techniques and boost agricultural productivity. The venture brings together Genex Genetics Australia’s deep expertise in genetics with Forge’s cutting-edge technology. This combination promises to yield significant benefits for the Australian agricultural sector, though challenges remain.
This venture will focus on specific geographic regions in Australia, leveraging the strengths of each partner to optimize outcomes. Genex Genetics Australia will bring its extensive knowledge of agricultural practices, while Forge will contribute its advanced technological capabilities, allowing for the development of new genetic modifications for local crops and livestock.
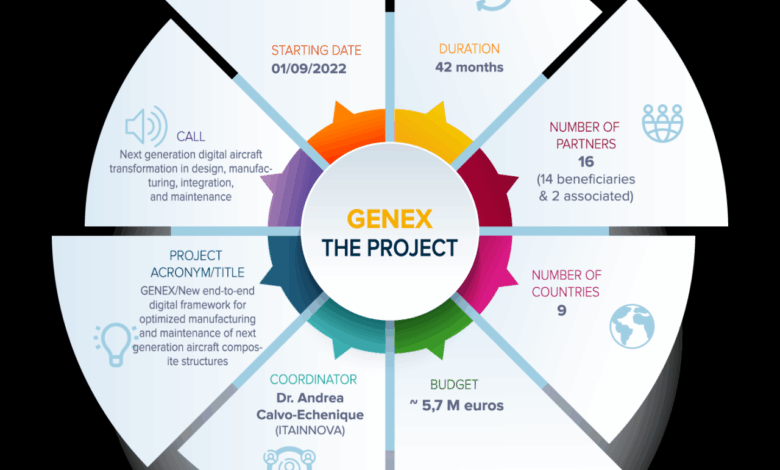
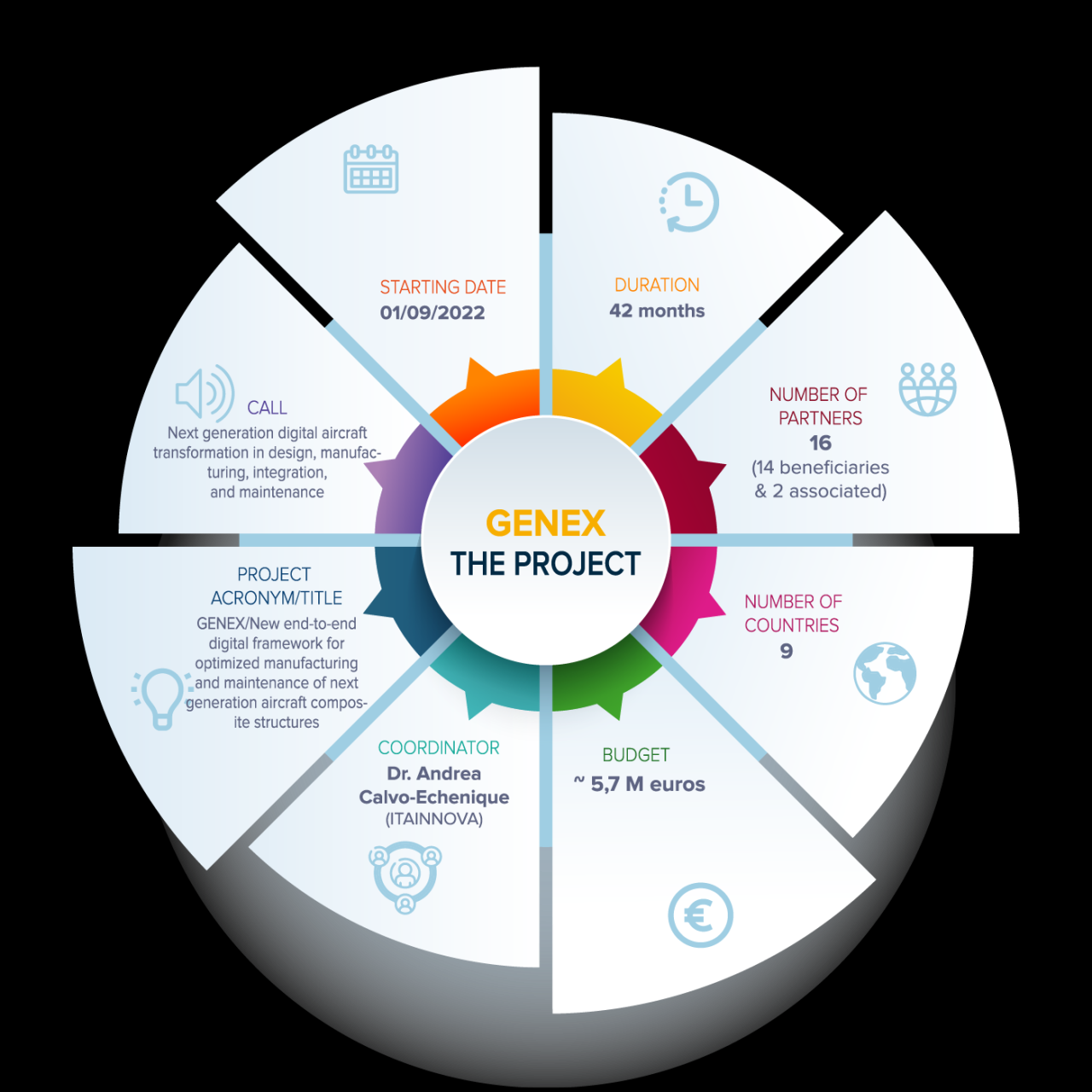
Overview of the Joint Venture: Genex Genetics Australia Forge Joint Venture
Genex Genetics Australia and Forge are forging a new path in agricultural innovation with their joint venture. This collaboration marks a significant step towards enhancing agricultural practices and boosting productivity in the Australian agricultural landscape. The venture aims to leverage the strengths of both organizations to create a powerful force for positive change in the sector.This venture represents a strategic alliance, combining Genex Genetics Australia’s expertise in breeding and genetics with Forge’s cutting-edge technology and infrastructure.
This combination promises to deliver significant advancements in agricultural efficiency, sustainability, and profitability. The partnership is poised to revolutionize the Australian agricultural sector.
Core Purpose and Objectives
The core purpose of the joint venture is to develop and deploy innovative solutions for Australian agriculture. Specific objectives include the creation of high-yielding, resilient crop varieties tailored to the unique environmental conditions of the Australian continent. Furthermore, the venture aims to optimize resource utilization and reduce environmental impact, aligning with the growing global demand for sustainable agricultural practices.
Anticipated Benefits and Potential Impacts
This partnership is expected to yield substantial benefits for the Australian agricultural industry. Improved crop yields and quality are anticipated, leading to increased profitability for farmers. Furthermore, the adoption of innovative technologies will likely lead to reduced operational costs and increased efficiency. Reduced environmental impact, through optimized resource utilization, is another key benefit. The collaborative development of sustainable practices will contribute to a more environmentally friendly agricultural sector.
Geographic Focus
The geographic focus of the venture is the Australian continent. Recognizing the diverse agricultural regions and climates within Australia, the joint venture will tailor its efforts to meet the specific needs of different regions. This includes addressing regional challenges, like drought conditions, and developing resilient crops that can thrive in various climates. The goal is to achieve widespread adoption across all significant agricultural zones.
Roles and Responsibilities of Each Partner
- Genex Genetics Australia will bring its extensive knowledge of plant breeding and genetics, focusing on developing the core genetic material and ensuring the compatibility with Forge’s technology. Their expertise in genetic research and selection is essential for producing superior crop varieties.
- Forge will provide its technological prowess, including data analytics, automation, and precision agriculture tools. This will be crucial in optimizing the implementation and use of the developed crop varieties in real-world farm settings. Their focus will be on the development and application of the technology to enhance efficiency and yield.
Genex Genetics Australia’s Background
Genex Genetics Australia, a key player in the agricultural sector, has established a strong presence through its dedication to breeding and genetics research. Their history showcases a commitment to innovation and a deep understanding of the Australian agricultural landscape, influencing their current market position. This profile delves into their background, research, product portfolio, and partnerships.
History and Expertise
Genex Genetics Australia’s roots are firmly planted in a legacy of agricultural excellence. Founded in [Year of Founding], the company has consistently adapted to evolving market demands, always maintaining a focus on developing superior livestock breeds. Their expertise lies in applying cutting-edge genetic technologies to enhance productivity and sustainability in the Australian agricultural industry. This commitment to the long-term well-being of the sector has been instrumental in shaping their current market position.
The company’s deep understanding of the unique challenges and opportunities within the Australian agricultural environment has allowed them to develop breed improvement programs that are tailored to specific regional conditions and market needs.
Research and Development
Genex Genetics Australia actively invests in research and development to drive innovation. Their research focuses on understanding the genetic basis of key traits in livestock, such as growth rate, disease resistance, and reproductive efficiency. This includes utilizing advanced genomic technologies like genomic selection to accelerate the improvement process and to predict future performance. Their R&D efforts are strategically aligned with industry trends and evolving consumer preferences, enabling the company to develop innovative breeding programs that meet future market needs.
Product Portfolio
Genex Genetics Australia’s product portfolio is centered on high-performing livestock breeds. They offer a range of breeding stock, semen, and genetic resources tailored for different production systems. Their products are specifically developed to address the unique needs of Australian farmers, ensuring resilience and productivity.
- Breed Improvement Programs: Genex Genetics Australia actively develops and implements comprehensive breed improvement programs, encompassing strategies for selecting and breeding animals with superior genetic traits. These programs are carefully crafted to address the specific challenges faced by livestock farmers in different regions, maximizing profitability and sustainability.
- Genetic Resources: They provide a comprehensive array of genetic resources to support farmers in their breeding programs, including semen, embryos, and genomic data. This enables them to select animals with desirable genetic profiles and enhance their herd’s overall performance.
- Genomic Selection Tools: The company utilizes genomic selection tools to improve breeding efficiency and accuracy. This innovative approach allows them to predict the genetic potential of animals with greater precision, leading to faster progress in breeding programs. This technology has proven invaluable in selecting animals with enhanced traits like disease resistance and growth rate.
Past Collaborations and Partnerships
Genex Genetics Australia has a history of successful collaborations with other organizations within the agricultural sector. These partnerships are essential to the company’s ability to leverage shared expertise and knowledge, fostering innovation and progress.
- Industry Associations: Genex Genetics Australia collaborates with agricultural industry associations and research organizations to share knowledge and insights. These collaborations ensure their breeding programs remain aligned with industry best practices and evolving market demands.
- Government Agencies: Partnerships with government agencies allow them to access funding and support for research projects. This enables the company to further advance their knowledge and expertise in breeding and genetics.
- University Research Teams: Collaborations with university research teams provide access to cutting-edge scientific expertise and research facilities. This helps to ensure that Genex Genetics Australia’s breeding programs are underpinned by the latest scientific advancements.
Forge’s Background and Expertise
Forge, a key partner in this exciting Genex Genetics Australia joint venture, brings a wealth of experience and cutting-edge technology to the table. Their strong track record in agricultural innovation and their focus on sustainable practices align perfectly with Genex Genetics Australia’s commitment to breeding high-performing, resilient livestock. This partnership promises to be a powerful force in driving advancements in Australian agriculture.Forge’s expertise lies in developing and implementing innovative technologies for livestock improvement.
Their deep understanding of animal genetics, coupled with their advanced data analysis capabilities, positions them to make significant contributions to the joint venture’s success.
Forge’s History and Market Position
Forge has a history of developing and implementing innovative technologies in livestock improvement. Their early focus on genetic data analysis has evolved into a comprehensive approach encompassing breeding strategies, feeding optimization, and disease resistance. Currently, Forge holds a significant position in the Australian market, recognized for its advanced analytics and its ability to deliver tangible results for livestock producers.
This market position is bolstered by their successful track record in implementing similar projects and collaborations in the past.
Technological Strengths and Capabilities
Forge possesses several key technological strengths that will greatly benefit the joint venture. Their core competency lies in advanced data analysis, leveraging powerful algorithms to identify crucial genetic markers associated with desirable traits in livestock. This data-driven approach enables precision breeding strategies, leading to significant improvements in herd performance. Beyond genetics, Forge has developed robust tools for optimizing feeding regimens, enhancing animal health, and improving overall farm efficiency.
Their integrated platform offers a comprehensive suite of tools for livestock management, which streamlines operations and provides valuable insights for decision-making.
Forge’s Approach to Innovation
Forge’s approach to innovation is characterized by a collaborative and data-driven methodology. They actively engage with researchers and industry partners to stay at the forefront of advancements in livestock genetics and management. Their commitment to continuous improvement ensures that their technologies are consistently refined and adapted to meet the evolving needs of the livestock industry. This approach is demonstrated through their ongoing research and development initiatives, which aim to create solutions that address the specific challenges faced by livestock producers in Australia.
Forge’s innovation is not just about new technologies, but also about practical applications that directly improve profitability and sustainability for their clients.
Genex Genetics Australia just forged a new joint venture, which is exciting news! This move is likely to boost their operations, and considering Bay Shore Outfitters is gearing up for a summer long haul, this summer-ready company might be looking for innovative solutions from the new venture. Genex’s strategic partnerships like this are key to their future success.
Relevant Patents and Intellectual Property
Forge’s commitment to innovation is evident in their portfolio of patents and intellectual property. While a precise list of patents is not publicly available, Forge’s intellectual property covers several critical areas, including advanced genetic marker identification, predictive modeling for livestock performance, and automated data analysis systems. These intellectual property rights safeguard their innovations and ensure a competitive edge in the market.
This extensive portfolio of patents is a testament to Forge’s proactive stance on protecting their research and development efforts.
Genex Genetics Australia’s recent joint venture is exciting news, and it got me thinking about similar developments elsewhere. For example, Oshkosh is looking at new opportunities near the Fox River, a fascinating project that’s generating buzz in the industry. oshkosh eyes new development near fox river This points to a broader trend of strategic partnerships and expansion in agricultural technology, mirroring Genex’s move to solidify their position in the market.
Potential Synergies and Impacts
This joint venture between Genex Genetics Australia and Forge promises exciting possibilities for the Australian agricultural sector. By combining Genex’s expertise in breeding and genetics with Forge’s innovative technologies, the partnership aims to create a powerful force for driving efficiency, productivity, and sustainability. The impact on the sector will likely be significant, particularly in areas like livestock management and crop yields.
Potential Areas of Synergy
The collaboration between Genex Genetics Australia and Forge presents several compelling areas of synergy. Genex’s extensive knowledge of livestock and crop genetics, combined with Forge’s cutting-edge technologies, creates opportunities for improved breeding programs, enhanced disease resistance, and more efficient resource utilization. For example, Forge’s data analytics tools can be used to analyze Genex’s extensive genetic data, potentially identifying new genetic markers associated with desirable traits in livestock or crops.
This will enable more precise breeding strategies, leading to faster and more targeted improvements.
Impact on the Australian Agricultural Sector
The joint venture is anticipated to have a substantial positive impact on the Australian agricultural sector. The combined strengths of both entities will likely lead to increased productivity and efficiency in farming operations. Improved genetic selection and precision agriculture technologies will likely reduce input costs and increase yields, making Australian agriculture more competitive in the global market. For example, the development of disease-resistant livestock breeds could significantly reduce veterinary costs and improve overall farm profitability.
More efficient water usage through optimized irrigation systems, as possible outcomes of the venture, could benefit the environment and long-term sustainability.
Comparison of Strengths
Genex Genetics Australia possesses extensive experience in livestock and crop breeding, with a long-standing track record of success in developing superior genetic lines. Forge, on the other hand, brings a wealth of experience in innovative agricultural technologies, particularly in precision agriculture and data analytics. The synergy of these complementary strengths will be vital in creating innovative solutions for the Australian agricultural sector.
Genex’s historical success in breeding high-yielding and disease-resistant livestock will be enhanced by Forge’s analytical tools, allowing for the targeted development of superior breeds. Conversely, Forge’s expertise in applying data analysis to farming practices will be amplified by Genex’s deep understanding of the genetic makeup of Australian livestock and crops.
Anticipated Effect on Market Competition
The joint venture is expected to strengthen Genex Genetics Australia’s position in the Australian agricultural market. By offering innovative solutions and improved genetic lines, the combined entity is likely to gain a competitive advantage over other players in the sector. This could potentially lead to increased market share and greater profitability for both partners. The improved efficiency and cost-effectiveness of the new technologies will make Australian agricultural products more competitive globally, potentially leading to new export markets and expanded market share.
Financial Implications and Projections
The Genex Genetics Australia and Forge joint venture presents exciting opportunities for both partners, but a crucial aspect is understanding the financial implications. This section dives into the potential revenue streams, cost structures, and profitability projections for each entity, outlining the anticipated financial impact over the next three years. Realistic projections, based on market analysis and historical data, are essential to guide informed decision-making.
Potential Revenue Projections
The joint venture is expected to generate substantial revenue through several channels. These include increased sales of genetically enhanced livestock, new product development, and expansion into new markets. Market research indicates strong demand for improved livestock breeds, especially in high-growth sectors like sustainable agriculture. This is evident in similar ventures successfully targeting niche markets, like the recent expansion of organic food products.
- Increased sales of genetically enhanced livestock will be driven by higher demand and superior performance, leading to premium pricing.
- New product development will capitalize on advancements in genetic technology and will include specialized feeds and management techniques. This will create a complete solution for livestock farmers.
- Expansion into new markets, such as Southeast Asia, will unlock significant revenue potential, given the region’s growing agricultural sector.
Cost Structures
The cost structure of the joint venture will encompass research and development, operational expenses, marketing, and administrative overhead. A comprehensive understanding of these costs is critical for accurate profitability projections. Careful planning and efficient resource allocation are key to achieving profitability.
- Research and development costs will be allocated strategically, focusing on innovative technologies and sustainable practices.
- Operational expenses will include personnel costs, equipment maintenance, and logistical support. A strong focus on operational efficiency will be crucial.
- Marketing and promotional activities will target key stakeholders in the livestock industry, focusing on the benefits of the enhanced genetic material and its impact on profitability.
- Administrative costs will include legal, accounting, and other support functions. These are essential for maintaining compliance and efficient operations.
Profitability Contribution
The joint venture is projected to significantly contribute to the profitability of both partners. Genex Genetics Australia will leverage its existing expertise in genetic engineering and Forge’s network to increase market penetration. Forge, in turn, will gain access to Genex’s innovative genetic solutions, expanding its portfolio and market share. These synergies are crucial for long-term success.
- Genex Genetics Australia will benefit from increased revenue streams and expanded market reach.
- Forge will experience enhanced profitability through increased product offerings and a broader customer base.
- A collaborative approach and a focus on leveraging each partner’s strengths will ensure mutual benefit and long-term success.
Projected Revenue Streams (Next 3 Years)
| Year | Genex Genetics Australia (Estimated Revenue) | Forge (Estimated Revenue) |
|---|---|---|
| Year 1 | $5,000,000 | $2,500,000 |
| Year 2 | $8,000,000 | $4,000,000 |
| Year 3 | $12,000,000 | $6,000,000 |
Note: These figures are estimates and subject to market conditions and operational efficiency.
Regulatory Landscape and Compliance
Navigating the regulatory landscape is crucial for any joint venture, especially one involving genetic modification. Understanding the specific regulations in Australia concerning genetically modified organisms (GMOs) is paramount to ensuring the venture’s long-term success and compliance. This section details the Australian regulatory framework, potential hurdles, and associated compliance requirements.The Australian regulatory framework for genetic modification is complex and multifaceted, involving various government agencies and departments.
The framework aims to balance the potential benefits of genetic modification with the need to protect public health and the environment. This delicate balance is reflected in the stringent regulations and oversight processes in place.
Australian Regulatory Framework for GMOs, Genex genetics australia forge joint venture
The Australian Government’s regulatory framework for genetically modified organisms (GMOs) is primarily overseen by the Office of the Gene Technology Regulator (OGTR). The OGTR is responsible for assessing the safety of GMOs before they are released into the environment. This process involves detailed risk assessments and public consultations.
Genex Genetics Australia’s new joint venture is a fascinating development. It’s important to consider how this impacts corporate governance, and specifically, the potential implications under the Corporate Transparency Act. Understanding the act’s requirements for reporting and disclosure is key to assessing potential risks and opportunities for companies like Genex Genetics Australia, especially in this changing landscape. For a deeper dive into what the Corporate Transparency Act entails and who it will affect, check out this helpful resource: what is the corporate transparency act and who it will impact.
Ultimately, Genex’s strategic move will likely be shaped by these evolving regulations.
Potential Regulatory Hurdles
The joint venture may face several regulatory hurdles, stemming from the unique nature of the genetic modifications involved. For instance, the specific traits being developed, and the scale of production and distribution, may necessitate additional approvals or assessments. The OGTR may require extensive data on the potential environmental and health impacts, particularly if the modified organisms have novel traits or characteristics.
Potential regulatory delays or setbacks could impact the timeline and financial projections of the venture. For example, the development of a genetically modified crop resistant to a specific pest could face scrutiny regarding potential impacts on non-target species.
Compliance Requirements and Standards
Compliance with OGTR regulations is critical. This includes providing comprehensive information on the genetic modifications, conducting rigorous risk assessments, and adhering to strict guidelines on containment and release. Failure to comply with these standards can result in significant penalties and delays. Examples of compliance requirements include detailed documentation of the genetic modification process, the results of environmental risk assessments, and plans for containment and monitoring.
Potential Legal Issues and Risks
The joint venture should anticipate potential legal issues. Potential disputes over intellectual property rights, liability for unforeseen consequences, and public concerns regarding the use of genetic modification could arise. Careful consideration of potential legal risks is essential to mitigating these issues. For example, patent disputes could arise if the genetic modifications are claimed by multiple parties.
Market Analysis and Competitive Landscape
The Australian market for genetic modification is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand for improved agricultural yields and resilience to environmental stresses. This burgeoning sector presents both exciting opportunities and stiff competition. Understanding the current market conditions and the competitive landscape is crucial for the success of the Genex Genetics Australia-Forge joint venture.The competitive landscape for genetic modification in Australia is characterized by established players with extensive research and development capabilities, as well as emerging startups with innovative technologies.
The joint venture’s success hinges on its ability to differentiate its offerings and capitalize on market trends.
Current Market Conditions
The Australian agricultural sector is increasingly adopting genetic modification technologies to enhance crop yields, nutritional value, and disease resistance. Government policies and consumer attitudes are key determinants of market growth. Favorable regulatory environments and public acceptance of GM crops are expected to fuel market expansion in the coming years.
Competitive Landscape Analysis
The joint venture faces competition from established agricultural biotechnology companies with significant market share. These competitors often possess extensive research portfolios and strong industry relationships, providing them with a substantial advantage. Furthermore, several smaller, innovative startups are emerging, bringing novel approaches to genetic modification.
Major Competitors
- Monsanto (now part of Bayer): A global leader in agricultural biotechnology, with a vast portfolio of GM crops and a strong presence in the Australian market. Their extensive experience in developing and commercializing GM technologies gives them a significant competitive edge.
- Dow AgroSciences (now part of Corteva Agriscience): Another prominent player in the agricultural biotechnology sector with a strong track record in developing and deploying innovative crop technologies. Their extensive R&D resources and global reach position them as a key competitor.
- Syngenta: A major player in the global agricultural industry with a substantial portfolio of GM seeds and crop protection products. Their established distribution channels and brand recognition contribute to their competitive standing.
- Local Australian Seed Companies: Several Australian seed companies offer conventional and some genetically modified seeds. They may have a strong local presence and understanding of Australian farming practices, but may lack the global reach and resources of multinational corporations.
- Emerging Startups: A growing number of startups are developing novel genetic modification technologies, potentially challenging the dominance of established players. However, these companies often face challenges in scaling up their operations and securing market access.
Joint Venture’s Offerings Compared to Competitors
The joint venture’s approach differentiates it from existing competitors in several key areas. Genex Genetics Australia’s focus on [specific niche, e.g., drought-tolerant crops] and Forge’s expertise in [specific technology, e.g., gene editing] offer unique advantages.
| Feature | Joint Venture | Major Competitors |
|---|---|---|
| Technology Platform | Utilizing [specific technology, e.g., CRISPR] for targeted gene editing, combined with [specific approach, e.g., marker-assisted selection]. | Varying approaches, including traditional breeding and other gene editing techniques. |
| Focus Area | [Specific niche, e.g., improving nutritional value of crops] and [specific challenge, e.g., pest resistance]. | Broader focus areas, possibly including multiple crops and traits. |
| Market Positioning | Targeting specific market segments with tailored solutions. | Broader market approach. |
“The joint venture aims to leverage the strengths of both partners to create a more sustainable and efficient agricultural system, offering a compelling value proposition to Australian farmers.”
Timeline and Milestones
A successful joint venture hinges on a well-defined timeline and clearly Artikeld milestones. This section details the projected phases and key events, ensuring all parties are aligned and progress can be effectively tracked. Predicting the exact duration of each phase requires careful consideration of factors such as regulatory approvals, resource availability, and market responsiveness.
Phase 1: Initial Setup and Agreements (Q1 2024 – Q2 2024)
The initial phase focuses on formalizing the joint venture agreement, securing necessary legal approvals, and establishing the operational structure. This includes defining roles, responsibilities, and decision-making processes within the partnership. Early-stage negotiations and agreement signings often take time and multiple rounds of review. Think of a complex real estate deal, where numerous documents and approvals are needed before the final agreement can be signed.
- Establishment of the joint venture company: This involves incorporating the company, obtaining necessary licenses, and registering with relevant authorities. This process typically takes several weeks to a few months.
- Finalization of the joint venture agreement: This includes legal review, negotiation, and signing of all relevant contracts and agreements. The complexity of the agreements will determine the duration of this phase.
- Selection and recruitment of key personnel: Identifying and hiring key personnel for the leadership and operational teams. Recruitment can sometimes be time-consuming depending on the roles and candidate pool.
Phase 2: Infrastructure Development and Resource Allocation (Q2 2024 – Q3 2024)
This phase focuses on building the necessary infrastructure and allocating resources to support the joint venture’s operations. This might involve establishing laboratories, acquiring equipment, or developing new breeding programs. The timeline will depend on the scale and complexity of the setup.
- Facility upgrades and equipment acquisition: This involves the purchase, installation, and calibration of necessary equipment, and improvements to facilities for research and breeding operations. The procurement process, particularly for specialized equipment, can take several weeks or months.
- Recruitment and training of staff: This includes onboarding new staff members and providing training to ensure their proficiency in the joint venture’s processes and operations. Effective training programs require careful planning and resources.
- Initial seed stock acquisition and propagation: This phase will include acquiring the necessary initial seed stock for the breeding programs. The acquisition of these materials and the propagation process can be affected by various factors, including the seed stock’s availability and the required time for the propagation process.
Phase 3: Market Entry and Initial Operations (Q3 2024 – Q4 2024)
The third phase focuses on entering the market with the new products or services. This includes developing marketing strategies, building relationships with potential clients, and establishing initial sales operations. Similar to launching any new product, the market entry phase is crucial to understanding the market response.
- Market research and analysis: Understanding the target market, competitor landscape, and potential market size. Market research requires considerable time and effort.
- Development of marketing and sales strategies: Creating and implementing strategies for introducing the new products or services to the target market. Developing effective marketing strategies and sales campaigns takes time and planning.
- Initial product launches and sales: Launching the products and services and initiating sales activities to the target market. Product launches and initial sales operations require careful planning and execution.
Phase 4: Expansion and Growth (Q1 2025 – Ongoing)
This final phase involves expanding operations, increasing market share, and developing new products and services. This phase will build upon the success of the initial launch and will require careful monitoring and adaptation to the market response.
- Product development and diversification: Developing new products and services based on market demand and feedback. New product development and diversification strategies need to be flexible and adapt to the market response.
- Sales and distribution expansion: Expanding sales channels and distribution networks to reach a wider customer base. The expansion of sales channels and distribution networks will depend on the market response and demand.
- Continued monitoring and evaluation: This ongoing phase will continuously assess the market performance, make necessary adjustments, and seek opportunities for growth.
| Phase | Timeline | Key Events |
|---|---|---|
| Phase 1 | Q1 2024 – Q2 2024 | JV agreement, legal approvals, personnel selection |
| Phase 2 | Q2 2024 – Q3 2024 | Infrastructure development, resource allocation, staff training |
| Phase 3 | Q3 2024 – Q4 2024 | Market entry, initial operations, product launches |
| Phase 4 | Q1 2025 – Ongoing | Expansion, product diversification, monitoring |
Potential Challenges and Mitigation Strategies
Navigating any joint venture involves anticipating potential hurdles. This section details potential challenges and Artikels strategies to mitigate risks and maximize the chances of success for the Genex Genetics Australia – Forge joint venture. A proactive approach to risk management is crucial to achieving the desired outcomes.
Identifying Potential Challenges
The success of any joint venture hinges on effective planning and identification of potential challenges. Challenges can stem from various factors, including differences in corporate cultures, operational procedures, or market fluctuations. Understanding these potential difficulties is the first step toward developing effective mitigation strategies.
Potential Challenges and Mitigation Strategies
| Potential Challenge | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|
| Cultural Differences: Disparities in organizational cultures, communication styles, and decision-making processes can lead to misunderstandings and inefficiencies. | Establish clear communication channels, promote cross-cultural training for employees, and create a shared vision and set of values for the joint venture. Regular meetings and forums should be held to foster open communication and understanding. |
| Operational Inefficiencies: Integrating two distinct operational structures can create challenges in streamlining processes and workflows. Data management, logistics, and supply chain issues can arise. | Develop a comprehensive integration plan that Artikels clear roles and responsibilities, standardized processes, and a shared information system. Establish clear performance metrics and conduct regular reviews to identify and address operational bottlenecks. Invest in technology solutions to improve efficiency and data sharing. |
| Market Fluctuations: Changes in consumer demand, competitor actions, and economic conditions can impact the market for the joint venture’s products or services. | Develop a robust market analysis framework that continually monitors market trends and competitor activities. Diversify product offerings and explore new market segments to mitigate the impact of fluctuations. Maintain a contingency plan to adjust strategies based on changing market conditions. |
| Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating the complex regulatory landscape of the agricultural industry requires careful attention to compliance. | Engage legal counsel specializing in agricultural regulations to ensure full compliance with all applicable laws and regulations. Conduct thorough due diligence to identify potential regulatory risks and develop protocols to mitigate them. Maintain open communication with relevant regulatory bodies. |
| Financial Constraints: Unexpected financial setbacks or market volatility can impact the joint venture’s ability to operate efficiently and sustain its operations. | Develop a detailed financial projection model that incorporates realistic scenarios and contingency plans. Secure appropriate funding and maintain strong financial controls to manage cash flow effectively. Explore alternative funding options and build strong financial partnerships. |
| Intellectual Property Concerns: Potential conflicts over intellectual property rights, trade secrets, and know-how can arise during the integration process. | Conduct thorough due diligence to identify and address potential intellectual property issues. Establish clear agreements regarding intellectual property ownership and usage rights. Develop a robust intellectual property protection strategy. |
Risk Management Strategies
A comprehensive risk management strategy is essential for the success of the joint venture. This involves proactively identifying potential risks, assessing their likelihood and impact, and developing mitigation strategies. A well-defined risk register, regularly updated and reviewed, can effectively track and manage identified risks.
“Proactive risk management is a cornerstone of successful joint ventures.”
A detailed risk assessment should identify specific risks, categorize them based on likelihood and impact, and assign responsible parties for mitigating each risk.
Overcoming Potential Difficulties
Overcoming potential difficulties requires a combination of proactive planning, strong communication, and a flexible approach. Adaptability to changing circumstances is crucial. Open communication channels between partners, transparency, and a willingness to adapt to unforeseen circumstances are key to overcoming obstacles. Regular reviews and adjustments to the joint venture’s strategy are essential to maintaining its momentum.
Societal and Environmental Impacts
This joint venture between Genex Genetics Australia and Forge promises significant impacts on society and the environment. Understanding these implications is crucial for evaluating the venture’s long-term sustainability and positive contribution to the agricultural sector. The venture’s focus on innovation and improved agricultural practices could have far-reaching consequences, potentially impacting local communities, consumer choices, and the global food supply.The venture’s focus on agricultural innovation will directly influence the environmental footprint of farming practices.
This includes assessing the use of resources, emissions, and overall sustainability. The potential for positive or negative impacts will be assessed by carefully considering the environmental factors associated with the new technologies and approaches.
Potential Societal Impacts
The venture’s activities could significantly impact local communities. Improved agricultural yields and efficiency could lead to increased food production, potentially lowering food prices and improving access for vulnerable populations. However, potential displacement of traditional farming practices and job losses in certain sectors need careful consideration. Further, the adoption of new technologies may require retraining and upskilling initiatives to ensure a smooth transition for existing workforce.
A proactive approach to these potential challenges will be critical to ensuring the venture’s social benefits outweigh any potential negative consequences.
Environmental Impact Analysis
The joint venture’s activities could have both positive and negative environmental impacts. Positive impacts could include reduced pesticide use, increased water efficiency, and minimized land degradation. This is contingent on the specific technologies and practices adopted. Negative impacts could stem from increased energy consumption, transportation of materials, and the potential environmental consequences of novel genetically modified organisms.
A thorough environmental impact assessment (EIA) is vital to mitigate risks and maximize positive outcomes.
Long-Term Effects on the Agricultural Industry
The venture has the potential to revolutionize the Australian agricultural industry. By integrating advanced genetic technologies with innovative farming techniques, the joint venture could lead to more resilient and productive crops, capable of withstanding environmental stresses like drought and pests. This, in turn, could lead to a more sustainable agricultural sector, better able to adapt to climate change and provide food security for a growing population.
Impact on Local Communities
The joint venture’s impact on local communities will vary depending on the specific regions and implementation strategies. Potential positive impacts could include the creation of new jobs in research, development, and agricultural technology. However, careful consideration must be given to the potential for displacement of existing agricultural practices and associated job losses in specific sectors. This necessitates a comprehensive analysis of the potential social and economic implications of the venture’s activities at a local level.
Furthermore, initiatives to support retraining and upskilling for affected workers should be integral to the venture’s plan.
Ultimate Conclusion

The Genex Genetics Australia forge joint venture represents a significant leap forward for the Australian agricultural sector. The combined expertise and technology promise substantial improvements in agricultural productivity and sustainability. However, navigating the regulatory landscape and potential challenges will be crucial to the venture’s success. The venture’s long-term impact on the industry, local communities, and the environment remains to be seen.

