Aligning Cybersecurity Policies with Third-Party Vendors
Aligning cybersecurity policies with third party vendors – Aligning cybersecurity policies with third-party vendors is crucial in today’s interconnected business world. This involves ensuring that your organization’s security standards are met by the companies you work with, from data handling to incident response protocols. Understanding these complexities is vital for safeguarding your business’s sensitive data and reputation.
This comprehensive guide dives into the critical aspects of aligning cybersecurity policies with third-party vendors, covering everything from risk identification to incident response planning. We’ll explore the practical steps necessary to establish and maintain a secure partnership with your vendors, focusing on proactive measures to mitigate potential threats.
Defining Cybersecurity Policy Alignment
Modern businesses rely heavily on third-party vendors for various services, from cloud storage to software development. This reliance necessitates a robust approach to ensure consistent cybersecurity standards across the entire ecosystem. Aligning cybersecurity policies with third-party vendors is crucial for maintaining data protection, preventing breaches, and safeguarding the organization’s reputation.Aligning cybersecurity policies with third-party vendors means establishing shared understanding and consistent implementation of security measures.
This ensures that vendors operate within the same framework as the organization, minimizing risk and vulnerabilities. It involves clear communication, well-defined expectations, and ongoing monitoring to maintain alignment. This is particularly important in today’s interconnected world, where a single security lapse by a vendor can have widespread consequences.
Importance of Alignment in Modern Business
Effective alignment mitigates risks. Third-party breaches can expose sensitive data, leading to financial losses, regulatory penalties, and damage to brand reputation. Consistent policies reduce the likelihood of such events. Furthermore, compliance with industry regulations like GDPR or HIPAA requires a standardized approach across the entire supply chain, which policy alignment facilitates.
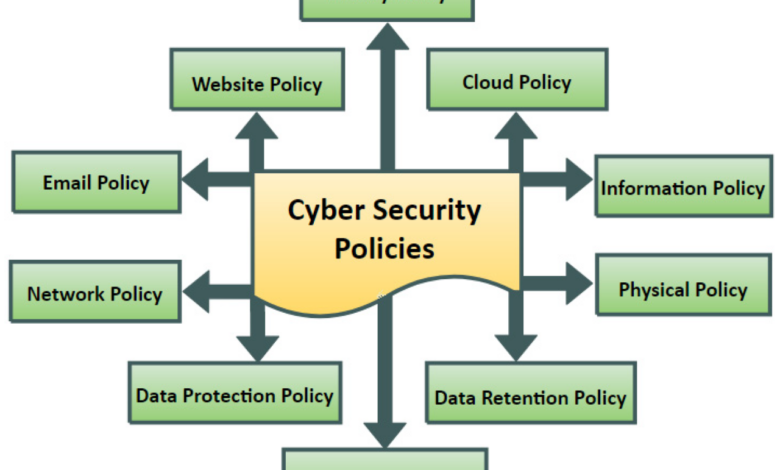
Types of Cybersecurity Policies
Several key types of cybersecurity policies need consideration when aligning with third-party vendors. These include policies related to data handling, access controls, and incident response.
- Data Handling Policies dictate how sensitive data is collected, stored, processed, and transmitted. This includes establishing secure data storage protocols, encrypting sensitive information, and implementing data loss prevention measures.
- Access Control Policies define who has access to what data and resources within the organization and its third-party vendors. Implementing robust authentication methods, role-based access controls, and multi-factor authentication is essential to protect against unauthorized access.
- Incident Response Policies Artikel the procedures for responding to security incidents. These policies should specify how to detect, contain, investigate, and recover from breaches. This includes clear communication protocols, escalation paths, and reporting requirements.
Key Components of a Robust Cybersecurity Policy
A robust cybersecurity policy should encompass various aspects. This comprehensive approach helps ensure consistent security across the entire organization and with all third-party vendors.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Protection | Establish clear data classification, storage, and handling procedures. Enforce encryption and access controls for sensitive data. |
| Incident Response | Define procedures for detecting, containing, investigating, and recovering from security incidents. Ensure clear communication channels and escalation paths. |
| Access Controls | Implement role-based access controls and multi-factor authentication. Establish clear access permissions for all data and systems. |
| Security Awareness Training | Provide regular training for employees and third-party personnel on security best practices. |
| Vendor Management | Establish a clear process for vetting, monitoring, and managing third-party vendors. Include cybersecurity clauses in vendor contracts. |
| Compliance | Ensure adherence to relevant industry regulations and standards. Include compliance requirements in policies. |
Identifying Third-Party Vendor Risks
Third-party vendors play a crucial role in modern organizations, handling everything from customer service to crucial data processing. However, this reliance also introduces security vulnerabilities. Understanding these risks and their potential impact is paramount for maintaining a strong security posture.Identifying and mitigating these risks requires a proactive approach, encompassing thorough vendor due diligence and ongoing monitoring.
Ensuring your cybersecurity policies are on point with third-party vendors is crucial. It’s like prepping your business for a sale – you need a clear picture of everything, especially when it comes to external partners. Think about those five tips for selling a business, five tips for selling a business , and apply a similar meticulousness to vendor agreements.
Robust cybersecurity policies with third-party vendors protect your sensitive data and, ultimately, your business’s future.
Common Security Risks Associated with Third-Party Vendors
Third-party vendors often lack the same level of security controls as the organization they serve. This disparity creates several potential vulnerabilities. Common security risks include inadequate security policies, insufficient access controls, weak passwords, outdated software, and vulnerabilities in their systems. Moreover, human error, such as phishing attacks targeting vendor employees, can also pose a significant threat. Poorly configured or maintained systems are another critical factor.
- Inadequate Security Policies: Vendors might not have comprehensive security policies in place, or they may not be consistently enforced. This can lead to unauthorized access to sensitive data.
- Insufficient Access Controls: Vendors may not adequately control who has access to sensitive information. This can expose data to unauthorized personnel.
- Weak Passwords: Vendors might use weak or easily guessed passwords, creating opportunities for attackers to gain unauthorized access.
- Outdated Software: Use of outdated software with known vulnerabilities can be exploited by malicious actors. Failure to update software regularly exposes the organization to significant risks.
- Vulnerabilities in Third-Party Systems: Vendors’ systems might contain known vulnerabilities, allowing attackers to exploit weaknesses and gain unauthorized access to the organization’s data.
- Human Error: Phishing attacks targeting vendor employees can compromise sensitive information or lead to the installation of malware on the organization’s network.
- Poorly Configured or Maintained Systems: Insufficiently configured or maintained systems can be vulnerable to attacks and data breaches.
Potential Impact on an Organization’s Security Posture
The security posture of an organization can be significantly impacted by vulnerabilities in third-party systems. A breach in a vendor’s system can expose sensitive data, compromise intellectual property, disrupt business operations, and damage the organization’s reputation.The impact of these risks can vary in severity, depending on the nature and extent of the vulnerability. For instance, a breach exposing customer credit card information can lead to substantial financial losses and regulatory penalties.
Examples of Security Breaches Caused by Vulnerabilities in Third-Party Systems
Numerous instances of security breaches have been linked to vulnerabilities in third-party systems. One notable example involved a major retailer whose payment processing vendor suffered a breach, exposing millions of customer credit card numbers. Another example highlighted a software development vendor whose code contained critical vulnerabilities, leading to unauthorized access to confidential data.
“Third-party risk is not a theoretical concept; it’s a very real and present threat in today’s interconnected world.”
Comparison of Third-Party Vendor Risk Assessments
Different types of third-party vendor risk assessments utilize various methodologies and approaches. Each method offers a unique perspective, with varying levels of detail and depth.
| Assessment Type | Methodology | Focus | Depth |
|---|---|---|---|
| Security Questionnaire | Standard set of questions about security practices | Basic security controls and policies | Low |
| Security Audit | On-site or remote assessment of security controls | Detailed review of security controls and processes | Medium |
| Vulnerability Scanning | Automated scan of vendor systems for known vulnerabilities | Identification of vulnerabilities in vendor systems | Medium |
| Penetration Testing | Simulated attack on vendor systems to identify vulnerabilities | Evaluation of the effectiveness of security controls | High |
Establishing Effective Communication Channels: Aligning Cybersecurity Policies With Third Party Vendors
Building strong relationships with third-party vendors hinges on open communication. Transparent discussions about cybersecurity policies foster trust and ensure that everyone is on the same page regarding security measures. This proactive approach helps mitigate risks and strengthens the overall security posture of your organization.
Importance of Open Communication Channels
Effective communication with third-party vendors is crucial for successful cybersecurity policy alignment. Open lines of communication facilitate a shared understanding of security responsibilities, allowing for proactive risk mitigation and incident response. This approach ensures that everyone is working towards the same security goals, reducing the likelihood of breaches and data compromises. A proactive approach fosters trust and collaboration, ultimately strengthening your organization’s security posture.
Strategies for Establishing Clear Communication Protocols
Establishing clear communication protocols with third-party vendors is vital for ensuring alignment with your cybersecurity policies. This involves defining specific communication channels, frequency of updates, and escalation procedures for security concerns. Defining roles and responsibilities within your organization and the vendor’s organization ensures accountability and clarity.
- Define communication channels: Specify the preferred methods for communication, such as email, dedicated security portals, or regular conference calls. This clarity prevents confusion and ensures timely information exchange.
- Establish a clear escalation path: Artikel the process for reporting security incidents or policy deviations. A well-defined escalation procedure ensures that concerns are addressed promptly and effectively.
- Document expectations: Clearly document your security policy requirements and expectations for third-party vendors. This documentation should be easily accessible and understood by all parties involved.
Methods for Regular Security Updates and Policy Reviews with Vendors
Regular security updates and policy reviews are essential for maintaining alignment with third-party vendors. These updates should include any changes to your cybersecurity policies, emerging threats, and best practices. This proactive approach ensures that your vendors are prepared for evolving security landscapes and are equipped to handle potential risks.
- Scheduled policy reviews: Conduct regular meetings or calls to review and update cybersecurity policies. These meetings provide an opportunity to address any questions or concerns.
- Security awareness training: Provide security awareness training for vendors’ employees. This empowers them to recognize and report potential security threats.
- Threat intelligence sharing: Share relevant threat intelligence with vendors to keep them updated on emerging threats and potential vulnerabilities.
Example Vendor Communication Plan
| Activity | Frequency | Responsible Party | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Security Policy Updates | Quarterly | Security Team | Distribute updated policies, outlining expectations and responsibilities. |
| Security Awareness Training | Annually | Security Team and Vendor Training Team | Provide training modules to vendor employees on recognizing and reporting potential security threats. |
| Incident Reporting | As Needed | Vendor Security Contact and Security Team | Establish a clear process for reporting security incidents, including escalation procedures and communication channels. |
| Regular Security Meetings | Monthly | Security Team and Vendor Security Contact | Schedule meetings to discuss security posture, emerging threats, and potential vulnerabilities. |
“Regular communication and proactive engagement with third-party vendors are paramount for maintaining a strong security posture.”
Implementing Policy Enforcement Mechanisms
Ensuring third-party vendors adhere to your cybersecurity policies is crucial for maintaining a strong overall security posture. A robust policy enforcement strategy, encompassing clear communication, measurable metrics, and consistent follow-up, is vital. This approach not only protects your organization but also builds trust and transparency with your vendors.Implementing effective mechanisms for enforcing cybersecurity policies with third-party vendors involves a multi-faceted approach that goes beyond simply issuing a policy document.
It requires proactive engagement, clear communication channels, and a structured process for handling non-compliance. This section dives into the specifics of implementing these mechanisms, from contract provisions to handling violations.
Different Methods for Enforcing Cybersecurity Policies
Several methods can be employed to enforce cybersecurity policies with third-party vendors. These methods should be tailored to the specific vendor, the nature of the services provided, and the sensitivity of the data involved. Examples include:
- Regular Security Audits: Conducting periodic security audits of vendor systems and processes helps verify compliance with established protocols. This might include penetration testing, vulnerability assessments, and code reviews, depending on the vendor’s role and the nature of the data they handle.
- Security Awareness Training: Providing security awareness training to vendor personnel is a critical component of enforcement. This training should cover relevant security policies and procedures, such as password management, phishing awareness, and data handling best practices.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Integration: Integrating with vendor SIEM systems allows for real-time monitoring of security events. This helps identify and respond to potential security breaches or suspicious activities promptly.
- Security Monitoring and Reporting: Establishing regular reporting mechanisms from vendors about security incidents, vulnerabilities, and compliance activities. These reports should be reviewed and analyzed to ensure adherence to the established policies.
Ensuring Vendor Adherence to Security Protocols
This necessitates clear and specific contractual obligations regarding security. The contract should Artikel the expected security measures and procedures, including access controls, data encryption, and incident response plans. Detailed descriptions of security measures and expected protocols are crucial.
Contract Provisions for Ensuring Compliance, Aligning cybersecurity policies with third party vendors
Contractual provisions play a vital role in enforcing security policies. These provisions should explicitly Artikel the vendor’s obligations regarding security, including:
- Specific security requirements: Define the exact security controls that the vendor must implement, such as encryption standards, access control protocols, and incident response procedures. The contract should also state the expected frequency and format of reporting.
- Penalties for non-compliance: Clearly Artikel the consequences for violating security policies, such as penalties, termination of the contract, or other repercussions. This helps deter non-compliance and provides a clear course of action.
- Regular security assessments: Stipulate the frequency of security audits or assessments conducted by the vendor. This is crucial to proactively identify and address potential security vulnerabilities before they escalate.
- Data breach notification procedures: Define a process for the vendor to notify you of any security breaches that may occur. This ensures timely response and mitigation.
Procedure for Handling Vendor Non-Compliance
A well-defined procedure for handling non-compliance is essential for maintaining the security posture. This should include:
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Initial Notification: Send a formal written notification to the vendor outlining the specific areas of non-compliance. |
| 2 | Timeline for Corrective Actions: Provide a reasonable timeframe for the vendor to address the identified issues. |
| 3 | Follow-up and Monitoring: Monitor the vendor’s progress and compliance with the corrective actions. |
| 4 | Escalation and Remediation: Escalate the issue if the vendor fails to comply within the stipulated timeframe. Consider potential contract penalties or termination if necessary. |
“A proactive approach to cybersecurity policy enforcement with third-party vendors is crucial for mitigating risk and ensuring compliance. A well-defined process and clear contract provisions are vital components of this approach.”
Monitoring and Evaluating Compliance
Staying ahead in cybersecurity requires constant vigilance, especially when dealing with third-party vendors. Effective monitoring and evaluation of compliance ensures that policies are not just written, but actively enforced and maintained. This proactive approach helps identify vulnerabilities and adapt to evolving threats. The key is to move beyond a one-time check and establish continuous monitoring that adapts to changes in the vendor’s operations or the cybersecurity landscape.
Continuous Monitoring Strategies
Continuous monitoring of third-party vendor compliance is crucial for maintaining a secure environment. This involves regularly assessing their adherence to established policies. Automated tools can track security events, log file analysis, and real-time threat intelligence feeds. By incorporating these strategies, organizations can effectively detect potential breaches or non-compliance issues proactively.
Assessing Policy Effectiveness
Assessing the effectiveness of implemented policies requires a structured approach. Key performance indicators (KPIs) should be defined to measure compliance levels. Metrics such as the number of security incidents, the time taken to resolve issues, and the rate of policy violations can provide valuable insights. Regular reporting and analysis of these KPIs help identify areas needing improvement and demonstrate the value of the alignment process.
Measuring Alignment Success
Measuring the success of the alignment process hinges on clear and measurable objectives. These objectives should be tied to specific metrics, like a reduction in security incidents involving third-party vendors or an increase in the number of vendors adhering to the policies. Quantifiable data allows for objective assessment and demonstrates the effectiveness of the alignment strategy. Regular reporting and trend analysis are critical for demonstrating the return on investment of the entire process.
Keeping cybersecurity policies in line with third-party vendors is crucial, much like ensuring brand authenticity is vital to building trust. After all, if your third-party partners aren’t secure, your entire system is vulnerable. Just as authenticity is essential to brand building , consistent security practices across the board, including third-party vendors, builds a stronger, more resilient system overall.
This ultimately strengthens your brand’s reputation and protects your customer base.
Third-Party Vendor Security Posture Checklist
Regular assessments of third-party vendor security posture are essential for maintaining a strong security posture. This proactive approach helps identify vulnerabilities and risks early on, enabling organizations to take corrective actions before incidents occur. This checklist provides a structured approach for evaluating the security posture of vendors.
Securing your data with third-party vendors requires careful policy alignment. Just like the future of sustainable energy looks to alternative materials like advanced battery technologies ( the future of sustainable energy looks to alternative materials ), businesses need to adapt their cybersecurity strategies. This means proactively assessing the security measures of potential partners and ensuring your policies are robust enough to handle the changing landscape of data protection.
- Security Policies and Procedures: Does the vendor have documented security policies and procedures? Are these policies regularly reviewed and updated? Do they align with industry best practices and relevant regulations?
- Vulnerability Management: Does the vendor have a vulnerability management process in place? How frequently do they conduct vulnerability scans and penetration testing? What is their response plan for discovered vulnerabilities?
- Incident Response Plan: Does the vendor have a documented incident response plan? Is it regularly tested and updated? What is their communication protocol in case of a security incident?
- Access Controls and Authentication: Are access controls and authentication mechanisms robust and secure? Does the vendor follow the principle of least privilege? What are their user account management practices?
- Data Security: Does the vendor implement appropriate measures to protect sensitive data? Are data encryption and access controls implemented for data at rest and in transit? How does the vendor handle data breaches?
- Physical Security: What are the vendor’s physical security measures? How are their physical facilities secured, and what are their policies for handling sensitive materials?
- Third-Party Risk Assessment: Does the vendor have a process to identify and assess the security risks associated with its own third-party vendors? This demonstrates a proactive approach to managing security across their supply chain.
- Employee Training and Awareness: Does the vendor provide regular security awareness training to their employees? How does the vendor ensure employees understand and adhere to security policies?
- Compliance Certifications: Does the vendor hold relevant security certifications (e.g., ISO 27001, SOC 2)? Certifications demonstrate a commitment to established security standards.
Addressing Security Incidents Involving Third-Party Vendors
Protecting your organization’s sensitive data extends beyond your internal walls. Third-party vendors, critical to many businesses, can introduce vulnerabilities if their security posture is inadequate. Proactive measures and well-defined incident response plans are crucial for mitigating risks and minimizing damage in case of a security breach.A robust incident response plan for third-party vendors ensures swift and coordinated action when a security incident occurs.
This plan, crucial for maintaining business continuity, Artikels the procedures for identifying, containing, and resolving incidents. This structured approach, when implemented effectively, reduces the potential for escalating problems and minimizes the impact on your organization.
Incident Response Planning and Procedures
Effective incident response planning requires detailed procedures for handling security incidents originating from third-party vendors. These procedures should be clear, concise, and easily accessible to all relevant personnel. This includes outlining roles and responsibilities, communication channels, and the escalation process. A documented incident response plan serves as a vital reference during a crisis.
- Establish clear communication channels: Define the process for immediately contacting the third-party vendor and their security team. This includes specifying contact points and expected response times. Clear communication channels are essential for effective collaboration and timely information sharing.
- Define roles and responsibilities: Clearly Artikel the roles and responsibilities of internal personnel involved in the incident response. This includes designating individuals responsible for investigation, containment, communication, and reporting. This structured approach ensures accountability and efficiency during a crisis.
- Develop a containment strategy: Establish a process for containing the incident to limit the potential damage. This includes steps to isolate affected systems and data, and preventing further unauthorized access. The containment strategy should be adaptable to various scenarios.
- Establish a notification procedure: Define procedures for notifying relevant stakeholders, including management, legal counsel, and regulatory bodies, depending on the nature and severity of the incident. This ensures timely and appropriate actions are taken.
Communication and Collaboration in Incident Response
Effective communication and collaboration are paramount during a security incident involving a third-party vendor. Transparency and clear communication channels are essential for maintaining trust and ensuring a swift and coordinated response. Prompt and accurate information sharing with both the vendor and internal stakeholders is critical.
- Establish a dedicated communication channel: Creating a dedicated communication channel for incident response, such as a dedicated email address or a secure messaging platform, will ensure streamlined communication during a crisis. This dedicated channel prevents the mixing of urgent incident-related communications with other general inquiries.
- Establish a joint incident response team: Forming a joint incident response team composed of representatives from both your organization and the third-party vendor can facilitate collaborative efforts in resolving the incident. This joint team ensures a holistic approach to the problem.
- Document and share information: Maintain a detailed record of all communication, actions, and findings during the incident response process. This documented history is invaluable for future incident response planning and for potential legal or regulatory requirements.
Effective Incident Response Strategies
Several strategies can enhance the effectiveness of incident response involving third-party vendors. These strategies are critical for minimizing the impact and ensuring a swift resolution. Learning from previous incidents is also vital for improving future responses.
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Proactive Vendor Assessments | Regularly assess the security posture of your third-party vendors to identify potential vulnerabilities before a breach occurs. This proactive approach allows for mitigation before an incident occurs. |
| Establish Service Level Agreements (SLAs) with Incident Response Provisions | Include specific incident response clauses in your SLAs with vendors. These clauses should Artikel the vendor’s responsibilities in case of a security incident. |
| Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Integration | Integrate SIEM systems to monitor third-party vendor activity for suspicious patterns or anomalies. This proactive monitoring can help identify potential security issues early on. |
| Regular Security Awareness Training for Vendor Staff | Implement security awareness training for vendor staff to improve their understanding of security risks and best practices. This educational approach empowers staff to identify and report potential issues. |
Illustrative Examples of Successful Implementations

Successfully aligning cybersecurity policies with third-party vendors is crucial for modern organizations. This involves more than just signing contracts; it necessitates a proactive, ongoing approach to risk management. Effective implementations often leverage a combination of robust policies, clear communication channels, and consistent monitoring. These successful implementations demonstrate the tangible benefits of a well-defined strategy.
Retail Giant’s Vendor Risk Management Program
A major retail chain successfully implemented a comprehensive vendor risk management program. They identified key third-party vendors with high exposure to sensitive data, like payment processors and cloud storage providers. This process involved rigorous due diligence, including security assessments, penetration testing, and audits of vendor security controls. They developed detailed security questionnaires for all new vendors and required contracts to include specific security clauses, ensuring alignment with the company’s security standards.
“By implementing a proactive approach to vendor risk, we were able to significantly reduce the attack surface and bolster our overall security posture.”
Security Director, Retail Chain
The benefits included reduced vulnerabilities, improved compliance with regulations (e.g., PCI DSS), and a demonstrable decrease in data breaches. The challenges included the initial investment in personnel and tools, and the need to educate both internal teams and vendors about the new policies. The implementation steps included creating a centralized vendor risk management team, developing a standardized risk assessment framework, and providing extensive training for all employees involved.
Financial Institution’s Multi-Layered Approach
A large financial institution implemented a multi-layered approach to cybersecurity policy alignment with third-party vendors. This involved a phased rollout, starting with high-risk vendors. They employed a combination of automated tools for initial screening and manual assessments for deeper analysis. This allowed them to tailor the level of scrutiny based on the vendor’s risk profile. Vendor questionnaires were customized to address specific data handling practices and security protocols.
“Our layered approach ensures a consistent level of security across all third-party relationships, minimizing the risk of vulnerabilities and potential breaches.”
Chief Information Security Officer, Financial Institution
The benefits included enhanced data protection, improved compliance with industry regulations (e.g., GDPR), and increased trust with vendors. The challenges included maintaining the consistency of the assessment process across a vast number of vendors and ensuring vendor cooperation with the assessments. The implementation steps included defining clear roles and responsibilities within the security team, establishing a standardized assessment methodology, and conducting regular audits to ensure adherence to policies.
Cloud Service Provider’s Security Posture Assessment
A cloud service provider developed a comprehensive security posture assessment process for its clients. This involved assessing the security practices of their clients’ third-party vendors to ensure compliance with the provider’s security standards. The assessment framework encompassed a variety of factors, including data encryption, access controls, and incident response plans. They used a standardized checklist to guide the assessments, ensuring consistency across all engagements.
“We’ve established a comprehensive framework for security assessments that not only protects our clients but also enhances their own security posture.”
Head of Security, Cloud Service Provider
The benefits included improved security for clients and the cloud provider itself. The challenges included the need to adapt the assessment process to the diverse needs of different clients and ensuring ongoing compliance from vendors. The implementation steps included developing a clear and concise assessment methodology, creating a dedicated team for conducting assessments, and providing training for staff on the methodologies.
Future Trends in Third-Party Vendor Security
Navigating the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity requires a proactive approach, especially when dealing with third-party vendors. The reliance on external providers for services and functionalities necessitates a sophisticated understanding of emerging threats and the adaptation of security policies accordingly. This section will delve into anticipated future trends, highlighting the potential impact of emerging technologies, and the proactive steps organizations must take to maintain a robust security posture.
The Rise of Cloud-Based Services
The increasing adoption of cloud-based services by third-party vendors necessitates a careful evaluation of security protocols. Cloud environments present unique challenges, such as shared responsibility models and the potential for vulnerabilities in cloud infrastructure. Organizations need to assess the security posture of their cloud-based vendors, considering their adherence to industry best practices and regulatory compliance. The focus should be on scrutinizing the vendor’s security controls, data encryption procedures, and incident response plans.
Security audits and penetration testing of cloud environments are becoming crucial to ensure the safety of sensitive data.
The Impact of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are transforming various sectors, including cybersecurity. While AI offers opportunities to enhance threat detection and response, it also introduces new potential vulnerabilities. Third-party vendors utilizing AI or ML must be vetted for robust security protocols to mitigate the risks associated with AI-powered systems. AI models can be susceptible to adversarial attacks, and these attacks can exploit vulnerabilities in vendor systems.
Organizations must ensure that third-party AI systems are regularly updated and patched to address emerging vulnerabilities.
The Growing Importance of Zero Trust Security
Zero Trust security is evolving from a concept to a critical security imperative. The adoption of this model by third-party vendors is becoming essential. Zero Trust operates on the principle of never trusting, always verifying, and this principle applies to all access requests, regardless of location or identity. This approach necessitates strong authentication mechanisms and granular access controls for third-party vendors, reducing the potential for unauthorized access and data breaches.
It also mandates the implementation of micro-segmentation techniques to isolate different parts of the vendor’s network.
The Need for Enhanced Threat Intelligence Sharing
The sharing of threat intelligence among organizations and vendors is becoming increasingly critical. Organizations should establish channels for timely and accurate threat intelligence sharing with third-party vendors. This collaboration is essential to proactively mitigate emerging threats. A shared threat intelligence platform allows vendors to identify and address threats more quickly, which strengthens the overall security posture. This approach fosters a collaborative environment that allows organizations to proactively respond to evolving threats.
Proactive Adaptation Strategies
Organizations must adopt a proactive approach to adapting to future trends in third-party vendor security. Regular security assessments of third-party vendors are crucial. Organizations should incorporate continuous monitoring and evaluation of vendor security practices. The development of a comprehensive security framework is necessary to ensure a standardized approach to security policy alignment across all vendors. This framework should Artikel the expected security controls, protocols, and incident response procedures for all third-party vendors.
This ensures a robust, adaptive, and resilient security posture for the future.
Outcome Summary
In conclusion, aligning cybersecurity policies with third-party vendors is not a one-time task but an ongoing process demanding constant vigilance and adaptation. By proactively addressing risks, fostering open communication, and implementing robust enforcement mechanisms, organizations can significantly enhance their overall security posture and mitigate potential vulnerabilities. Remember, a strong security foundation starts with the vendors you trust.

