
Climbing the Attendance Ladder A Guide
Climbing the attendance ladder isn’t just about showing up; it’s about mastering consistency and reaping the rewards. This comprehensive guide delves into the strategies, motivations, and challenges of improving attendance, whether in school, the workplace, or community events. We’ll explore different interpretations, effective strategies, and the profound impact of consistent presence on individual and collective success.
From understanding the core concepts to implementing practical steps, this guide provides a roadmap to elevate your attendance and unlock its hidden potential. We’ll examine the motivations behind wanting better attendance and analyze the specific strategies that work in various settings, like education, business, or community involvement.
Defining “Climbing the Attendance Ladder”
The phrase “climbing the attendance ladder” evokes a sense of progression and improvement in the consistency and frequency of attendance. It suggests a deliberate and often incremental effort to enhance one’s presence at various locations, whether it’s school, work, or community events. This upward trajectory isn’t just about showing up; it’s about cultivating a reliable and consistent presence, a cornerstone for success in many aspects of life.This concept transcends simple punctuality.
It implies a commitment to regular participation, reflecting a dedication to engagement and contribution. The “ladder” metaphor highlights the upward movement through different levels of attendance, implying an increasing value placed on consistent presence and engagement over time. The specific meaning and application of this phrase can vary considerably depending on the context.
Interpretations and Variations
Different contexts offer unique interpretations of “climbing the attendance ladder.” In a school setting, it might mean consistently attending classes and extracurricular activities. In a workplace, it could involve punctuality, regular attendance at meetings, and participation in team projects. Community events might interpret it as a commitment to attending regular meetings, volunteering, and participating in group activities.
Common Characteristics and Goals
The common characteristics associated with “climbing the attendance ladder” include:
- Regularity: Consistent presence is key, implying a dedication to showing up on schedule.
- Punctuality: Arriving on time demonstrates respect for schedules and commitments.
- Active Participation: Engagement in the activities at hand is essential, whether it’s actively participating in class discussions or contributing to team projects.
- Improved Performance: Consistent attendance often correlates with better academic or professional performance, as well as stronger community involvement.
Motivations for Attendance Improvement
Several motivations fuel the desire to improve attendance, including:
- Academic Success: Students may strive for better grades and academic achievement through consistent attendance in classes and extra-curricular activities.
- Professional Advancement: Employees may aim for promotions or career growth by demonstrating reliability and consistent participation in work activities.
- Community Involvement: Individuals may seek to deepen their engagement within a community by regularly attending meetings and events.
- Personal Development: Consistent attendance can foster a sense of responsibility and commitment, which contributes to personal growth.
Attendance Improvement Strategies
Different settings require tailored strategies for attendance improvement.
| Setting | Strategies |
|---|---|
| Education |
|
| Business |
|
| Community Events |
|
Strategies for Improvement

Climbing the attendance ladder requires a multifaceted approach that goes beyond simply rewarding attendance. Understanding the underlying reasons for low attendance is crucial to developing effective strategies. A well-defined plan considers the specific context of the group or organization, focusing on both individual and systemic factors that influence attendance.Effective attendance improvement initiatives require a deep dive into understanding why people aren’t consistently present.
Is it a logistical issue, a lack of engagement, or a combination of factors? Addressing these root causes is critical for creating sustainable solutions, not just temporary fixes. This necessitates a proactive and adaptable approach, as the best strategies might vary based on the specific group or organization.
Incentive Programs
Incentive programs can be powerful tools for boosting attendance, but they must be carefully designed and implemented to be effective. These programs need to align with the organization’s values and the specific needs of the attendees. A one-size-fits-all approach is unlikely to produce lasting results.
- Types of Incentives: Incentives can range from simple rewards like gift cards or small prizes to more substantial benefits like discounts, recognition, or opportunities for professional development. The key is to identify incentives that are attractive and motivating to the target audience.
- Reward Structure: Attendance incentives can be structured as rewards for reaching specific attendance targets (e.g., a bonus for attending 90% of meetings). Alternatively, incentives can be awarded for consistent attendance over a period of time (e.g., a monthly prize for perfect attendance).
- Fairness and Transparency: The incentive program should be transparent and clearly communicated to all participants. This ensures that the system is perceived as fair and equitable. It’s vital to avoid any appearance of bias or favoritism.
Overcoming Obstacles
Understanding and addressing obstacles to attendance is critical for sustained improvement. Often, these obstacles stem from practical difficulties, lack of engagement, or insufficient communication. By proactively addressing these issues, organizations can significantly improve attendance rates.
- Logistical Challenges: Transportation issues, scheduling conflicts, or childcare responsibilities can significantly impact attendance. Implementing flexible scheduling options, providing transportation assistance, or offering childcare support can help overcome these obstacles.
- Engagement and Motivation: Attendees need to feel that their participation is valued and meaningful. Improving the quality of meetings, incorporating interactive elements, or recognizing and rewarding contributions can increase engagement and motivation.
- Communication Breakdown: Poor communication about meeting times, locations, or agendas can lead to missed opportunities. Clear, concise, and consistent communication channels are vital for effective attendance management.
Step-by-Step Procedure for Implementing an Attendance Improvement Plan
A structured approach is essential for implementing an attendance improvement plan. This involves a series of well-defined steps that ensure the plan is effectively rolled out and monitored.
- Assessment: Analyze current attendance data to identify trends, patterns, and potential causes for low attendance. This step requires a thorough examination of existing records.
- Goal Setting: Establish clear and measurable attendance goals. The goals should be realistic and achievable, aligning with the organization’s overall objectives.
- Strategy Development: Develop specific strategies to address identified obstacles and improve attendance. This includes implementing incentive programs and addressing logistical challenges.
- Implementation: Put the developed strategies into action. Ensure that all relevant stakeholders are aware of and on board with the plan.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Continuously monitor attendance rates and evaluate the effectiveness of the implemented strategies. Adjust strategies as needed to optimize outcomes.
Examples of Successful Initiatives
Numerous organizations have successfully improved attendance through innovative initiatives. For example, a software company implemented flexible work hours and remote work options, which significantly increased employee attendance and satisfaction.
- Flexible Work Arrangements: Offering flexible work schedules, remote work options, and compressed workweeks can significantly improve employee attendance, especially in knowledge-based industries.
- Improved Communication: Clearly communicating meeting details and agendas, using multiple communication channels, and actively engaging attendees in discussions can greatly enhance attendance rates.
- Enhanced Meeting Structure: Implementing interactive sessions, incorporating real-time feedback mechanisms, and ensuring meeting agendas are relevant and engaging can greatly improve attendance rates.
Pros and Cons of Incentive Programs
| Incentive Program Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Gift Cards | Simple, cost-effective, widely appealing | Potential for perceived triviality, limited long-term impact |
| Professional Development Opportunities | High motivational value, enhances skills | Higher cost, potential for conflicts in scheduling |
| Recognition and Awards | Boosts morale, creates a sense of community | Requires ongoing effort to maintain impact |
Impact and Benefits of Increased Attendance

Consistent attendance isn’t just about showing up; it’s a powerful driver of individual and group success. It fosters a sense of commitment, builds stronger relationships, and ultimately unlocks greater potential for achievement. Regular presence demonstrates a dedication to the shared goals and activities, paving the way for deeper engagement and more meaningful contributions.Higher attendance translates to richer experiences and more impactful outcomes.
Individuals gain more from workshops, meetings, and learning opportunities, while teams benefit from a more cohesive and productive environment. This increased engagement creates a virtuous cycle, leading to further motivation and a stronger desire for continued participation.
Positive Effects on Individuals
Regular attendance cultivates a stronger sense of belonging and engagement. Individuals who consistently participate in group activities feel more connected to the community and invested in its success. This sense of belonging can significantly impact mental well-being and foster a more positive and supportive environment. Consistent presence also enhances the learning experience, enabling individuals to fully grasp concepts, actively participate in discussions, and develop deeper understanding.
Positive Effects on Groups
Increased attendance within groups fosters a more cohesive and productive environment. Teams and organizations benefit from the combined knowledge, skills, and perspectives of all members. A greater number of participants leads to more diverse viewpoints and solutions, enriching discussions and decisions. This increased engagement directly correlates with a more dynamic and productive group environment. Active participation and consistent presence lead to a stronger sense of shared responsibility and collective ownership.
Impact on Productivity and Performance
Attendance directly impacts productivity and performance. Regular participation in meetings, workshops, and projects allows for a more focused and efficient work environment. Missed meetings lead to information gaps and potential delays, whereas consistent attendance keeps everyone informed and on track. This, in turn, leads to a more effective and timely completion of tasks.
Attendance and Success in Various Fields
The connection between attendance and success is evident across various fields. In education, regular attendance correlates with improved grades and academic achievement. In the workplace, consistent presence is often linked to career advancement and professional growth. In sports, consistent participation is crucial for skill development and team success. In any field, consistent engagement builds a strong foundation for achieving goals.
Case Studies Demonstrating the Impact
Numerous case studies demonstrate the positive impact of increased attendance. A study on student attendance in a particular high school showed a direct correlation between increased attendance and improved academic performance. In a software development team, implementing a reward system for consistent attendance resulted in a noticeable increase in project completion rates and overall team morale. These examples underscore the value of regular attendance in achieving desired outcomes.
Correlation Between Attendance and Outcomes
| Situation | High Attendance | Low Attendance |
|---|---|---|
| Academic Performance | Improved grades, higher test scores, increased knowledge retention | Lower grades, poorer test scores, difficulty in grasping concepts |
| Project Completion | Projects completed on time and within budget, higher quality deliverables | Projects delayed, incomplete deliverables, increased risk of failure |
| Team Cohesion | Stronger team bonds, increased collaboration, enhanced communication | Weakened team bonds, decreased collaboration, communication breakdowns |
| Skill Development | Improved skills and knowledge through active participation | Limited skill development due to missed opportunities |
Challenges and Obstacles
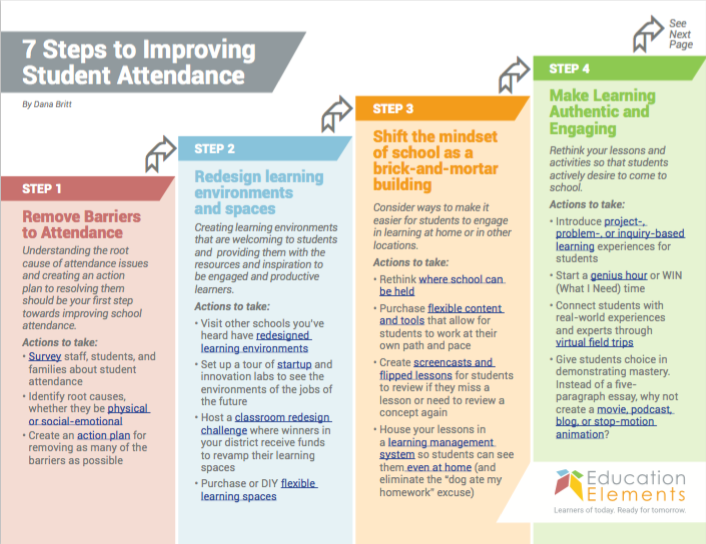
Consistently high attendance is a goal many organizations and individuals strive for, but achieving it isn’t always straightforward. Obstacles can arise from various sources, requiring proactive identification and strategies to overcome them. Understanding these challenges is the first step towards developing effective solutions.Potential obstacles in attendance improvement are numerous, and they can stem from individual circumstances, organizational policies, or external factors.
These difficulties can significantly hinder efforts to build a strong and engaged community or team.
Individual Factors Affecting Attendance
Understanding the reasons why individuals might struggle with consistent attendance is crucial. Personal commitments, such as family responsibilities or other significant obligations, often take precedence. Health issues, including illness or injury, can also significantly impact an individual’s ability to attend regularly. Work-life balance concerns, including job demands and commuting difficulties, are frequently cited as challenges to maintaining consistent attendance.
Furthermore, lack of motivation, perceived lack of value in the activity, or a sense of disconnect from the group can contribute to inconsistent attendance.
Organizational Factors Hindering Attendance
Organizational policies and practices can also play a role in hindering attendance. Scheduling conflicts, inflexible meeting times, or insufficient notice regarding events can make it difficult for individuals to attend consistently. A perceived lack of value in the activity, lack of clear communication about the importance of attendance, and insufficient recognition for participation can discourage consistent attendance.
Climbing the attendance ladder can be tough, but sometimes external factors can help propel you forward. For example, the recent redesignation of the Stevens Points Breast Care Center, as highlighted in this article, stevens points breast care center receives redesignation , could lead to increased community engagement and boost overall attendance numbers. This, in turn, could inspire others to prioritize similar healthcare initiatives, ultimately making a positive impact on the attendance ladder’s overall trajectory.
External Factors Affecting Attendance
External factors, such as weather conditions, transportation issues, or unforeseen circumstances, can also disrupt attendance patterns. Events beyond an individual’s control can make it challenging to maintain a consistent attendance record. Unforeseen personal emergencies or crises can also make it difficult to maintain attendance.
Addressing and Overcoming Obstacles
Effective strategies for motivating individuals to improve attendance are vital. Open communication and active listening are crucial. Creating a supportive and inclusive environment can foster a sense of belonging and encourage participation. Flexible scheduling options and alternative meeting formats can accommodate various needs and preferences. Providing incentives or rewards for consistent attendance can motivate individuals to participate more actively.
Building a sense of community and shared purpose can make participation more engaging and meaningful.
Motivational Strategies
Effective motivational strategies can help overcome these obstacles. Recognizing and appreciating the efforts of individuals who consistently attend is important. Making the activity more engaging and relevant to attendees’ interests can enhance motivation. Building strong relationships and fostering a sense of community among participants can encourage participation. Creating a supportive environment that values and respects each individual’s contributions can enhance attendance.
Table: Challenges and Potential Solutions for Attendance Improvement
| Challenge | Potential Solution |
|---|---|
| Individual commitments (family, health) | Flexible scheduling, alternative meeting formats, understanding and empathy |
| Organizational policies (rigid scheduling) | Flexible scheduling options, clear communication, adjusting meeting times to accommodate diverse needs |
| External factors (weather, transportation) | Providing clear notice, offering alternative formats, adjusting schedules |
| Lack of motivation/engagement | Making activities more engaging, offering incentives, recognition for participation |
| Lack of communication | Open communication, clear communication of importance of attendance |
Measuring and Tracking Progress
Tracking attendance improvement requires a systematic approach to monitoring and analyzing data. A well-defined process for gathering, recording, and interpreting attendance information is crucial for identifying patterns, trends, and areas needing adjustment in attendance improvement strategies. This allows for informed decision-making and ultimately leads to more effective interventions.
Methods for Tracking and Measuring Attendance
Effective attendance tracking involves utilizing a combination of methods tailored to specific needs. Manual logs, while simple, can be prone to errors. Digital tools offer greater accuracy, automated data entry, and more robust reporting capabilities. These tools often integrate with existing scheduling and communication systems. Furthermore, implementing a clear attendance policy, communicated effectively to all stakeholders, ensures consistent application and understanding of attendance expectations.
Comprehensive Procedure for Monitoring Attendance Data
A structured procedure for monitoring attendance data streamlines the process, minimizing errors and maximizing the value of collected information. This involves establishing clear guidelines for recording attendance, including the specific time of arrival and departure, and defining acceptable absences. Regularly reviewing and updating attendance records is essential to maintaining accuracy. Regular reports summarizing attendance data, broken down by department, team, or individual, provide key insights into attendance patterns and potential issues.
Climbing the attendance ladder can be tough, but it’s rewarding. It’s about more than just showing up, though. It’s about engaging and contributing, and that’s where organizations like sustaining our waters the fox wolf watershed alliance come in. They’re working hard to improve water quality, and that directly impacts our communities and our ability to participate in activities.
So, let’s keep showing up and making a difference, both in our attendance and in the larger picture.
Analyzing Attendance Patterns and Trends
Analyzing attendance patterns and trends requires careful examination of the data. Identifying recurring patterns, such as unusually high or low attendance on specific days or during particular periods, can pinpoint potential issues or highlight successful strategies. Consider factors like holidays, events, or external influences. Analyzing attendance data over time reveals trends, allowing for proactive adjustments and predictions.
For instance, a consistent dip in attendance on Mondays might indicate a need for team-building activities or a shift in work schedules.
Using Data to Inform Adjustments to Attendance Improvement Strategies
Data analysis provides valuable insights into the effectiveness of implemented attendance improvement strategies. Identify areas where strategies are yielding positive results and areas where adjustments are needed. For instance, if a particular training session on time management correlates with improved attendance, replicate successful elements in other areas. Conversely, if a strategy is not improving attendance, identify the root cause, such as poor communication or lack of clarity in expectations.
Visualizing Attendance Data
Visual representations of attendance data make it easier to understand trends and patterns. Different visualization methods can highlight different aspects of the data. Effective visualization aids in identifying patterns and anomalies in attendance.
Table Summarizing Data Visualization Methods
| Visualization Method | Description | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Line Graph | Shows trends over time. | Tracking attendance fluctuations over months or years. |
| Bar Chart | Compares attendance across categories. | Comparing attendance between departments or teams. |
| Scatter Plot | Identifies correlations between factors. | Determining if factors like specific projects or events correlate with attendance levels. |
| Heatmap | Highlights areas with high or low attendance. | Identifying days or periods with unusually high or low attendance. |
| Pie Chart | Shows the proportion of attendance in different categories. | Illustrating the percentage of employees who are consistently present. |
Motivational Factors and Incentives
Fueling consistent attendance requires understanding the driving forces behind employee engagement. Simply implementing a reward system isn’t enough; it’s crucial to recognize the complex interplay of intrinsic and extrinsic motivators that shape attendance behavior. Understanding these factors allows for a more targeted and effective approach to boosting attendance rates.Intrinsic motivators, such as a sense of purpose, personal growth opportunities, and a positive work environment, play a significant role in employee engagement.
Climbing the attendance ladder can be tough, but sometimes a fresh perspective helps. Oshkosh, for example, is looking at new development near the Fox River, which could bring a lot of new opportunities and potentially boost the local economy. This kind of growth can really fuel the community, creating a ripple effect that ultimately makes it easier for individuals to achieve their goals, including scaling that attendance ladder.
So, keep your eyes peeled for future developments in Oshkosh, and keep striving for that attendance win! oshkosh eyes new development near fox river
Extrinsic motivators, such as incentives and rewards, can also powerfully influence attendance, but they are most effective when aligned with intrinsic values. A holistic approach, addressing both intrinsic and extrinsic factors, is key to cultivating a culture of consistent attendance.
Identifying Key Drivers of Attendance Behavior
Attendance behavior is multifaceted and driven by a combination of factors. Personal circumstances, job satisfaction, and perceived value of the work environment all contribute to the decision to attend. Understanding the specific drivers within a particular organization is crucial for tailoring motivational strategies. Recognition programs and opportunities for skill development are examples of strategies that address these drivers.
Examples of Attendance-Encouraging Incentives
Incentives can take various forms, ranging from tangible rewards to intangible recognition. Effective incentives are those that resonate with the values and motivations of the employees. Financial rewards, such as bonuses or gift cards, can be powerful motivators. Non-monetary rewards, such as extra time off, preferential parking, or opportunities for professional development, can also be highly effective.
Designing a Reward System to Promote Consistent Attendance
A well-designed reward system should be transparent, easily understood, and consistently applied. Clear criteria for earning rewards should be established, ensuring fairness and predictability. The reward should be proportional to the effort and consistent attendance demonstrated. A tiered system, offering progressively larger rewards for increasing attendance levels, can be particularly effective in motivating sustained improvement.
Strategies for Maintaining Motivation Over Time
Maintaining motivation requires continuous reinforcement and adaptation. Regular reviews of the reward system and employee feedback sessions are essential to ensure the system remains relevant and engaging. Introducing new and varied incentives, recognizing individual contributions, and fostering a positive work culture are key strategies to maintain motivation over time. Regular communication about the importance of attendance and the benefits of the reward system helps to reinforce the message.
Different Types of Incentives and Their Potential Impact
| Type of Incentive | Potential Impact on Attendance | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Financial Rewards | Significant impact on attendance, particularly for short-term gains. | Bonuses, gift cards, paid time off, increased salaries |
| Non-Financial Rewards | Strong impact on long-term motivation and job satisfaction. | Public recognition, employee of the month, opportunities for professional development, additional training, flexible work arrangements |
| Recognition and Appreciation | Boost morale and increase engagement. | Verbal praise, written thank-you notes, company-wide acknowledgments |
| Opportunities for Growth | Attract and retain employees with higher attendance rates. | Promotions, mentorship programs, skill-building workshops |
Attendance in Different Contexts: Climbing The Attendance Ladder
Attendance expectations and practices vary significantly across different settings, from the structured environment of a classroom to the dynamic atmosphere of a retail store. Understanding these variations is crucial for implementing effective attendance policies and strategies that resonate with the specific context and culture. These differences also highlight the need for flexible approaches to attendance management, recognizing the unique challenges and opportunities within each environment.Understanding the diverse factors influencing attendance—from industry standards to cultural norms—is essential for creating effective and fair policies.
This involves recognizing the specific needs and expectations of employees and students in various sectors, as well as the legal requirements and potential ethical considerations.
Attendance Expectations in Education
Educational institutions prioritize consistent attendance for student success. This is because regular attendance is directly correlated with better academic performance and overall development. Students who regularly attend classes are better equipped to grasp concepts, participate in discussions, and form relationships with peers and instructors. However, the specific attendance policies and expectations can vary depending on the educational level and institution type.
Elementary schools often have more lenient attendance policies, while higher education institutions might have stricter guidelines. Attendance in extracurricular activities may also have varying attendance requirements depending on the school’s policies and the program’s nature.
Attendance Requirements in Healthcare
Healthcare settings, including hospitals and clinics, demand high levels of attendance due to the critical nature of the work. Patient safety and care rely heavily on the consistent presence of qualified personnel. Healthcare professionals need to maintain consistent schedules to ensure seamless patient care and emergency response. The required attendance may vary depending on the specific role, with some roles requiring more frequent and consistent presence than others.
Moreover, adherence to hospital policies regarding attendance is crucial to maintain operational efficiency and maintain patient safety standards. The potential for serious consequences from non-compliance necessitates strict adherence to policies and procedures.
Attendance in Retail Environments, Climbing the attendance ladder
Retail settings often prioritize attendance based on staffing needs and customer service demands. Maintaining adequate staffing levels is crucial for meeting customer expectations and ensuring smooth store operations. Retail environments have unique challenges related to attendance, often influenced by employee scheduling, seasonal fluctuations in customer traffic, and the need for flexibility in meeting fluctuating demands. Attendance policies in retail frequently involve scheduling systems and flexibility to accommodate both employee needs and business demands.
Cultural Influences on Attendance Behaviors
Cultural norms significantly influence attendance behaviors. In some cultures, punctuality and consistent attendance are highly valued, while in others, flexibility and adaptability are more emphasized. Cultural differences regarding attendance expectations must be considered when developing attendance policies and procedures. Understanding and respecting cultural differences can lead to more effective communication and improved employee or student relations. Strategies that acknowledge cultural sensitivities can lead to greater employee satisfaction and engagement.
Legal Considerations Regarding Attendance
Legal considerations regarding attendance vary across different contexts. For instance, laws related to employee attendance rights and regulations differ significantly from laws related to student attendance. Understanding and adhering to legal requirements for attendance is essential to avoid potential legal ramifications. Policies should align with applicable laws and regulations to prevent conflicts and maintain compliance.
Table: Attendance Policies and Procedures in Various Sectors
| Sector | Attendance Policy Highlights | Challenges | Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Education | Regular attendance is crucial for student success. Policies vary by level and institution. | Student absenteeism, tardiness, and extracurricular commitments. | Clear attendance policies, communication with families, flexible attendance options. |
| Healthcare | Consistent staffing is critical for patient safety and care. | Staffing shortages, unexpected absences, emergency situations. | Robust scheduling systems, backup staffing, clear communication protocols. |
| Retail | Maintaining adequate staffing to meet customer needs. | Employee scheduling conflicts, seasonal fluctuations, unexpected absences. | Flexible scheduling, adequate staffing levels, clear communication regarding attendance expectations. |
Final Review
In conclusion, climbing the attendance ladder is a journey of self-improvement and strategic planning. By understanding the motivations, implementing effective strategies, and overcoming obstacles, individuals and groups can cultivate a culture of consistent attendance. This leads to enhanced productivity, stronger relationships, and ultimately, greater success in any endeavor. The key takeaway is that consistent presence, when approached strategically, unlocks significant benefits.




