
Getting Ahead of the Skilled Trade Demand Game
Getting ahead of the skilled trade demand game is crucial for staying competitive in today’s market. The demand for skilled tradespeople is soaring, but how can you position yourself and your workforce to capitalize on this opportunity? This post explores the current landscape, strategies for anticipating future needs, and steps to prepare the workforce for success.
Understanding the current skilled trade workforce demographics and projected demand over the next 5-10 years is essential. This involves analyzing key skills, available training programs, and the impact of automation. We’ll also discuss strategies to attract and retain skilled workers, bridge the education-industry gap, and integrate technology into training programs.
Understanding the Skill Gap
The skilled trades are experiencing a significant shift in demand, driven by factors like population growth, infrastructure development, and technological advancements. Understanding this dynamic is crucial for individuals and institutions seeking to navigate the labor market effectively. A deep dive into current workforce demographics, projected demand, and the necessary skills will provide a clear picture of the future of skilled trades.
Current Skilled Trade Workforce Demographics
The current skilled trade workforce often exhibits a demographic imbalance. Many trades have an aging workforce, with a substantial portion nearing retirement age. This presents a looming shortage of experienced professionals. Additionally, there are significant variations in workforce demographics across different trades, with some experiencing greater attrition rates than others.
Projected Demand for Skilled Trades (2024-2034)
The demand for skilled trades is projected to increase substantially over the next decade. This growth is anticipated across various sectors, from construction and manufacturing to energy and maintenance. The specific growth rates vary considerably by trade, with some sectors showing more rapid growth than others. For example, the demand for electricians and plumbers is expected to remain strong due to ongoing construction and renovation projects.
Key Skills and Competencies
Beyond basic technical proficiency, highly in-demand skills include problem-solving, adaptability, and the ability to work effectively in diverse teams. Technological literacy, including proficiency in utilizing modern tools and equipment, is also increasingly crucial. Tradespeople who can quickly learn new technologies and adapt to changing demands will be most sought after.
Current Training and Education Programs
A variety of training programs and apprenticeships exist for aspiring skilled tradespeople. These programs range from vocational schools to employer-based apprenticeships. The quality and effectiveness of these programs can vary significantly. Some programs provide comprehensive theoretical knowledge, while others focus primarily on practical application.
Comparison of Training Models
Apprenticeship programs, combining classroom learning with on-the-job training, are often considered effective for fostering practical skills and providing real-world experience. However, vocational schools can offer a broader theoretical foundation, preparing individuals for diverse applications within a specific trade. The effectiveness of each model often depends on the specific trade, the individual’s learning style, and the quality of the program itself.
Impact of Automation and Technology
Automation and technology are transforming the skilled trades landscape. While some tasks may be automated, the need for skilled technicians to maintain, repair, and troubleshoot automated systems is increasing. The demand for skilled tradespeople who understand and can work with these technologies is projected to grow significantly.
Overview Table
| Trade | Current Demand | Projected Demand (2024-2034) | Key Skills | Training Programs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electrician | High | High Growth | Troubleshooting, electrical safety, understanding of codes | Apprenticeships, vocational schools |
| Plumber | Moderate | Moderate Growth | Plumbing codes, water system knowledge, repair and maintenance | Apprenticeships, vocational schools |
| HVAC Technician | Moderate | High Growth | HVAC system knowledge, repair and maintenance, energy efficiency | Apprenticeships, vocational schools |
| Construction Worker | High | Moderate Growth | Safety procedures, construction techniques, equipment operation | Apprenticeships, vocational schools, on-the-job training |
Strategies for Anticipating Demand: Getting Ahead Of The Skilled Trade Demand Game
Staying ahead of the curve in the skilled trades requires proactive strategies for anticipating future demand. This involves more than simply reacting to current trends; it necessitates a deep understanding of industry evolution, emerging technologies, and the evolving needs of businesses and consumers. Predicting the future isn’t about crystal balls, but about leveraging data, analysis, and industry partnerships to create a roadmap for success.Understanding the current skill gap is a crucial first step, but it’s not enough.
The real challenge lies in anticipating how that gap will change and what new skills will be in high demand in the years to come. This requires a forward-looking approach, combining market research with insights from industry experts and emerging technologies.
Different Approaches to Anticipating Future Trends
Anticipating future skilled trade demand requires a multi-faceted approach. This involves examining historical trends, analyzing current market conditions, and proactively seeking out emerging technologies and their implications. A blend of quantitative and qualitative methods is crucial for creating a comprehensive understanding of future needs.
Staying ahead of the skilled trades demand curve is crucial. One key aspect is understanding how to position your business for a profitable sale, and that’s where five tips for selling a business comes in handy. Knowing the right strategies for selling your business will give you a significant edge in the long run and position you well for future opportunities within the skilled trade sector.
Framework for Assessing Evolving Industry Needs
A robust framework for assessing evolving industry needs should incorporate multiple data sources and perspectives. This framework must include:
- Historical data analysis: Examining past trends in skilled trade demand, including economic cycles, technological advancements, and shifts in consumer preferences.
- Market research: Conducting surveys, focus groups, and interviews with industry professionals, potential employers, and employees to gain a better understanding of current and future needs.
- Expert insights: Consulting with industry leaders, trade associations, and educational institutions to identify emerging trends and potential skill gaps.
- Technological advancements: Assessing the impact of new technologies, such as automation, robotics, and AI, on existing trades and identifying new opportunities for skilled workers.
Impact of Emerging Technologies on Future Skills
Emerging technologies are reshaping the skilled trades landscape. Understanding their impact is crucial for anticipating future demand.
- Automation and Robotics: These technologies are transforming manufacturing, construction, and other sectors, requiring skilled workers who can operate and maintain automated systems.
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): This technology is changing product design and manufacturing, creating new opportunities for skilled machinists, engineers, and designers.
- Internet of Things (IoT): IoT is impacting various industries, creating a need for skilled technicians who can install, maintain, and troubleshoot connected devices.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is influencing decision-making and process optimization across numerous industries, creating a demand for skilled professionals who can leverage and integrate AI tools.
Importance of Industry Partnerships
Strong industry partnerships are essential for anticipating future demand. Collaboration with businesses, educational institutions, and trade associations provides valuable insights and fosters a shared understanding of future needs. Joint initiatives can also help to develop and implement training programs that equip workers with the necessary skills.
Roadmap for Staying Ahead of the Curve
Developing a roadmap for staying ahead of the curve involves a proactive and iterative process.
Staying ahead of the skilled trade demand game requires a proactive approach. Thinking about the future of our water systems is key to long-term success, and organizations like sustaining our waters the fox wolf watershed alliance highlight the importance of responsible practices. Ultimately, a sustainable future for our water resources directly impacts the availability and quality of resources needed for skilled trades, making this a crucial consideration in getting ahead of the game.
- Continuous Monitoring: Constantly monitoring market trends, technological advancements, and economic shifts is crucial.
- Proactive Skill Development: Investing in training programs that prepare workers for emerging demands.
- Industry Collaboration: Fostering partnerships with businesses, educational institutions, and trade associations.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Using data and insights to inform strategic decisions and investments.
Emerging Markets and Industries Driving Demand
Certain markets and industries are expected to drive future demand for specific skilled trades.
- Renewable Energy: The growing demand for renewable energy sources is creating opportunities for electricians, solar installers, and wind turbine technicians.
- Construction of Smart Cities: Smart cities require specialized technicians to manage and maintain advanced infrastructure.
- Advanced Manufacturing: The demand for skilled machinists, engineers, and technicians is growing as manufacturing processes become more complex and sophisticated.
Successful Anticipatory Strategies in Other Industries
Analyzing successful anticipatory strategies in other industries can provide valuable lessons.
- Technology sector: Companies like Google and Amazon have demonstrated a proactive approach to anticipating future talent needs, investing heavily in education and training programs.
- Healthcare sector: The need for specialized medical professionals, such as nurses and technicians, is continuously evolving. Hospitals and healthcare organizations proactively invest in training programs and adapt to the growing needs of their communities.
Preparing the Workforce
Attracting and retaining skilled tradespeople is crucial for meeting the growing demand in the industry. A well-trained and motivated workforce is the cornerstone of any successful skilled trades enterprise. Addressing the skills gap through targeted training initiatives, promoting apprenticeships, and fostering a supportive environment are key to building a strong and adaptable talent pool. This focus on workforce development ensures a continuous supply of qualified individuals to meet future demands.
Attracting and Retaining Skilled Trades Professionals
A competitive compensation package, including benefits, is often a key factor in attracting and retaining skilled trades professionals. Beyond pay, offering opportunities for professional development, recognition for expertise, and a positive work environment are crucial. Providing clear career paths and demonstrating opportunities for advancement are also essential for retaining talent. Companies should actively engage with local educational institutions to establish partnerships and promote trades as desirable career paths.
Promoting Apprenticeships and Vocational Training Programs
Apprenticeships and vocational training programs offer structured pathways to skilled trades careers. These programs provide hands-on learning experiences, combining classroom instruction with practical application. Public-private partnerships between businesses and educational institutions can leverage resources and expertise to create high-quality programs. Strong mentorship programs within these training structures are essential for providing guidance and support. Marketing these programs effectively to potential participants and highlighting the benefits of these career paths is critical.
Staying ahead of the skilled trade demand game is crucial, and recent developments like Oshkosh’s plans for new construction near the Fox River highlight the growing need for skilled labor. Oshkosh eyes new development near fox river shows the potential for job opportunities, and this underscores the importance of proactively preparing for future demands in the industry.
Ultimately, understanding these trends and anticipating the needs of employers is key to securing a future in the skilled trades.
Addressing the Skills Gap Through Targeted Training Initiatives
Targeted training initiatives must be tailored to address specific skills gaps within the industry. These initiatives should focus on equipping individuals with the technical skills required for current and future job roles. This could include upgrading existing skills through specialized training programs or developing entirely new skill sets. Using technology in training, such as virtual reality simulations, can enhance the learning experience and make it more engaging and effective.
Innovative Approaches to Teaching and Learning Within Skilled Trades
Modernizing training methods is crucial to meet the evolving demands of the industry. Blending traditional hands-on experience with technology, such as utilizing virtual reality simulations for safety training or online learning platforms for theoretical knowledge, can create more engaging and effective learning experiences. Integrating project-based learning into apprenticeships allows for practical application and problem-solving development.
Upskilling and Reskilling Existing Workforce Members
Upskilling and reskilling existing workforce members is a vital strategy for adapting to changing industry needs. Providing opportunities for ongoing professional development through workshops, online courses, and certifications can keep employees current with the latest industry standards and technologies. This continuous learning can help employees remain competitive and valuable assets. Offering incentives and making the upskilling process easily accessible are key to success.
Examples of Successful Workforce Development Programs
Numerous successful workforce development programs exist, demonstrating effective strategies for attracting and training skilled tradespeople. Programs that combine theoretical knowledge with hands-on experience, such as apprenticeship programs, are often highly effective. A program in a specific region that has seen a noticeable increase in the skilled trades workforce through targeted advertising and partnerships with local high schools and colleges serves as a positive example.
Role of Educational Institutions in Preparing the Future Workforce
Educational institutions play a vital role in preparing the future workforce for skilled trades careers. Collaborations between schools and businesses can create curriculum that aligns with industry needs and prepares students with the necessary skills and knowledge. Integrating industry professionals into the curriculum can ensure that students receive practical and relevant instruction. Providing access to cutting-edge tools and technologies within the educational setting can give students a head start in the workforce.
Training Method Comparison
| Training Method | Description | Effectiveness | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apprenticeship | Combination of on-the-job training and classroom instruction. | High | Practical, real-world experience, industry-recognized credentials. | Can be slow-paced, requires employer commitment. |
| Vocational Training Programs | Structured programs focusing on specific trades. | High | Focused skill development, structured curriculum. | May not provide as much on-the-job experience. |
| Online Courses/Platforms | Distance learning opportunities for theoretical knowledge. | Moderate (dependent on structure and support) | Flexibility, cost-effectiveness. | Requires self-discipline, may lack hands-on experience. |
| Virtual Reality Simulations | Interactive training using VR technology. | High | Realistic simulations for safety and practical skills, reduced risk. | Requires specialized VR equipment, can be expensive. |
Bridging the Education-Industry Gap
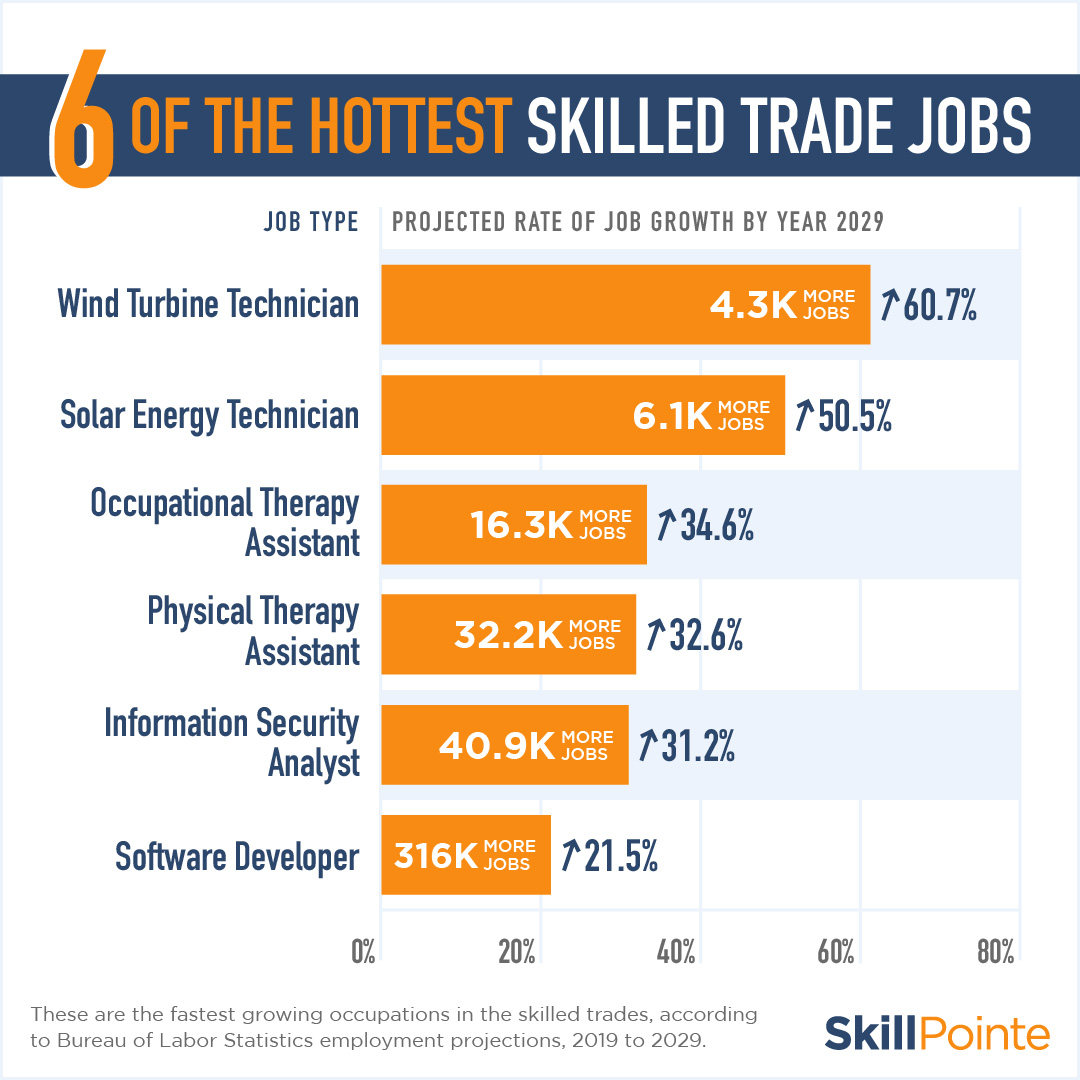
The skilled trades are facing a significant workforce shortage, and bridging the gap between education and industry is crucial for addressing this challenge. Simply training individuals isn’t enough; we need to ensure the training aligns with the specific needs of the industries, preparing individuals for immediate employment and long-term career growth. This requires a collaborative effort, integrating industry expertise into curriculum development and fostering ongoing partnerships.Effective training programs must go beyond theoretical knowledge and encompass practical, real-world applications.
The success of these programs depends heavily on the active involvement of industry professionals, who provide invaluable insights into current practices, emerging technologies, and future skill requirements. This collaboration is essential for ensuring graduates are equipped with the specific skills demanded by employers.
Importance of Industry Input in Curriculum Development, Getting ahead of the skilled trade demand game
Industry input is critical for curriculum development in skilled trades. This input ensures that training programs are directly relevant to the needs of employers and prepares graduates for immediate job opportunities. Without industry input, training programs may not adequately address the specific technical skills or soft skills required in the field. This disconnect can result in graduates being unprepared for the complexities of real-world job situations.
Different Models for Industry-Education Collaboration
Several models for industry-education collaboration exist, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. One common model involves establishing advisory boards composed of industry professionals. These boards can provide ongoing feedback on curriculum relevance, identify emerging skill needs, and offer mentorship opportunities. Another model is the establishment of joint training programs, where educators and industry professionals work together to design and deliver training.
A third model focuses on apprenticeships, with industry mentors guiding apprentices through the learning process. Each model has the potential to create a strong synergy, ultimately improving the quality of skilled trades training.
Mentorship Programs
Mentorship programs between experienced professionals and apprentices are invaluable. Mentors provide guidance, support, and practical experience, enabling apprentices to develop essential soft skills like communication and problem-solving, in addition to technical proficiency. This hands-on approach provides invaluable insights into the realities of the trade and prepares apprentices for the challenges they will encounter in their careers.
Real-World Projects in Training Programs
Incorporating real-world projects into training programs is essential for practical application of learned skills. Projects can simulate real-world scenarios, providing students with the opportunity to apply theoretical knowledge in a practical context. This approach also encourages critical thinking, problem-solving, and teamwork – skills that are highly valued in the workplace.
Strategies for Fostering Strong Industry Partnerships
Building strong industry partnerships requires proactive communication, collaboration, and shared goals. Regular meetings, joint projects, and shared resources can foster mutual respect and understanding. Open communication channels facilitate a two-way exchange of information, enabling educators to adapt training programs to meet the evolving needs of the industry.
Ongoing Skill Assessments and Certifications
Ongoing skill assessments and certifications are crucial for demonstrating competency and ensuring quality standards. These assessments can track progress, identify areas needing improvement, and provide evidence of competency to employers. Certifications can validate skills and enhance job prospects, demonstrating a commitment to continuous learning and professional development.
Examples of Effective Industry-Education Collaborations
Numerous examples of successful industry-education collaborations exist. One example is a local community college partnering with a major construction company to develop a specialized construction technology program. The program integrates theoretical knowledge with practical construction projects, ensuring graduates are well-prepared for immediate employment. Another successful collaboration involves a vocational school working with a local manufacturing company to develop an apprenticeship program in CNC machining.
The program’s success is directly linked to the company’s input in curriculum design and the integration of real-world projects.
Technological Integration in Training
Staying ahead in the skilled trades requires embracing technological advancements. Virtual and augmented realities, simulations, and online learning platforms are not just futuristic concepts; they are practical tools that can revolutionize training, bridge skill gaps, and prepare a workforce ready to meet evolving industry demands. By integrating these technologies effectively, we can ensure that apprentices and journeymen receive the most up-to-date and relevant training possible.Integrating technology into training programs goes beyond simply adding computers to the classroom.
It’s about fundamentally changing how skills are taught and learned, leveraging the power of interactive simulations and digital resources to create more engaging, effective, and efficient learning experiences. This approach fosters practical application, enhances knowledge retention, and prepares skilled workers for the demands of the modern workplace.
Potential of Virtual and Augmented Reality
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) offer immersive training environments that allow apprentices to practice complex procedures and troubleshoot scenarios in a risk-free digital space. This eliminates the need for costly or dangerous physical environments, and can allow for repeated practice without the limitations of real-world constraints. For instance, an electrician could practice wiring a complex circuit in a VR environment, receiving immediate feedback on their work, and avoiding costly mistakes in a live setting.
AR overlays digital information onto the real world, allowing apprentices to visualize complex systems or receive real-time guidance during a procedure. Imagine a plumber using AR to see a 3D model of a hidden pipe system overlaid onto the existing structure.
Benefits of Simulations for Practical Training
Simulations provide realistic scenarios for hands-on practice. They allow apprentices to develop problem-solving skills and critical thinking abilities in a controlled environment. This approach fosters a deeper understanding of procedures and processes, and allows for continuous practice without the limitations of real-world constraints. A pipefitter, for example, can practice fitting pipes in various configurations within a simulated environment, adjusting parameters and resolving issues without risking damage to materials or causing safety hazards.
Simulations can be tailored to replicate real-world challenges, making the training experience highly effective.
Role of Online Learning Platforms and Digital Resources
Online learning platforms provide access to a vast library of resources, including videos, tutorials, and interactive exercises. These resources can supplement traditional training programs, offering flexibility and accessibility for learners. Mobile learning applications can provide on-demand support and practice materials, particularly useful for workers who need to upskill or reskill in a field-based environment. For example, a carpenter could access a digital library of blueprints and techniques, or review instructional videos on specific woodworking techniques, allowing them to practice and learn at their own pace.
Examples of Successful Technology Integration
Several trades have successfully integrated technology into their training programs. For instance, some automotive repair shops use VR simulations to train technicians on complex diagnostic procedures, while HVAC companies use AR applications to guide technicians through installations and maintenance procedures. The key to success is to tailor the technology to specific trade requirements and incorporate it into existing training programs seamlessly.
Challenges and Considerations in Implementing New Technologies
Implementing new technologies in skilled trades training requires careful consideration of factors such as cost, accessibility, and training for instructors. Ensuring that the technology is user-friendly and compatible with existing infrastructure is critical. Furthermore, addressing digital literacy gaps among apprentices and instructors is essential.
Integrating Digital Tools into Existing Programs
Integrating digital tools into existing training programs can be achieved by incorporating interactive exercises, simulations, and online resources into the curriculum. This might include assigning specific modules for online learning, scheduling time for hands-on practice with digital tools, and integrating virtual assessments to measure skills acquisition.
Table Summarizing Technologies and Applications
| Technology | Application in Trade Training |
|---|---|
| Virtual Reality (VR) | Simulating complex procedures, practicing in a risk-free environment, troubleshooting scenarios. |
| Augmented Reality (AR) | Overlaying digital information onto the real world, providing real-time guidance, visualizing complex systems. |
| Simulations | Replicating real-world scenarios, developing problem-solving skills, practicing procedures in a controlled environment. |
| Online Learning Platforms | Access to a vast library of resources, flexibility and accessibility for learners, supplementing traditional training programs. |
Attracting and Retaining Talent

The skilled trades face a significant challenge in attracting and retaining talent in a competitive job market. Understanding the factors driving this issue and implementing effective strategies to address it are crucial for long-term success. A proactive approach that goes beyond simply offering competitive wages is vital to creating a positive and sustainable workforce.A focus on employer branding, creating a supportive work environment, and offering opportunities for employee growth are essential to not only attract but also retain skilled tradespeople.
Attracting and retaining skilled workers requires a comprehensive approach that addresses their needs and aspirations beyond just financial compensation.
Effective Recruitment Strategies
Attracting skilled trades candidates requires a multi-faceted approach. Reaching the right demographics and showcasing the positive aspects of the industry are key elements in recruitment. Targeted recruitment campaigns focusing on specific demographics and showcasing the value proposition of the skilled trades are effective. Utilizing online job boards, vocational schools, and apprenticeship programs can broaden the reach and attract individuals interested in hands-on careers.
Competitive Compensation and Benefits Packages
Competitive compensation and benefits packages are essential to attract and retain skilled tradespeople. This encompasses not just base salary but also comprehensive benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, paid time off, and professional development opportunities. Furthermore, offering incentives like signing bonuses or performance-based rewards can be highly effective in attracting top talent.
Successful Employer Branding Strategies
Strong employer branding strategies can significantly influence candidates’ perceptions of the skilled trades. Demonstrating a commitment to safety, employee well-being, and professional development can be effective in promoting the industry as a desirable career path. High-quality company websites and social media profiles can showcase the culture and values of the company and demonstrate its commitment to its employees.
Positive testimonials from employees, highlighting job satisfaction and career progression opportunities, can also strengthen the employer brand.
Creating a Positive and Supportive Work Environment
A positive and supportive work environment is crucial for employee retention. Open communication, recognition of achievements, and opportunities for professional development foster a sense of belonging and purpose. Promoting a culture of respect and teamwork can significantly reduce stress and increase job satisfaction.
Employee Recognition and Development Programs
Implementing employee recognition and development programs can further enhance employee engagement and motivation. These programs can include formal recognition programs, mentorship opportunities, and tuition reimbursement for further education. These initiatives show employees that their contributions are valued and that the company invests in their professional growth.
Reducing Employee Turnover
Reducing employee turnover requires a proactive approach that addresses potential dissatisfaction. Regular feedback mechanisms, opportunities for career advancement, and addressing any workplace concerns promptly can significantly reduce turnover. Understanding the reasons behind employee departures allows companies to implement targeted solutions.
Recruitment Strategies and Impact
| Recruitment Strategy | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Targeted advertising on vocational school websites and job boards | Increased visibility among prospective candidates with specific skills and interests. |
| Partnerships with vocational schools and apprenticeship programs | Direct access to a pool of skilled labor ready to enter the workforce. |
| Strong employer branding through online platforms and social media | Positive brand image and reputation attracting qualified candidates. |
| Competitive compensation and benefits packages | Attracting and retaining high-quality skilled labor. |
| Positive work environment and employee recognition programs | Increased job satisfaction and reduced turnover rates. |
Closure
In conclusion, successfully navigating the skilled trade demand game requires a proactive approach. By understanding the current and future needs, implementing effective workforce preparation strategies, bridging the education-industry gap, and embracing technological integration, you can position yourself and your organization for long-term success. This comprehensive approach ensures that you’re not just meeting current demand but also anticipating and fulfilling future workforce needs.

