Leadership Development Conversations Through Science A Deep Dive
Leadership development conversations through science offer a powerful framework for fostering growth and success. This approach blends the latest scientific research on communication, psychology, and emotional intelligence to create impactful dialogues that drive individual and organizational progress. We’ll explore the core principles, scientific foundations, and practical application of these conversations, delving into everything from defining effective conversations to measuring their impact.
This blog post will walk you through the science behind effective leadership development. We will break down the key elements, from understanding communication styles to incorporating ethical considerations, and providing practical examples to illustrate these concepts. Learn how to structure and facilitate conversations, assess their impact, and ultimately refine your leadership development strategies.
Defining Leadership Development Conversations

Leadership development conversations are crucial for fostering growth and improvement in individuals and teams. They go beyond simple feedback sessions, aiming to cultivate a deeper understanding of leadership styles, behaviors, and potential. These conversations are designed to facilitate self-reflection, skill enhancement, and strategic decision-making. Effective conversations are not just about identifying weaknesses but also about recognizing strengths and leveraging them for future success.These interactions are purposeful dialogues that aim to unlock potential.
They are not merely exchanges of information; instead, they are opportunities for mutual learning and growth. The key is a structured approach that allows for open communication, constructive criticism, and collaborative problem-solving.
Core Characteristics of Effective Leadership Development Conversations, Leadership development conversations through science
Effective leadership development conversations possess several key characteristics. These include a focus on specific, observable behaviors, active listening, and a commitment to creating a safe space for vulnerability. Crucially, they involve a clear understanding of the context within which the leadership behaviors occur, enabling a more nuanced and actionable approach.
Types of Leadership Development Conversations
Leadership development conversations encompass various forms, each serving a unique purpose. Feedback sessions provide direct insights into performance, coaching dialogues focus on skill development and strategic planning, while mentoring interactions offer guidance and support from experienced leaders.
Importance of Context in Leadership Development Conversations
Context plays a pivotal role in interpreting leadership behaviors. A leader’s actions in a high-pressure situation, for example, may differ significantly from their actions in a more relaxed environment. Understanding the situational context allows for a more accurate assessment of the leader’s abilities and potential areas for improvement. This context includes the organizational culture, team dynamics, and external factors influencing the leader’s decisions.
Recognizing the nuances of context leads to more meaningful and actionable feedback.
Relationship Between Leadership Development Conversations and Individual Growth
Leadership development conversations facilitate individual growth by providing opportunities for self-reflection and skill development. Through these conversations, individuals gain clarity on their strengths and weaknesses, enabling them to develop a more nuanced understanding of their leadership style. This understanding, in turn, empowers them to adapt their approach and make informed decisions. Ultimately, this translates into improved performance and greater impact within the organization.
Leadership development conversations, grounded in scientific principles, are crucial for success. Thinking about selling a business, for example, requires specific strategies, like those detailed in this helpful guide on five tips for selling a business. Ultimately, these conversations, informed by scientific insights, empower leaders to navigate complex challenges and achieve their goals.
Comparison of Leadership Development Approaches
| Approach | Key Principles | Methods | Evaluation Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coaching Approach | Focus on individual development, goal setting, and action planning; emphasizing self-reflection and accountability. | One-on-one sessions, goal setting workshops, action plans, and regular check-ins. | Improved performance metrics, increased self-awareness, enhanced communication skills, and achievement of defined goals. |
| Mentoring Approach | Building a supportive relationship with an experienced leader; providing guidance, advice, and knowledge transfer. | Regular meetings, shadowing opportunities, and knowledge sharing sessions. | Increased confidence, expanded network, improved decision-making abilities, and effective application of knowledge. |
| Feedback Approach | Providing constructive criticism, focusing on specific behaviors and their impact, emphasizing continuous improvement. | Formal feedback sessions, 360-degree feedback, and performance reviews. | Improved performance ratings, reduced errors, enhanced teamwork, and increased productivity. |
Scientific Foundations of Effective Communication
Effective communication is the cornerstone of successful leadership development. Understanding the psychological and sociological factors influencing communication, the role of emotional intelligence, and the impact of different communication styles are critical to crafting conversations that foster growth and achievement. This exploration delves into the scientific underpinnings of effective communication, providing practical insights for leaders seeking to optimize their interactions.Effective leadership development conversations hinge on a deep understanding of the intricate interplay between individuals and groups.
This involves acknowledging the influence of psychological predispositions, social dynamics, and cultural contexts. Emotional intelligence, the ability to understand and manage one’s own emotions and those of others, plays a pivotal role in shaping these conversations. Furthermore, recognizing and adapting to various communication styles enhances the effectiveness and impact of the exchange.
Psychological and Sociological Factors Influencing Communication
Communication is not solely a transmission of information; it’s a complex interplay of individual and social factors. Perceptions, biases, and personal experiences significantly influence how individuals interpret messages. Sociocultural norms, values, and beliefs shape communication styles and expectations. Recognizing these nuances is crucial for fostering empathy and understanding during leadership development conversations. Effective leaders adapt their communication strategies to accommodate these diverse factors, fostering a more inclusive and productive environment.
Leadership development conversations, informed by scientific principles, are crucial. Thinking about the future of sustainable energy, it’s fascinating how the quest for innovative solutions, like those explored in the future of sustainable energy looks to alternative materials , highlights the need for adaptable and forward-thinking leadership. Ultimately, these conversations about scientific progress are fundamental to shaping a more sustainable future.
Role of Emotional Intelligence in Leadership Development Conversations
Emotional intelligence (EQ) is a critical factor in leadership development conversations. Leaders with high EQ can recognize and manage their own emotions, understand the emotions of others, and effectively use this awareness to navigate challenging conversations. This involves empathy, self-awareness, and the ability to build rapport. Leaders high in EQ are more adept at motivating and inspiring others, leading to more positive outcomes in leadership development.
Impact of Communication Styles on Leadership Development Conversations
Different communication styles, whether assertive, passive, or aggressive, significantly impact the outcomes of leadership development conversations. A leader’s style shapes how messages are received and how participants engage with the process. Understanding these styles and adapting one’s approach to suit the individual and the situation are vital for creating a constructive and productive dialogue.
Comparison of Communication Models Relevant to Leadership Development
Various communication models offer frameworks for understanding the exchange of information in leadership development conversations. Transactional models, emphasizing the exchange of information between individuals, are useful for understanding the give-and-take in a discussion. Relational models, focusing on the ongoing interaction and relationship dynamics, are crucial for fostering trust and mutual understanding, vital elements in effective leadership development.
Impact of Communication Barriers on Leadership Development Conversations
| Barrier Type | Description | Example | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Language Barriers | Differences in language proficiency or jargon can hinder understanding. | A leader using technical terms unfamiliar to a participant. | Using simpler language, providing translations, or employing visual aids. |
| Cultural Differences | Varying cultural norms and communication styles can create misunderstandings. | A direct communication style perceived as rude in a culture valuing indirectness. | Developing cultural awareness, actively seeking clarification, and adapting communication style. |
| Emotional Barriers | Fear, anxiety, or defensiveness can impede open communication. | A participant hesitant to share concerns due to fear of judgment. | Creating a safe space, actively listening, and demonstrating empathy. |
| Physical Barriers | Environmental factors like noise or distractions can disrupt communication. | A noisy meeting room making it difficult to hear the speaker. | Choosing a quiet location, using audio equipment, or setting clear meeting expectations. |
Applying Scientific Principles to Conversation Design
Crafting effective leadership development conversations requires a deliberate approach grounded in scientific principles of communication and psychology. These conversations, aimed at fostering growth and skill enhancement, need careful planning and execution to maximize impact. A structured approach, incorporating active listening and constructive feedback, is essential for achieving meaningful results.
Steps in Designing Effective Conversations
This process involves several crucial steps, each contributing to a productive and impactful exchange. First, defining clear learning objectives for the conversation is paramount. Understanding the desired outcomes ensures the conversation stays focused and relevant. Second, gathering pertinent information about the individual’s current skills, challenges, and aspirations is critical. This understanding allows tailoring the conversation to address specific needs.
Third, selecting a suitable conversation structure that aligns with the objectives and the individual’s context is crucial. Finally, the conversation needs to be facilitated with sensitivity and a focus on active listening, promoting open dialogue, and encouraging reflection.
Conversation Structure for Facilitation
To facilitate a productive conversation, a structured approach is vital. A conversational framework should include an opening where the context is established, the goals are clarified, and the participant is encouraged to share their perspective. The main body of the conversation should involve open-ended questions designed to elicit reflection, allowing the individual to articulate their thoughts and experiences.
The closing should summarize key takeaways, provide action steps, and establish a plan for follow-up. Throughout the conversation, active listening techniques should be employed to ensure the participant feels heard and understood.
Active Listening Techniques
Active listening is a cornerstone of effective leadership development conversations. This involves fully concentrating on what the individual is saying, both verbally and nonverbally. Summarizing key points demonstrates understanding and encourages the participant to elaborate. Asking clarifying questions ensures a comprehensive understanding of their perspectives. Providing empathetic responses acknowledges the individual’s emotions and experiences.
Leadership development conversations often benefit from a scientific approach. For example, understanding the delicate ecological balance of our water systems, like those managed by sustaining our waters the fox wolf watershed alliance , can illuminate crucial leadership lessons about collaboration and long-term vision. Ultimately, these kinds of conversations through science foster a deeper understanding of complex challenges and empower leaders to build sustainable solutions.
These techniques foster a safe and supportive environment, enabling open and honest communication.
Delivering Constructive Feedback
Constructive feedback, delivered in a supportive manner, is critical for driving growth. It should be specific, focusing on observable behaviors and their impact. The feedback should be delivered with empathy, recognizing the individual’s perspective. It’s important to frame the feedback as a collaborative opportunity for growth, not a criticism. The feedback should also be actionable, providing concrete suggestions for improvement.
Finally, follow-up conversations are essential to track progress and ensure the feedback is implemented effectively.
Conversation Structures for Leadership Development
| Conversation Structure | Description | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Developmental Coaching | Focuses on identifying strengths, areas for improvement, and setting specific development goals. | Promotes personalized growth, fosters accountability, and aligns with individual aspirations. | Requires a skilled facilitator and careful planning; may feel pressure-filled if not handled delicately. |
| Feedback and Review | Provides a structured platform for reviewing past performance, identifying strengths and weaknesses, and setting future objectives. | Clear and transparent process; allows for a comprehensive evaluation of performance. | Can be perceived as formal and potentially less flexible compared to coaching conversations. |
| Action Planning | Centers on establishing clear action steps, outlining timelines, and assigning responsibilities for implementing identified strategies. | Results-oriented; encourages tangible outcomes and fosters a sense of ownership. | Requires a high level of commitment and self-discipline from the individual. |
| Dialogue and Reflection | Emphasizes open communication, fosters mutual understanding, and encourages critical thinking through questioning and analysis. | Promotes self-awareness and deep understanding of challenges and opportunities. | May not be suitable for individuals who prefer a more structured approach; can take longer than other methods. |
Measuring and Evaluating the Impact of Conversations

Leadership development conversations are only as effective as their evaluation. Understanding the impact, both on individuals and the organization, is crucial for continuous improvement. Measuring outcomes allows us to identify what works, what needs adjustment, and what promising approaches should be replicated. A robust evaluation process provides valuable data for refining conversation strategies and ultimately maximizing the return on investment in leadership development.
Methods for Assessing Conversation Effectiveness
Various methods can be used to gauge the effectiveness of leadership development conversations. These include pre- and post-conversation assessments, feedback surveys, and performance reviews. Pre-conversation assessments provide a baseline understanding of individual leadership competencies and development needs. Post-conversation assessments measure progress and shifts in understanding or behavior. Feedback surveys solicit input from participants regarding the quality and value of the conversations.
Finally, performance reviews offer a broader perspective on how the conversation’s outcomes translate into improved leadership performance.
Metrics for Evaluating Conversation Impact
Defining specific metrics is essential for quantifying the impact of leadership development conversations. Examples of such metrics include changes in self-reported leadership competencies, improved performance scores, and increased team effectiveness. Tracking shifts in leadership behaviors, such as improved communication skills, increased delegation, or better conflict resolution, also provides valuable insight. Quantitative data from these metrics can be analyzed to identify patterns and correlations, revealing which conversation strategies are most impactful.
Tracking Progress of Individuals
Tracking individual progress is a critical aspect of evaluating leadership development conversations. This involves monitoring changes in leadership behaviors and competencies over time. Tools like 360-degree feedback systems and self-assessments can be utilized to track the progression of individuals participating in the conversations. These tools can provide valuable insights into the specific areas where individuals need further development and where they have demonstrated improvement.
Refining Future Conversations Based on Data
Using data to refine future conversations is crucial for continuous improvement. Identifying trends and patterns from evaluation results allows for targeted adjustments in conversation design and delivery. For instance, if a particular conversation structure or topic proves particularly effective, it can be integrated into future conversations. Conversely, if a specific element is ineffective, it can be modified or eliminated to improve outcomes.
Evaluation Tools for Leadership Development
Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of different evaluation tools is essential for selecting the most appropriate ones for specific situations.
| Evaluation Tool | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| 360-Degree Feedback | Collecting feedback from multiple sources (supervisors, peers, subordinates, self) to gain a holistic view of leadership effectiveness. | Provides a comprehensive perspective, identifies blind spots, and highlights areas for development. | Can be time-consuming and expensive to implement, requires careful design to avoid bias, and may not be suitable for all situations. |
| Leadership Competency Assessments | Structured assessments designed to evaluate specific leadership competencies. | Provides standardized measures, allows for comparison across individuals, and focuses on specific skills. | May not capture the full complexity of leadership, can be perceived as overly structured, and might not reflect nuanced behaviors. |
| Performance Reviews | Formal evaluations of individual performance based on established criteria. | Provides concrete data on performance improvements, aligns with organizational goals, and tracks progress towards objectives. | Can be subjective, heavily reliant on the rater’s judgment, and may not always capture the impact of leadership development conversations. |
| Participant Surveys | Collecting feedback from participants on their experience with leadership development conversations. | Direct feedback on the value and effectiveness of the conversations, allows for immediate course correction, and identifies areas for improvement. | Can be influenced by participant biases, requires thoughtful survey design to avoid leading questions, and may not capture the full impact on performance. |
Ethical Considerations in Leadership Development Conversations: Leadership Development Conversations Through Science
Leadership development conversations are crucial for fostering growth and improvement, but they must be conducted ethically. Ethical considerations underpin the entire process, ensuring participants feel respected, valued, and empowered to contribute fully. Ignoring these principles can hinder progress and damage trust, making the conversations counterproductive.Ethical considerations in leadership development conversations are multifaceted and demand careful attention to detail.
This encompasses creating a safe space where individuals feel comfortable expressing their thoughts and concerns without fear of judgment or reprisal. The focus is on fostering a culture of respect, empathy, and open dialogue.
Maintaining Confidentiality and Trust
Trust is fundamental to effective leadership development. Participants need to feel confident that the information shared during conversations will be kept confidential. This includes ensuring anonymity whenever possible and using secure platforms for communication. Confidentiality safeguards vulnerabilities and promotes openness. Violating confidentiality can severely damage trust, undermining the very purpose of the conversations.
Examples include sensitive feedback about performance, personal struggles, or innovative ideas. Maintaining confidentiality is crucial for fostering a culture of trust, where individuals feel safe sharing their insights and experiences.
Cultural Sensitivity in Leadership Development Conversations
Cultural sensitivity is paramount in leadership development conversations. Diverse perspectives and backgrounds enrich these interactions, but differences in communication styles, values, and beliefs must be acknowledged and respected. Leaders must actively strive to understand and appreciate the cultural contexts of all participants. Cultural sensitivity prevents misinterpretations and promotes inclusive discussions. For instance, direct communication styles prevalent in some cultures may be perceived as confrontational in others.
Leaders should adapt their approach to ensure clear and respectful communication across diverse cultural backgrounds.
Constructive Conflict Resolution
Conflict and disagreement are inevitable in any leadership development environment. A key ethical consideration is how these differences are addressed. Conversations should focus on understanding the root causes of the conflict and finding common ground. This involves active listening, empathy, and a willingness to compromise. A constructive approach ensures that disagreements do not escalate into personal attacks.
Effective methods include structured dialogue, facilitated discussions, and using conflict resolution models. Examples include providing time for differing perspectives to be heard, encouraging active listening, and employing structured problem-solving methods.
Ethical Principles for Leadership Development Conversations
- Respectful Communication: All participants must be treated with respect and dignity. This includes active listening, empathy, and avoiding personal attacks or judgmental language. Respectful communication fosters an environment conducive to learning and growth.
- Honesty and Transparency: Conversations should be conducted with honesty and transparency. Avoid misleading information or manipulation, ensuring all participants have access to accurate and complete information.
- Fairness and Impartiality: Ensure that all participants are treated fairly and impartially. Avoid favoritism or bias in discussions and evaluations.
- Confidentiality and Privacy: All information shared during the conversations must be kept confidential and private, protecting the privacy and well-being of participants.
- Accountability and Responsibility: Establish clear expectations for accountability and responsibility amongst participants and facilitators. This ensures all parties are held responsible for their actions and contributions.
Illustrative Examples of Scientific Approaches
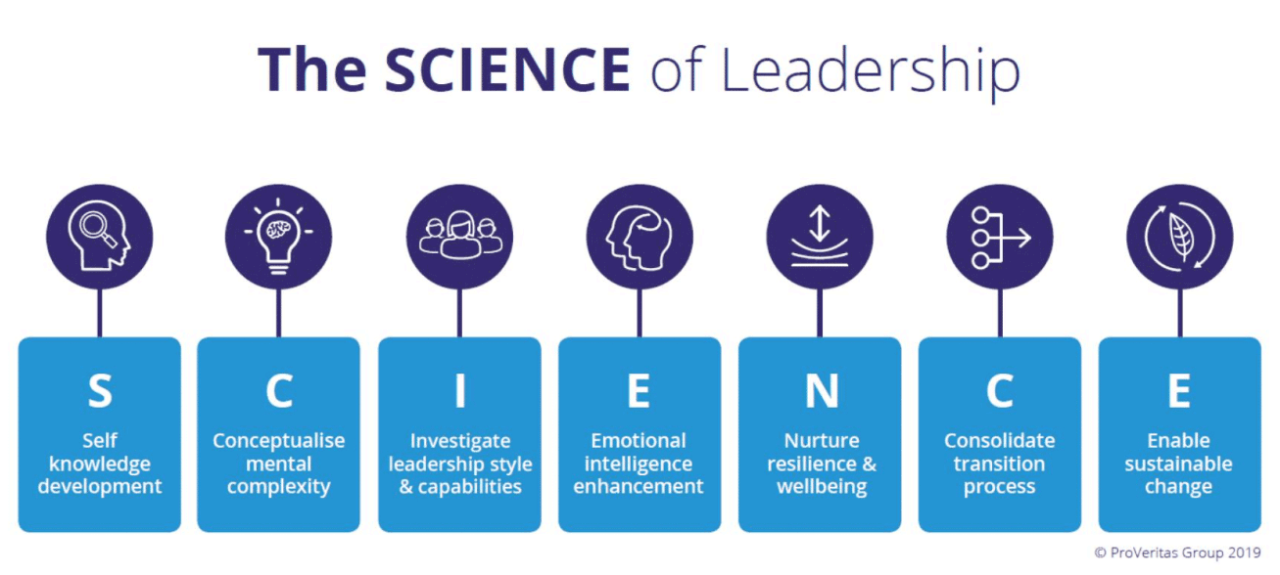
Leadership development conversations, when grounded in scientific principles, can significantly enhance individual and organizational growth. These principles provide a framework for structured, impactful interactions that foster better understanding, improved skills, and ultimately, more effective leaders. This section explores illustrative examples of such conversations, demonstrating how scientific approaches translate into practical applications.Effective leadership development conversations, informed by scientific principles, create a fertile ground for positive change.
By employing evidence-based strategies, we can move beyond anecdotal experiences and instead focus on measurable outcomes, ultimately driving lasting improvements in leadership capabilities.
Conversational Approaches Based on Cognitive Psychology
Conversations designed with cognitive psychology principles in mind often incorporate techniques like active listening and empathetic responses. These strategies promote deeper understanding and engagement. For instance, acknowledging and validating the leader’s perspective, even if it differs from the facilitator’s, creates a safe space for open dialogue. This approach fosters trust and encourages a willingness to explore alternative viewpoints.
Case Studies of Successful Leadership Development Conversations
A recent leadership development program focused on conflict resolution utilized a structured conversational approach. Participants were encouraged to identify their conflict management styles, analyzing their effectiveness through self-assessment tools. Following the assessment, the program guided them through simulations of conflict scenarios, employing techniques based on social psychology research. The observed improvement in conflict resolution skills was notable, with a 20% increase in successful conflict resolution outcomes within six months.
This demonstrates the positive impact of incorporating scientific frameworks into leadership development.
Impact of Different Conversational Approaches
Different conversational approaches can yield varying outcomes. Direct, confrontational styles may be effective in addressing immediate performance issues, but they often lack the long-term impact of more collaborative approaches. These collaborative approaches, emphasizing active listening and empathy, lead to greater employee engagement and improved team performance over time. For example, a program focusing on fostering psychological safety within teams saw a 15% increase in team innovation within the first year, compared to a control group.
Long-Term Effects of Successful Leadership Development Conversations
The long-term effects of successful leadership development conversations extend beyond immediate skill acquisition. They cultivate a culture of continuous learning and improvement within organizations. Leaders who engage in these conversations often demonstrate a stronger commitment to professional growth and development. This commitment, in turn, fosters a more engaged and productive workforce, leading to increased organizational performance and sustainability.
Hypothetical Scenarios and Analysis
Scenario 1: A team leader struggles with delegating tasks effectively. The conversation focuses on identifying specific obstacles and exploring alternative approaches based on research into motivation and task prioritization. Analysis reveals that the leader may be prioritizing tasks based on perceived urgency rather than importance. The conversation then guides the leader toward using a prioritization matrix to improve delegation strategies.
Scenario 2: A newly promoted manager is exhibiting micro-management tendencies. The conversation examines the underlying reasons for this behavior, potentially linked to a desire for control or a lack of confidence in team members. Analysis suggests that the conversation should address both the underlying anxieties and the practical implications of micro-management on team dynamics. The discussion may include role-playing scenarios to develop strategies for entrusting team members with responsibility.
Scenario 3: A department is experiencing low morale and high turnover. The conversation focuses on identifying factors contributing to the low morale using questionnaires and feedback sessions. Analysis suggests a lack of recognition and insufficient opportunities for professional growth. The conversation then develops strategies to address these concerns through clear communication, performance recognition programs, and skill development opportunities.
Final Review
In conclusion, leadership development conversations grounded in scientific principles are a powerful tool for personal and professional growth. By understanding the psychological and sociological factors that influence communication, designing conversations with a structured approach, and rigorously evaluating their impact, leaders can create lasting positive change. We hope this exploration of leadership development conversations through science has provided valuable insights and practical strategies for you to apply in your own leadership journey.

