
Making College More Accessible in Wisconsin
Making college more accessible for all Wisconsin students is a crucial endeavor, and this exploration dives deep into the multifaceted challenges and opportunities surrounding higher education affordability and access in the Badger State.
This discussion will cover financial aid, tuition, support services, technology access, housing, transportation, outreach, and curriculum, offering a comprehensive overview of the issues impacting students’ ability to pursue higher education in Wisconsin. We’ll analyze the current state of affairs, compare it to other states, and identify actionable strategies for improvement.
Financial Aid and Scholarships
Navigating the financial landscape of higher education can feel daunting, especially for students seeking to pursue their dreams in Wisconsin. Understanding the various financial aid programs and scholarships available is crucial for students to make informed decisions about their future. This section delves into the current financial aid programs in Wisconsin, comparing them to other states and outlining available options for Wisconsin students.Wisconsin’s financial aid system is designed to support students from diverse backgrounds, with a focus on need-based aid.
However, the system also acknowledges the importance of merit-based scholarships for those who excel academically.
Current Financial Aid Programs in Wisconsin
Wisconsin offers a multifaceted approach to financial aid, encompassing federal grants, state grants, and institutional scholarships. Federal grants, such as Pell Grants, are based on demonstrated financial need, while state grants are often targeted at Wisconsin residents. Institutional scholarships, offered by individual colleges and universities, may be based on academic merit, specific extracurricular activities, or other criteria. The interplay of these programs creates a complex but potentially comprehensive support system for students.
Types of Scholarships Available
A variety of scholarships cater to different student needs and aspirations. Academic merit scholarships often reward high academic achievement, while need-based scholarships prioritize financial hardship. Some scholarships are specific to certain fields of study, encouraging specialization and providing targeted support. Scholarships may also be awarded for extracurricular activities, leadership roles, or demonstrated community involvement. The criteria and eligibility requirements for each type of scholarship vary considerably, requiring careful research and application.
Comparison with Other States’ Financial Aid Models
Comparing Wisconsin’s financial aid models with those of other states reveals areas for potential improvement. Some states might offer more comprehensive need-based aid packages, while others excel in providing scholarships for specific fields of study. Examining these differences allows for a clearer understanding of Wisconsin’s current system and potential avenues for enhancement. Wisconsin can learn from other state models to strengthen existing programs and expand opportunities for its students.
Financial Aid Options Table
This table provides a snapshot of various financial aid options available to Wisconsin students. It Artikels eligibility criteria, application deadlines, and potential award amounts. Note that specific details may vary by institution.
| Aid Type | Eligibility Criteria | Application Deadlines | Estimated Amount |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pell Grant | Demonstrated financial need; U.S. citizenship or eligible non-citizen status; enrollment as a degree-seeking undergraduate | Vary by institution | $6,895 (2024) |
| Wisconsin State Grant | Wisconsin residency; demonstrated financial need; enrollment as a degree-seeking undergraduate | Vary by institution | $1,000-$3,000+ |
| Academic Merit Scholarship | High academic standing; GPA requirements; standardized test scores | Vary by institution | $500-$10,000+ |
| Need-Based Scholarship | Demonstrated financial need; specific criteria based on income and family resources | Vary by institution | $1,000-$5,000+ |
Tuition and Fees
Tuition costs at Wisconsin’s public colleges and universities have become a significant barrier for many students. While financial aid plays a crucial role in mitigating these costs, understanding the tuition and fee structure itself is essential to crafting effective solutions. This section delves into the current landscape of tuition and fees, exploring potential impacts on student accessibility and exploring potential strategies for affordability.The current tuition and fee structure for Wisconsin’s public colleges and universities varies depending on the institution and the student’s residency status.
In-state residents generally pay lower tuition rates compared to out-of-state students. This difference reflects the state’s commitment to supporting its own residents in pursuing higher education. However, even in-state tuition rates can pose a financial challenge, especially for students from lower-income families.
Wisconsin Public College and University Tuition Structure
Wisconsin’s public colleges and universities use a multifaceted tuition model. This model often includes a base tuition rate, which can vary considerably between institutions. Additional fees are typically added for specific services like labs, technology, and student activities. The costs can also differ depending on the student’s major and course load. For example, some specialized programs might have higher associated costs.
Impact of Tuition Increases on Student Accessibility, Making college more accessible for all wisconsin students
Tuition increases over time have a significant impact on student accessibility. As tuition costs rise, more students, particularly those from lower-income backgrounds, face difficulty affording college. Increased tuition rates can lead to decreased enrollment rates for qualified students, ultimately impacting the educational opportunities available within the state. This is a critical issue as Wisconsin aims to maintain a robust workforce and a skilled citizenry.
Tuition Policies in Other States
Several states have implemented innovative tuition policies to improve affordability. For example, some states offer tuition discounts or waivers for students demonstrating financial need. Others explore tiered tuition structures, charging lower rates for students with demonstrated academic performance or participation in specific programs. The state of Minnesota, for instance, has a system of tuition subsidies that targets students from families with lower incomes.
Studying these policies can inform potential solutions for Wisconsin.
Strategies to Reduce Tuition and Fees While Maintaining Quality Education
Reducing tuition and fees without compromising the quality of education requires a multi-pronged approach. One strategy involves exploring innovative funding models, such as increased state funding for higher education or more robust partnerships with industry. Another approach focuses on efficiency improvements within the university system, looking for opportunities to cut unnecessary costs while preserving vital academic resources. Furthermore, a focus on grants and scholarships that target students from low-income backgrounds can make a considerable difference.
Tuition Cost Comparison Across Wisconsin Institutions
| Institution | In-State Tuition (Estimated) | Out-of-State Tuition (Estimated) |
|---|---|---|
| University of Wisconsin-Madison | $10,000 | $30,000 |
| University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee | $9,000 | $28,000 |
| University of Wisconsin-Stevens Point | $8,000 | $25,000 |
| UW-Eau Claire | $8,500 | $26,000 |
| UW-La Crosse | $7,500 | $24,000 |
Note
These figures are estimates and may vary based on specific programs and individual circumstances. Actual costs should be verified directly with the institution.*
Making college more accessible for all Wisconsin students is crucial, and supporting initiatives like sustaining our waters the fox wolf watershed alliance demonstrates a broader commitment to community well-being. After all, a healthy environment directly impacts the well-being of students and the future of Wisconsin. Ultimately, these efforts will contribute to a brighter future for all Wisconsin students, by fostering a holistic approach to success.
Support Services for Students
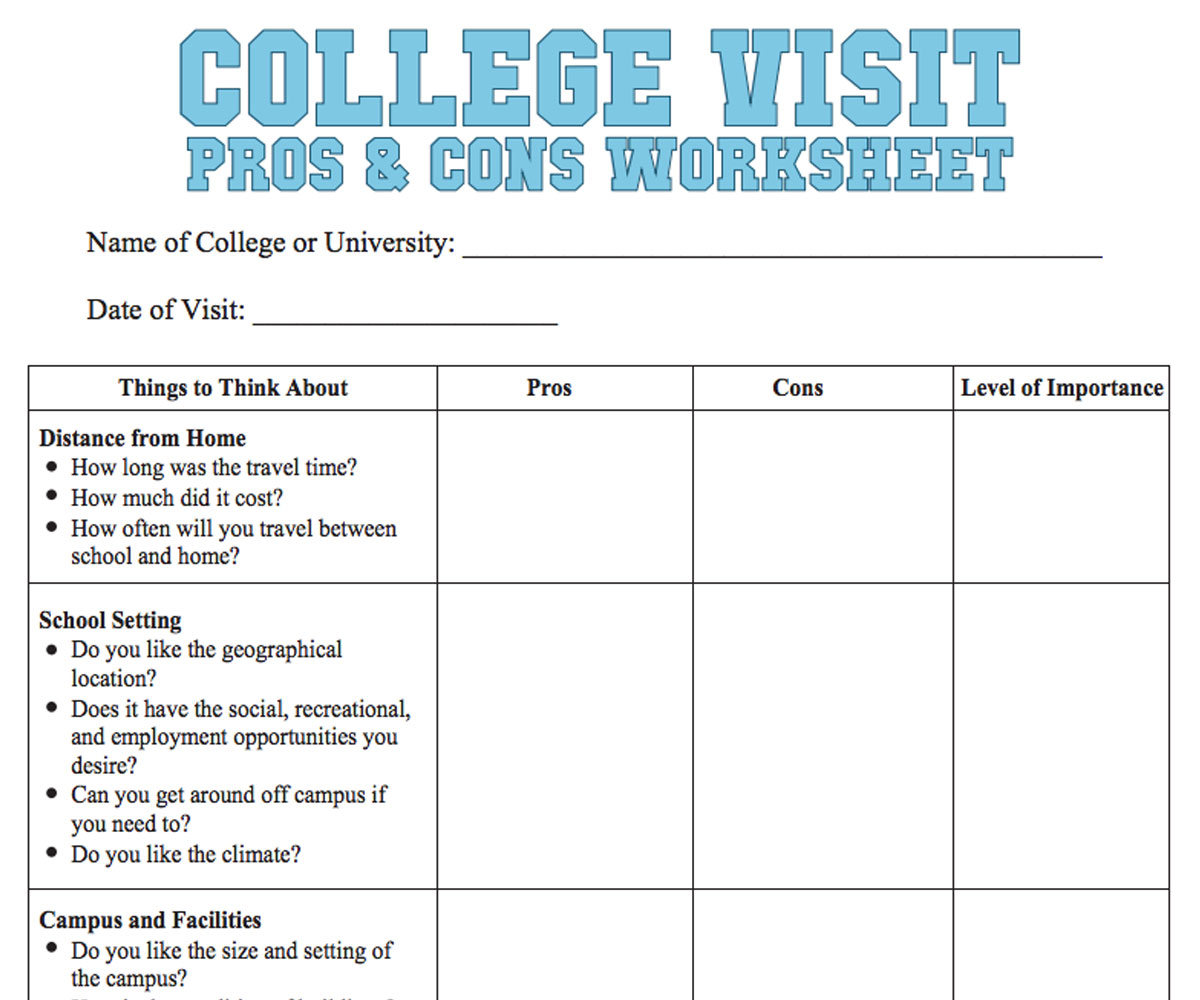
Making college accessible isn’t just about affordability; it’s about providing comprehensive support to help students thrive. Wisconsin’s colleges and universities offer valuable resources, but gaps remain, particularly for underrepresented students. This section explores existing support services, identifies potential areas for improvement, and suggests best practices from other states to inform a more inclusive system.Existing support services vary widely across Wisconsin’s institutions, reflecting differences in size, mission, and student demographics.
Many colleges offer academic advising, tutoring, and career counseling, while some have robust mental health services. However, the availability and quality of these services can fluctuate, impacting a student’s ability to succeed.
Existing Support Services in Wisconsin
Wisconsin institutions typically provide a range of support services to help students navigate the challenges of college life. These services often include academic advising, tutoring, career counseling, and sometimes even mental health support. However, the level of resources and access to these services can differ significantly between institutions.
- Academic Advising: Many institutions offer academic advising to help students develop academic plans, choose appropriate courses, and manage their course load effectively. This service is crucial for ensuring students stay on track towards graduation and achieve their academic goals. Academic advisors play a critical role in guiding students through their academic journey, addressing any concerns, and providing valuable feedback.
Strong academic advising is a key factor in student success.
- Tutoring Services: Dedicated tutoring programs provide extra support for students struggling in specific subjects. These services can significantly improve academic performance and boost student confidence.
- Career Counseling: Career services support students in developing job search skills, creating resumes, and preparing for interviews. These services are crucial for students transitioning from academics to the workforce. This includes resume workshops, mock interviews, and networking opportunities.
- Mental Health Resources: While mental health services are becoming more prevalent in colleges, the extent of these services varies greatly across institutions. Some institutions have dedicated counseling centers offering individual and group therapy, while others have partnerships with external providers.
Gaps in Support Services
Despite the efforts of many institutions, some gaps remain in support services, hindering the accessibility of higher education for certain student groups. Students from low-income backgrounds, first-generation college students, and students with disabilities may experience barriers in accessing or utilizing these services effectively. Cultural competency is also a critical component of support services. Advisors should be trained to understand and address the specific needs of diverse student populations.
- Inadequate Mental Health Resources: Insufficient mental health support services can significantly impact student well-being and academic performance. A lack of accessible and affordable mental health resources may discourage students from seeking help when needed. This can lead to worsening mental health issues and academic struggles.
- Limited Accessibility for Students with Disabilities: Students with disabilities may face barriers in accessing accommodations and support services. This may include insufficient assistive technology, inaccessible physical spaces, or lack of specialized support staff.
- Lack of Cultural Competency in Support Services: Support services may not adequately address the specific needs and experiences of diverse student populations. This can include lack of culturally sensitive academic advising, limited access to culturally appropriate mental health resources, and insufficient representation on support staff.
Examples of Successful Support Programs
Several states have implemented successful support programs that Wisconsin could replicate. For instance, some states offer comprehensive mental health services, including on-campus therapists, group counseling sessions, and crisis intervention teams.
- Comprehensive Mental Health Support: Some states have successfully integrated mental health support into the broader college experience, offering dedicated mental health centers, on-site counselors, and crisis intervention teams. This approach promotes early intervention and support for students experiencing mental health challenges. This approach prioritizes student well-being, reducing barriers and promoting academic success.
- Specialized Advising for Underrepresented Students: Dedicated advising programs for first-generation students or students from low-income backgrounds can provide personalized support and guidance. These programs can offer mentorship, academic resources, and career counseling tailored to the specific needs of these student groups.
Importance of Comprehensive Support Services
Comprehensive support services are vital for student success and accessibility. They not only address academic needs but also promote overall well-being.
- Academic Success: Strong academic advising and tutoring can significantly improve academic performance and increase graduation rates.
- Mental Health and Well-being: Access to mental health resources is crucial for students to manage stress, anxiety, and other mental health concerns.
- Career Development: Career counseling helps students transition from academics to the workforce, preparing them for future success.
Support Service Availability Across Wisconsin Institutions
| Institution | Academic Advising | Tutoring | Career Counseling | Mental Health Resources |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| University of Wisconsin-Madison | High | High | High | High |
| University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee | High | Medium | Medium | Medium |
| Other UW System Institutions | Variable | Variable | Variable | Variable |
Note: This table provides a general overview. Specific offerings and availability may vary between different campuses and programs.
Access to Technology and Resources
Bridging the digital divide is crucial for ensuring equitable access to higher education in Wisconsin. Students from diverse backgrounds often face varying levels of access to technology and digital resources, impacting their ability to succeed academically. This section explores the current landscape of technology access in Wisconsin colleges and universities, highlighting disparities and proposing strategies to improve digital equity for all students.The digital age has fundamentally reshaped the learning experience.
Making college more accessible for all Wisconsin students is a huge goal, and it’s something I’m passionate about. Sharing practical skills, like the benefits of homesteading with others, could actually contribute to that goal. For example, teaching essential life skills through sharing the benefits of homesteading with others could potentially create a self-sufficient and financially savvy student body, which could make college more affordable and achievable for all.
This is just one way to foster a stronger and more resourceful Wisconsin student community.
From online classes and research to collaborative projects and virtual tutoring, technology has become an indispensable tool for modern education. However, unequal access to reliable internet and necessary digital skills can create significant barriers to academic success for students from disadvantaged backgrounds. This disparity can perpetuate existing inequalities, hindering their ability to fully participate in and benefit from the educational opportunities available to them.
Current Availability of Technology and Digital Resources
Wisconsin colleges and universities generally provide some form of technology infrastructure, including computer labs, Wi-Fi access, and learning management systems. However, the quality and accessibility of these resources vary significantly across institutions and student populations. Many institutions have recognized the need for robust digital resources and are actively investing in improving their infrastructure and support services. For example, some schools are implementing initiatives like mobile hotspots and subsidized internet access for students facing connectivity challenges.
Comparison of Technology Access with Student Needs
Students from different backgrounds have varying needs when it comes to technology access. Students from low-income families may lack access to reliable home internet, while students with disabilities may require specialized software or hardware to support their learning. Students from rural areas might experience limited internet bandwidth, impacting their ability to participate in online classes and complete research assignments.
Furthermore, students may lack the digital literacy skills to effectively use the available technology. These differences highlight the need for targeted support and interventions that address the unique needs of diverse student populations.
Strategies for Improving Internet Access and Digital Literacy
Improving internet access and digital literacy requires a multi-pronged approach. One key strategy is to increase the availability of subsidized internet access, such as providing grants or scholarships for internet service or offering mobile hotspots to students in need. Digital literacy programs are essential to equip students with the necessary skills to navigate online learning environments effectively. Workshops, tutorials, and individualized support can help students develop critical digital skills, enabling them to succeed in their academic pursuits.
Partnerships with local internet providers and community organizations can further enhance access and support for students in underserved areas.
Digital Equity Initiatives Crucial for Student Success
Digital equity initiatives are crucial for fostering a more inclusive and equitable learning environment. These initiatives should address the unique needs of students from different backgrounds, ensuring that all students have access to the technology and digital literacy support they require. For instance, providing technology training sessions tailored to specific student needs, like those with disabilities or limited English proficiency, can significantly enhance their academic performance.
This comprehensive approach to digital equity will empower students from all backgrounds to fully participate in the educational process and reach their academic potential.
Technology Infrastructure Available in Wisconsin Institutions (Illustrative Example)
| Institution | Computer Labs | Wi-Fi Access | Learning Management System | Digital Literacy Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| University of Wisconsin-Madison | Extensive, modern labs | University-wide, high-speed | Canvas | Extensive workshops, tutorials |
| University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee | Multiple labs with various configurations | Campus-wide, reliable | Blackboard | Digital skills training, individualized support |
| UW-Stevens Point | Well-equipped labs, with specialized equipment | Reliable campus-wide | Desire2Learn | Digital learning support center |
| [Other Wisconsin University] | [Specify details] | [Specify details] | [Specify details] | [Specify details] |
This table is a simplified illustration of the technology infrastructure. Actual availability may vary depending on the specific institution, program, and student needs.
Housing and Transportation
Navigating the complexities of college life often means facing the added pressure of housing and transportation costs. These expenses can be significant barriers to pursuing higher education, particularly for students from lower-income backgrounds. Addressing these issues is crucial for ensuring that all Wisconsin students have equal opportunities to succeed in their academic endeavors.
Housing Affordability Challenges
Wisconsin’s diverse college towns, while vibrant and appealing, frequently present significant housing affordability challenges. Rising rents and limited availability of affordable student housing often force students to compromise on location, commute longer distances, or share housing with multiple roommates. This can impact their ability to focus on their studies and participate fully in campus life. The lack of affordable options can lead to financial strain, reducing students’ capacity to engage in extracurricular activities, internships, and other enriching experiences that are essential for personal and academic growth.
Strategies for Affordable Housing
Several strategies can help mitigate the housing affordability crisis. One key approach is developing more student housing options, including cooperatives, supportive housing initiatives, and shared living arrangements. Subsidized or reduced-cost housing options could be created through partnerships between universities, local governments, and non-profit organizations. Incentivizing private landlords to offer affordable housing units for students could also be considered.
These initiatives, combined with robust financial aid packages, would provide crucial support to students facing financial constraints.
Public Transportation Accessibility
Effective public transportation is essential for student mobility. Reliable and affordable bus routes, light rail systems, and other forms of public transit are crucial for enabling students to travel to and from campus, access necessary services, and explore their communities. Improving the accessibility of public transportation, especially during peak hours, is paramount for supporting students’ needs. Integrated transit systems connecting multiple college campuses and nearby areas can also be beneficial.
Comparative Costs: Wisconsin vs. Other States
Housing and transportation costs in Wisconsin vary significantly depending on the specific location and the type of housing. Comparing these costs with other states is important for understanding the unique challenges faced by Wisconsin students. For example, while some areas of Wisconsin may have lower costs compared to major metropolitan areas in other states, others might experience comparable or higher costs.
Cost Comparison Table: Housing and Transportation in Wisconsin College Areas
| College Area | Average Monthly Rent (Estimated) | Average Monthly Transportation Costs (Estimated) |
|---|---|---|
| Madison | $1,200 – $1,800 | $150 – $300 |
| Milwaukee | $1,000 – $1,500 | $100 – $250 |
| Green Bay | $800 – $1,200 | $50 – $200 |
| La Crosse | $700 – $1,100 | $50 – $150 |
Note: These figures are estimates and may vary depending on the specific location, type of housing, and transportation method.
Outreach and Recruitment Efforts
Reaching out to prospective students from diverse backgrounds is crucial for building a vibrant and inclusive campus community. Effective outreach ensures that all qualified students, regardless of their background or circumstances, feel welcome and supported in pursuing their higher education goals at Wisconsin colleges. A holistic approach that considers the specific needs of underrepresented groups is paramount to achieving this goal.
Current Outreach and Recruitment Strategies
Wisconsin colleges are employing various strategies to reach prospective students. These include online advertising campaigns targeting specific demographics, partnerships with high schools and community organizations, and participation in college fairs and outreach events. Many institutions are actively seeking out students from underrepresented backgrounds through targeted recruitment initiatives.
Promoting a Welcoming and Inclusive Environment
Creating a welcoming and inclusive environment for all students is essential for success. This involves fostering a sense of belonging, encouraging interaction among students from diverse backgrounds, and implementing anti-discrimination policies. Effective communication, clear guidelines, and a commitment to diversity and inclusion from the administration, faculty, and student body are vital.
Making college more accessible for all Wisconsin students is crucial. It’s about more than just tuition costs; it’s about a wide range of support systems. Understanding how corporate transparency legislation, like the Corporate Transparency Act, can impact the funding and resources available for educational initiatives is key. What is the Corporate Transparency Act and who it will impact will help us understand how these policies can influence the future of higher education and, in turn, support Wisconsin’s student population.
Ultimately, greater transparency and accountability are needed to ensure the ongoing financial viability of programs that make college more attainable for everyone.
Addressing the Specific Needs of Underrepresented Groups
Recognizing and addressing the specific needs of underrepresented groups is key to fostering a truly inclusive environment. These groups may face unique challenges, such as financial constraints, cultural barriers, or lack of access to resources. Institutions must actively seek out these challenges and provide tailored support systems, financial aid packages, and mentorship programs to help these students succeed.
For instance, some colleges offer specialized tutoring programs for students from low-income backgrounds, or provide cultural sensitivity training for faculty and staff.
Effective Recruitment Strategies in Other States
Successful recruitment strategies in other states offer valuable insights for Wisconsin colleges. Many institutions have seen success through innovative partnerships with community leaders, community organizations, and minority-serving organizations. For example, some colleges partner with local organizations to host workshops and seminars on college applications and financial aid. Another successful model involves hosting events and informational sessions in underserved communities, thereby providing direct access to information about college opportunities.
Example Recruitment Strategies by Wisconsin Colleges
| College | Outreach Strategy | Target Group | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| University of Wisconsin-Madison | Online advertising campaigns, partnerships with high schools, college fairs | Diverse student body | Utilizes a multi-faceted approach to reach a broad range of students. |
| University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee | Targeted recruitment events, partnerships with community colleges | First-generation college students, students from urban areas | Focuses on specific populations with unique needs. |
| University of Wisconsin-Stevens Point | Community outreach, partnerships with local organizations | Students from rural areas | Highlights the college’s connection to the local community. |
| UW-Eau Claire | Scholarships, mentorship programs | Students from underrepresented backgrounds | Provides financial support and guidance to help students succeed. |
Curriculum and Course Offerings: Making College More Accessible For All Wisconsin Students
Wisconsin’s college curricula, while diverse, often face challenges in catering to the needs of all students. The current offerings need careful evaluation and innovative adjustments to ensure equitable access and relevance. This exploration examines the current landscape, identifies areas for improvement, and suggests models from other states to inspire change.Wisconsin’s colleges and universities currently offer a wide array of undergraduate and graduate programs, covering traditional disciplines like engineering and humanities to emerging fields like data science and sustainability.
However, the curriculum design may not always reflect the diverse backgrounds and aspirations of today’s students, particularly first-generation college students or those from underrepresented communities.
Current Curriculum and Course Offerings
The current curriculum in Wisconsin colleges encompasses a wide range of disciplines, from the traditional liberal arts to specialized technical fields. Program structures vary across institutions, reflecting the specific missions and strengths of each college or university. General education requirements often provide a foundation for diverse areas of study, but the flexibility and tailoring of courses to individual needs may vary.
Areas for Improvement in Curriculum Design
Several areas require attention to better serve the needs of a diverse student population. A curriculum’s design should reflect evolving career paths and consider emerging technologies and global issues. A lack of interdisciplinary courses can limit students’ ability to explore connections between different fields and develop comprehensive perspectives.
Innovative Course Structures in Other States
Many states are experimenting with innovative course structures to enhance student engagement and learning outcomes. For instance, project-based learning, where students apply knowledge to real-world problems, is gaining popularity. Other models include competency-based education, allowing students to progress through courses at their own pace based on demonstrated mastery. These models provide more flexibility and cater to various learning styles and needs.
Strategies to Improve Accessibility and Relevance
Implementing strategies to improve the accessibility and relevance of courses involves several key approaches. First, incorporating more project-based and experiential learning opportunities can foster deeper understanding and practical application of knowledge. Second, offering courses in diverse formats, such as online, hybrid, and in-person options, can broaden access for students with varied schedules and learning preferences. Finally, fostering interdisciplinary collaboration among faculty and creating a culture of continuous improvement can enhance the curriculum’s adaptability to evolving societal needs.
Comparative Analysis of Course Offerings
| Institution | Focus Areas | Online Course Options | Experiential Learning Opportunities |
|---|---|---|---|
| University of Wisconsin-Madison | Research-intensive, broad range of disciplines | High | Significant |
| University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee | Urban focus, applied sciences | Moderate | Moderate |
| UW-Stevens Point | Liberal arts, teacher education | Low | Low |
| UW-Eau Claire | Arts & Sciences, Business | Moderate | Moderate |
Note: This table provides a simplified comparison. Actual course offerings and opportunities vary within each institution. Further research is recommended for detailed information.
Epilogue

In conclusion, ensuring accessible higher education for all Wisconsin students requires a multi-pronged approach. By addressing financial burdens, enhancing support services, improving technological access, and fostering a welcoming environment, we can pave the way for a more equitable and inclusive higher education system in the state. The tables provided offer a glimpse into the current landscape, while the FAQs will address additional questions and concerns.






