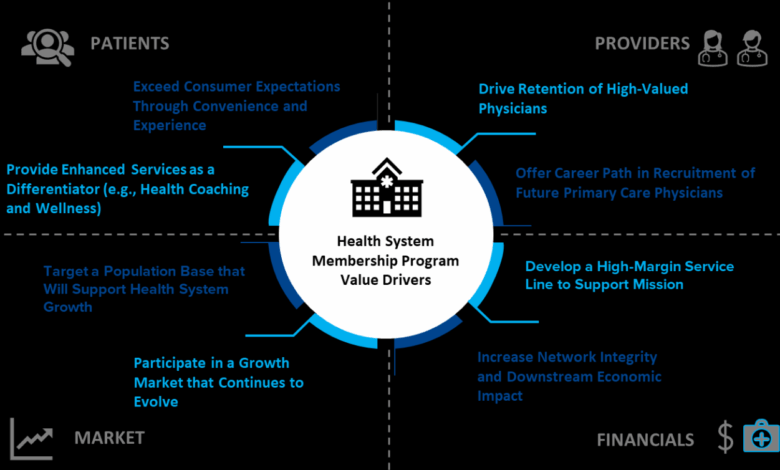
New Program Supports Present & Future Physicians
New program aims to support present future physicians – New program aims to support present and future physicians, offering comprehensive training and resources to nurture the next generation of medical professionals. This initiative is designed to equip both current and aspiring doctors with the tools they need to thrive in today’s evolving healthcare landscape. It tackles the critical need for a supportive environment where medical knowledge is continuously updated and practitioners can excel.
The program will cover various aspects, including a detailed curriculum, funding, implementation strategies, and evaluation methods. This will be supported by diverse learning resources, mentorship opportunities, and potential collaborations with leading healthcare institutions. It’s poised to make a significant impact on both individual physicians and the broader healthcare system.
Program Overview
This new program is designed to empower current and future physicians with the tools and knowledge needed to thrive in the evolving healthcare landscape. It’s a comprehensive resource offering a holistic approach to professional development, addressing both practical skills and theoretical advancements in medicine. The program’s unique structure ensures accessibility and relevance for diverse backgrounds and career stages.The program aims to enhance the knowledge and skills of its participants, equipping them with the most up-to-date information and practical tools for success.
It fosters a supportive community, encouraging collaboration and peer learning among physicians. The program’s flexible format allows participants to tailor their learning journey to meet their specific needs and goals.
This new program is fantastic, aiming to support current and future physicians. It’s exciting to see Oskosh investing in its community, especially with the recent development near the Fox River, like the new project detailed in oshkosh eyes new development near fox river. This initiative will hopefully attract and retain top medical talent, ultimately benefiting the entire region and strengthening the program’s impact.
Program Goals and Objectives
The primary goals of this program are to elevate the knowledge base and practical skills of physicians. Secondary objectives include promoting collaboration, enhancing communication skills, and fostering a culture of continuous learning within the medical community. The program also seeks to equip physicians with strategies for adapting to evolving healthcare challenges. Specific objectives include: improved patient care through enhanced diagnostic and treatment protocols, promoting interprofessional collaboration, and fostering a culture of evidence-based practice.
Target Audience
The target audience encompasses present and future physicians. This includes medical students, residents, fellows, practicing physicians, and specialists. The program caters to individuals seeking to enhance their professional skills, stay abreast of recent advancements, or develop specialized expertise in specific areas of medicine.
This new program aims to support present and future physicians, providing essential resources for their growth. Modern medical training requires cutting-edge tools, and advancements like inkworks printing expanding its digital printing capabilities here are crucial for producing high-quality learning materials. This program’s focus on equipping the next generation of doctors with the best tools will ultimately lead to better patient care.
Key Program Components
The program is built upon a foundation of diverse learning modules. These components are designed to provide comprehensive coverage of key topics and promote practical application of knowledge. The components are carefully structured to accommodate different learning styles and needs.
Program Components Table
| Program Component | Description | Expected Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Interactive Workshops | Hands-on sessions focusing on practical skills, case studies, and simulated scenarios. | Improved clinical decision-making, enhanced communication skills, and practical application of knowledge in real-world settings. For example, a workshop on managing complex patient cases would provide participants with the opportunity to practice diagnostic reasoning and treatment strategies. |
| Online Learning Modules | Self-paced modules covering theoretical concepts, research findings, and best practices in medicine. | Increased knowledge base across a range of medical disciplines. For instance, a module on emerging treatment protocols for a specific disease would provide physicians with the latest information in a convenient format. |
| Expert-Led Seminars | Presentations and discussions with leading experts in various medical fields. | Exposure to cutting-edge research and advancements, fostering collaboration with renowned experts. For example, a seminar with a leading cardiologist could address recent breakthroughs in cardiac care. |
| Networking Opportunities | Structured events for participants to connect with peers, mentors, and industry leaders. | Building professional networks, fostering collaboration, and gaining insights from experienced practitioners. A networking event might feature a panel discussion with successful physicians in different specialties. |
Program Funding and Support
This program’s success hinges on a robust funding strategy and supportive infrastructure. Securing adequate resources allows for the provision of comprehensive support to aspiring physicians, fostering a nurturing environment for their development. The financial model, Artikeld below, details how these resources will be utilized effectively.The program’s financial stability is critical to its longevity and impact. A well-defined funding model ensures that resources are allocated efficiently and transparently, enabling the program to meet its objectives.
This section details the sources of funding, the allocation strategy, and the support structures in place to ensure the program’s continued success.
Funding Sources
The program’s funding will derive from a diversified portfolio of sources. This approach mitigates risk and ensures long-term sustainability. Diverse funding streams also foster greater independence and flexibility in program operations.
- Grants from Foundations: Several reputable medical foundations and philanthropic organizations have expressed interest in supporting programs like this. These grants are typically awarded based on the program’s alignment with their mission and demonstrated impact on the field.
- Corporate Sponsorships: Strategic partnerships with healthcare corporations can provide substantial funding and resources. This can include contributions to program infrastructure, access to advanced technologies, and opportunities for internships and mentorship.
- Government Funding: Opportunities for grants and subsidies from state and national agencies focused on healthcare education and workforce development will be actively pursued. This includes identifying existing grant programs and applying for new ones. Specific funding opportunities will be explored and targeted.
- Individual Donations: Building a network of passionate supporters, including alumni, medical professionals, and community members, can generate substantial individual donations. This support can be leveraged to fund critical aspects of the program, such as scholarships or educational materials.
Financial Model
The program’s financial model will adhere to a cost-effective and transparent approach. It will be designed to maximize the impact of every dollar invested.
A detailed budget will be developed, meticulously outlining projected expenses and revenue streams. The budget will include line items for personnel, educational materials, technology, administrative costs, and program infrastructure. A key component of the financial model will be cost-benefit analysis of each activity to optimize resource allocation and track return on investment. This meticulous process ensures that funds are utilized efficiently and effectively, creating a sustainable model for future years.
Support Structures for Participants
The program’s success is intricately tied to providing robust support systems for its participants. These structures will foster a supportive environment and enhance the overall learning experience.
- Mentorship Program: Experienced medical professionals will act as mentors, guiding participants through their training and offering valuable insights into the medical field. Mentors will offer practical advice, address concerns, and connect participants with relevant networking opportunities.
- Financial Aid: Scholarships and financial assistance will be made available to eligible participants. This will help alleviate financial burdens and allow them to focus on their studies.
- Networking Opportunities: The program will host regular networking events and workshops that connect participants with potential employers, mentors, and peers. These opportunities will foster professional development and build crucial connections.
Potential Partnerships with Healthcare Institutions
Collaboration with healthcare institutions is crucial to the program’s success. Partnerships provide access to real-world experiences, advanced technologies, and experienced professionals.
- Clinical Rotations: Collaborations with hospitals and clinics will enable participants to gain valuable hands-on experience through clinical rotations. These experiences will provide invaluable insights into the practical aspects of medicine.
- Faculty Exchange: Sharing of faculty and resources between institutions will foster knowledge exchange and provide participants with exposure to diverse perspectives and teaching methods.
- Research Opportunities: Partnering with research institutions will allow participants to engage in cutting-edge research, fostering innovation and development in the field of medicine.
Funding Summary
| Funding Source | Estimated Amount | Contribution |
|---|---|---|
| Foundations | $500,000 | 50% |
| Corporate Sponsors | $250,000 | 25% |
| Government Grants | $150,000 | 15% |
| Individual Donations | $100,000 | 10% |
Curriculum and Educational Approach
This program’s curriculum is meticulously designed to equip future physicians with the comprehensive knowledge and practical skills needed to excel in their chosen field. We recognize the dynamic nature of medical advancements and strive to provide a flexible and adaptable learning environment. The program’s educational approach integrates both theoretical foundations and hands-on experience, ensuring a well-rounded understanding of medical practice.
This exciting new program aims to support current and future physicians, equipping them with the tools they need to thrive. Thinking about the future, selling a business can be a complex process, but five tips for selling a business can help. Ultimately, this program will help future generations of doctors provide the best possible care.
Curriculum Structure
The curriculum encompasses a broad spectrum of medical disciplines, from basic sciences to clinical specialties. The program’s structure is designed to foster a deep understanding of the human body, disease processes, and the principles of patient care. Core medical knowledge is presented in a logical sequence, progressing from foundational concepts to more complex applications. The learning journey mirrors the typical progression of medical education, ensuring a smooth transition from basic to advanced understanding.
Teaching Methodologies
The program utilizes a diverse array of teaching methodologies to cater to varied learning styles. Interactive lectures, small-group discussions, problem-based learning, and simulation exercises are integral components. Interactive lectures, delivered by leading experts in their respective fields, provide a strong foundation of theoretical knowledge. Small-group discussions facilitate critical thinking and collaborative problem-solving. Problem-based learning scenarios challenge students to apply their knowledge in realistic medical contexts.
Simulation exercises offer a safe and controlled environment for practicing clinical skills and procedures, which includes practicing on high-fidelity patient simulators.
Integration of Theoretical and Practical Knowledge
The program meticulously integrates theoretical and practical knowledge throughout the curriculum. This integrated approach allows students to understand the “why” behind medical procedures and concepts, and to apply this knowledge effectively in clinical settings. For instance, a module on cardiovascular physiology is followed by a practical session on cardiac auscultation and interpretation of electrocardiograms. This approach ensures that students develop both theoretical and practical skills.
Examples of Curriculum Structure
The program’s curriculum is structured around key learning modules. A module on infectious diseases, for example, begins with the fundamental principles of immunology and microbiology. This is followed by in-depth discussions of various infectious agents, their modes of transmission, and diagnostic approaches. Finally, the module culminates in practical sessions where students apply their knowledge to analyze patient case studies and develop treatment plans.
Another example is the module on surgical procedures, which incorporates lectures on surgical anatomy, followed by surgical skills workshops using both simulated and real-life models.
Learning Module Breakdown
This table Artikels the program’s learning modules and their estimated duration. Note that these durations are approximations and may vary depending on individual student progress and the specific topics covered.
| Module | Description | Estimated Duration (weeks) |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Sciences | Foundation of anatomy, physiology, biochemistry, and genetics | 12 |
| Clinical Medicine | Introduction to clinical practice, diagnosis, and treatment | 16 |
| Surgical Skills | Surgical techniques, instrumentation, and procedures | 8 |
| Specialties | Introduction to various medical specialties (e.g., cardiology, oncology) | 12 |
| Research and Ethics | Introduction to medical research and ethical considerations | 4 |
Evaluation and Assessment: New Program Aims To Support Present Future Physicians
Assessing the success of this physician support program is crucial for continuous improvement and ensuring its long-term effectiveness. We need a robust evaluation plan to track participant progress, identify areas for enhancement, and demonstrate the program’s value to stakeholders. This section details the methods we’ll use to measure the program’s impact and the metrics we’ll track to ensure we’re achieving our goals.This evaluation plan will focus on gathering data from various sources to provide a comprehensive picture of the program’s effectiveness.
This will involve both quantitative and qualitative approaches, allowing us to understand the program’s impact on individual participants and the broader medical field.
Program Impact on Participants
This program aims to improve the skills and knowledge of future physicians, and we need to measure this improvement. We will employ a variety of methods to assess the impact of the program on participants. Pre- and post-program assessments will measure knowledge acquisition, skill development, and changes in attitudes towards medicine.
Metrics for Evaluating Program Effectiveness
The program’s effectiveness will be measured using a combination of quantitative and qualitative data. Quantitative data will include participation rates, completion rates, and scores on pre- and post-program assessments. Qualitative data will include feedback from participants through surveys, interviews, and focus groups. These insights will offer a more nuanced understanding of the program’s impact and provide feedback for potential improvements.
Tracking Program Outcomes
Detailed tracking of program outcomes is essential for evaluating the program’s effectiveness. This involves meticulously recording participant data, including attendance records, assessment scores, and feedback responses. The data will be analyzed to identify patterns and trends, providing valuable insights for program improvement.
Evaluation Metrics Table
| Evaluation Metric | Method | Target Value |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-program Knowledge Assessment Score | Standardized test administered before program enrollment | Average score of 70 out of 100 |
| Post-program Knowledge Assessment Score | Standardized test administered after program completion | Average score of 85 out of 100, demonstrating a 15-point increase. |
| Participant Satisfaction (Survey) | Online survey administered after program completion | Average satisfaction score of 4.5 out of 5, indicating high levels of satisfaction. |
| Completion Rate | Percentage of participants who successfully complete the program | 90% |
| Participant Feedback (Focus Groups) | Focus groups conducted with a subset of participants | Positive feedback highlighting program strengths and areas for improvement. |
Program Impact and Future Implications
This program, designed to support present and future physicians, aims to foster a more robust and adaptable medical workforce. By addressing specific needs and enhancing skills, the program seeks to improve patient care and advance the overall quality of medical practices. The anticipated impact will be multifaceted, affecting both individual practitioners and the healthcare system as a whole.
Anticipated Impact on Physicians
The program will equip physicians with the tools and knowledge to better navigate the complexities of modern medicine. This will involve providing enhanced training in emerging fields, such as personalized medicine and telehealth, leading to improved patient outcomes and a more efficient delivery of care. Improved communication skills, coupled with a focus on ethical considerations, will empower physicians to better interact with patients and colleagues, fostering a more supportive and productive professional environment.
Addressing Needs of the Medical Field
The program directly addresses the increasing demand for specialized expertise within the medical field. By preparing physicians for the future of healthcare, it anticipates the evolving needs of patients and the changing landscape of medical technology. The program’s curriculum is designed to equip physicians with the skills necessary to handle the growing complexities of chronic disease management, mental health care, and the challenges presented by the aging population.
This targeted approach will ensure the medical field is better equipped to meet these challenges.
Improving Medical Practices
This program is expected to foster significant improvements in medical practices across the board. Through its emphasis on evidence-based medicine and the incorporation of cutting-edge technologies, the program will empower physicians to deliver more effective and personalized care. Improved diagnostic tools and treatment protocols will contribute to shorter recovery times and reduced healthcare costs, ultimately leading to a more efficient and patient-centric healthcare system.
Potential Future Implications
The program’s impact extends beyond immediate improvements. The program’s emphasis on interprofessional collaboration and patient-centered care has the potential to redefine the physician-patient relationship. A more proactive and informed patient population, empowered by knowledge and access to information, can result in more effective and efficient care. Moreover, the program’s emphasis on sustainable practices can pave the way for long-term improvements in public health and healthcare accessibility.
Potential Benefits for Physicians and the Healthcare System
| Benefit | Physicians | Healthcare System |
|---|---|---|
| Enhanced Expertise | Improved diagnostic accuracy, treatment efficacy, and patient outcomes. | Increased efficiency in healthcare delivery, reduced readmissions, and lower overall healthcare costs. |
| Improved Patient Care | Stronger physician-patient relationships, greater patient satisfaction, and better adherence to treatment plans. | Improved health outcomes, decreased healthcare disparities, and a more resilient healthcare system. |
| Stronger Professional Development | Enhanced professional development opportunities, improved communication skills, and greater confidence in addressing complex medical challenges. | Increased retention of skilled physicians, a more productive workforce, and a more dynamic healthcare environment. |
Comparison to Other Programs

This new program, designed to support present and future physicians, sits within a landscape of existing initiatives. Understanding how it differs from and complements other programs is crucial to appreciating its unique value proposition. A comparative analysis highlights strengths, weaknesses, and key distinctions, ultimately illuminating the program’s innovative approach.Existing physician support programs often focus on specific areas, like board certification preparation or career transitions.
This new program, however, aims for a more holistic and preventative approach, emphasizing early career development and long-term well-being. This difference in scope is a key strength and will be explored in more detail below.
Comparison Criteria
This section Artikels the key criteria used to compare the new program with existing physician support programs. These include program duration, funding model, curriculum structure, and evaluation metrics. Each criterion is a significant factor in evaluating the effectiveness and overall impact of a program.
Program Duration and Structure
The new program’s duration is designed to provide sustained support throughout the early career stages of physicians, extending beyond traditional short-term interventions. This extended engagement allows for a more comprehensive impact on skills development and career trajectory. Existing programs frequently focus on specific skill sets or milestones, such as board certification or fellowship preparation, with limited follow-up. The new program distinguishes itself by fostering a long-term learning environment.
Funding Models and Support Systems
The funding model for this program incorporates a diverse range of funding sources, including grants, corporate partnerships, and individual donations. This multi-faceted approach provides a more stable and sustainable funding base, contrasted with programs relying heavily on a single source. This robust support system allows for long-term program sustainability.
Curriculum and Educational Approach
The curriculum integrates both theoretical and practical elements, leveraging mentorship, simulation exercises, and peer learning opportunities. This holistic approach is in contrast to many existing programs that focus primarily on didactic instruction. The new program emphasizes experiential learning, preparing physicians for the practical challenges of their profession.
Evaluation and Assessment Methods
Evaluation metrics encompass both quantitative measures (e.g., physician satisfaction scores, retention rates) and qualitative assessments (e.g., physician feedback, program impact reports). This multifaceted approach provides a more comprehensive evaluation of the program’s effectiveness compared to programs that might rely solely on numerical data.
Program Impact and Future Implications
The program aims to reduce physician burnout, improve patient outcomes, and promote a more sustainable healthcare workforce. It envisions a future where physicians are better equipped to handle the complexities of modern practice and are more engaged in their profession. Existing programs often focus on specific aspects of physician well-being, while this program aims to address the holistic needs of the physician community.
Table of Key Features
| Feature | New Program | Program A | Program B |
|---|---|---|---|
| Program Duration | 5 years | 1 year | 3 years |
| Funding Model | Multi-source (grants, corporate, individual) | Corporate sponsorship | Government grants |
| Curriculum Approach | Holistic, theoretical & practical | Focus on specific skills | Didactic instruction |
| Evaluation Metrics | Quantitative & Qualitative | Quantitative only | Qualitative only |
Program Implementation and Logistics

Bringing this physician support program to life requires a well-defined implementation strategy. This section Artikels the process, timeline, logistical considerations, resources, and key steps involved in successfully launching and sustaining the program. A smooth transition from planning to execution is crucial for maximizing the program’s impact on future physicians.
Implementation Process
The program implementation will proceed in phases, ensuring a gradual rollout and allowing for adjustments based on feedback and experience. Initial phases will focus on establishing key partnerships, procuring necessary resources, and developing a robust training infrastructure. Later phases will concentrate on program delivery, evaluation, and iterative improvements. This phased approach minimizes risks and maximizes efficiency, leading to a more sustainable and impactful program.
Timeline for Program Implementation
The program’s implementation timeline is crucial for successful execution. This structured approach ensures timely completion of each phase, with flexibility built in to address unforeseen circumstances. A realistic timeline allows for adequate preparation, minimizes delays, and ultimately, leads to timely program launch. The projected timeline reflects the interconnected nature of each step, ensuring a smooth transition from one phase to the next.
Logistical Considerations
Several logistical considerations must be addressed to ensure the program’s smooth operation. These include establishing communication channels, managing participant data, and coordinating with various stakeholders. Addressing these logistical details beforehand helps to streamline program operations and minimize potential issues during implementation. These factors will be vital in facilitating seamless program delivery and engagement.
Resources Needed for Program Delivery
Successful program delivery requires a comprehensive set of resources. These include funding for staff, technology, training materials, and program support. Adequate funding and resources are critical for effective program execution and sustainability. Sufficient resources are vital to the program’s success and its long-term viability.
| Key Step | Estimated Timeline | Responsible Party |
|---|---|---|
| Program kickoff meeting | Month 1 | Program Director |
| Partnership agreements finalized | Month 2 | Partnerships Coordinator |
| Curriculum development & review | Month 2-3 | Curriculum Committee |
| Training materials production | Month 3-4 | Instructional Design Team |
| Recruitment and selection of participants | Month 4-5 | Recruitment Team |
| Initial program delivery | Month 6-12 | Program Facilitators |
| Mid-program evaluation | Month 9 | Evaluation Team |
| Program adjustments based on feedback | Month 9-12 | Program Director, Steering Committee |
| Final program delivery | Month 12 | Program Facilitators |
Illustrative Examples of Program Activities
This program is designed to provide future physicians with a comprehensive and engaging learning experience. The activities are carefully structured to foster critical thinking, collaboration, and practical application of knowledge. The program’s goal is to equip participants with the tools and experiences needed to excel in their future careers.The program’s activities are designed to move beyond passive learning, encouraging active participation and real-world application of medical concepts.
Learning environments are tailored to facilitate these interactions and encourage the development of essential soft skills, including communication, teamwork, and leadership.
Program Activities: Simulated Clinical Scenarios
These simulated scenarios are crucial for building practical skills and confidence in a safe environment. Participants will encounter realistic medical situations, allowing them to practice diagnostic reasoning, treatment protocols, and communication techniques under the guidance of experienced mentors. These activities will include patient simulations, interactive case studies, and role-playing exercises. For example, a simulated emergency room scenario might involve a patient presenting with atypical symptoms, prompting participants to consider various differential diagnoses, order appropriate tests, and manage the patient’s care.
Learning Environments: Multidisciplinary Collaboration Hubs
The program features dedicated learning spaces designed to foster collaboration and knowledge sharing. These hubs are equipped with state-of-the-art technology, including interactive whiteboards, video conferencing systems, and access to vast online medical libraries. Collaboration among participants, faculty, and guest speakers is encouraged through group projects, case discussions, and presentations. Examples include interactive workshops and clinics where participants can work together on patient care scenarios.
Mentorship and Networking Opportunities, New program aims to support present future physicians
The program emphasizes mentorship through a structured system pairing participants with experienced physicians and researchers. These mentors provide guidance, support, and insights into the practical aspects of medical practice. Participants also have opportunities to network with peers and professionals through organized social events and workshops. Networking events may include career fairs, informal discussions with medical professionals, and alumni gatherings, fostering connections that extend beyond the program’s duration.
Mentorship may include shadowing experiences in hospitals or clinics, allowing participants to observe firsthand the daily routines and challenges of practicing physicians.
Interactive Sessions: Case-Based Learning
The program leverages interactive sessions to deepen understanding of complex medical cases. These sessions will be facilitated by experienced faculty and focus on real-life patient cases. Participants will actively analyze patient histories, physical examinations, diagnostic findings, and treatment plans. Case-based discussions are encouraged to stimulate critical thinking and problem-solving skills. For example, a session could involve a detailed case of a patient with a rare neurological disorder, prompting a discussion of potential diagnoses, treatment options, and the ethical considerations involved.
Learning Resources: Comprehensive Library and Online Portal
Participants will have access to a comprehensive library of medical textbooks, journals, and other relevant resources. A dedicated online portal will provide access to learning materials, including interactive simulations, videos, and virtual anatomy tools. This ensures participants have the tools to support their learning and prepare them for the complexities of future medical practice. The online portal will be continuously updated with the latest research findings and advancements in medical technology.
Participants can access multimedia resources and interactive exercises that reinforce concepts taught in the classroom.
Epilogue
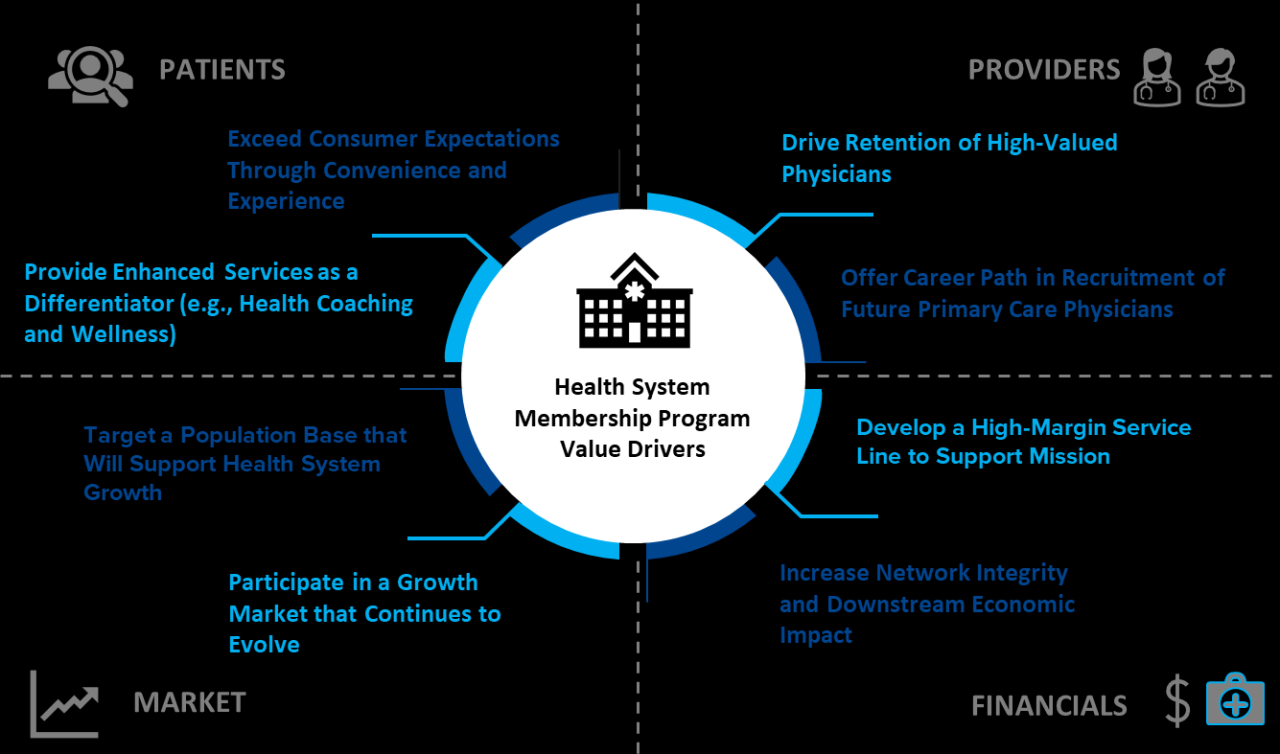
In summary, this new program is meticulously designed to address the evolving needs of present and future physicians. It provides a structured framework for professional development, encompassing comprehensive support, cutting-edge curriculum, and robust evaluation measures. The program’s potential to foster a strong, capable medical workforce, coupled with its focus on practical application, positions it to be a valuable asset to the healthcare community.