
Organizations Raise Awareness of Women in STEM
Organizations raise awareness of women in STEM, highlighting the vital role of female representation in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics. This initiative encompasses various approaches, from targeted campaigns to mentorship programs, all aimed at encouraging more women to pursue STEM careers.
This exploration delves into the strategies employed by organizations to promote women in STEM, examining their effectiveness and impact. It also identifies challenges, such as societal biases and lack of role models, and explores potential solutions and success stories.
Understanding the Scope of Initiatives
Promoting women in STEM is a crucial step towards a more equitable and innovative future. This involves recognizing the systemic barriers women face and actively working to dismantle them. A multitude of organizations are taking on this challenge, employing diverse strategies to raise awareness and create opportunities. This exploration delves into the range of initiatives, highlighting the approaches used and the impact they are making.Various organizations are dedicated to fostering a more inclusive environment for women in STEM.
These initiatives span across different regions and focus on a wide range of actions, from mentorship programs to advocating for policy changes. By understanding the breadth and depth of these efforts, we can better appreciate the multifaceted nature of the problem and the variety of solutions being implemented.
Examples of Active Organizations
Numerous organizations are dedicated to empowering women in STEM. For instance, the Society of Women Engineers (SWE) provides networking opportunities, mentorship programs, and resources for women engineers. Similarly, Girls Who Code focuses on introducing girls to computer science and technology through immersive coding programs. These are just two examples, with many other organizations dedicated to supporting women in specific fields or at particular career stages.
Types of Awareness Campaigns
These organizations utilize a range of awareness campaigns to achieve their goals. Some focus on outreach, targeting young girls and women with educational workshops and inspiring stories. Others concentrate on advocating for policy changes, lobbying for more equitable funding and opportunities. The methods employed vary depending on the organization’s mission and the needs of the target audience.
Approaches to Reach Diverse Audiences
Reaching diverse audiences within the STEM community is crucial for maximizing the impact of these initiatives. Organizations use various approaches to connect with women at different stages of their careers, backgrounds, and geographic locations. This includes leveraging online platforms, conducting targeted workshops, and collaborating with universities and institutions. The effectiveness of these strategies hinges on understanding the specific needs and preferences of each segment of the target audience.
Comparative Analysis of Strategies
| Organization | Primary Focus | Target Audience | Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Society of Women Engineers (SWE) | Engineering | Women engineers, aspiring engineers | Networking events, mentorship programs, scholarships, advocacy for policy changes |
| Girls Who Code | Computer Science | Girls in middle and high school | Coding workshops, summer programs, online resources |
| National Girls Collaborative Project | STEM Education | Girls K-12 | Teacher training, curriculum development, and outreach programs |
This table provides a basic comparison of the strategies employed by different organizations. The table highlights the diversity of approaches used, ranging from direct support to advocacy for policy changes. Understanding these differences is crucial for evaluating the impact of various initiatives and adapting strategies to better meet the needs of the community.
Impact and Effectiveness of Awareness Efforts
Raising awareness about women in STEM is crucial, but its true impact hinges on measurable results. Effective initiatives go beyond simple messaging; they must foster tangible change in attitudes, opportunities, and ultimately, representation. This section delves into the metrics used to gauge success, the short and long-term effects, and the varying effectiveness across different demographic groups.Understanding the scope of these efforts requires a nuanced perspective, moving beyond superficial impressions to examine the root causes of underrepresentation and the specific mechanisms that can counteract them.
We need to examine how various initiatives perform and identify areas where they excel or fall short. This examination allows for more targeted and impactful interventions in the future.
Key Metrics for Assessing Initiative Success
Evaluating the success of STEM awareness initiatives requires a multifaceted approach. Quantitative metrics like the increase in female enrollment in STEM-related courses, the number of women employed in STEM fields, and the proportion of women in leadership positions within these fields provide a clear picture of progress. Qualitative metrics, such as surveys gauging attitudes towards women in STEM and feedback from participants on the effectiveness of programs, provide valuable insight into the underlying reasons for change.
Data collected from these diverse sources allows for a comprehensive understanding of the impact of these initiatives.
Short-Term and Long-Term Impacts
Short-term impacts are often visible in immediate engagement with the program, such as increased participation in workshops or online courses. These programs can also cultivate positive attitudes towards STEM among young women, leading to a greater interest in pursuing STEM-related studies. Long-term impacts are more subtle but critical. They include a rise in the number of women pursuing advanced degrees in STEM, increased representation in leadership positions, and a significant change in societal perceptions regarding women in STEM fields.
For example, the increase in female professors in STEM departments often encourages more women to pursue advanced degrees.
Effectiveness Across Demographics
The effectiveness of STEM awareness initiatives varies across different demographics. Programs tailored to specific needs, such as those focused on underrepresented minority groups within the female population, often demonstrate higher impact. This highlights the importance of culturally sensitive approaches and the necessity for programs to address the unique barriers and challenges faced by different groups. Moreover, programs that offer mentorship and networking opportunities can significantly increase the likelihood of success, particularly for women from disadvantaged backgrounds.
Positive and Negative Outcomes of STEM Awareness Campaigns
| Positive Outcomes | Negative Outcomes |
|---|---|
| Increased female enrollment in STEM courses | Lack of sustained engagement after the program ends |
| Improved attitudes towards women in STEM fields | Difficulty in reaching diverse populations |
| Increased female representation in leadership positions | Limited resources to sustain long-term initiatives |
| Development of confidence and skills in STEM | Lack of program evaluation to identify areas for improvement |
| Increased interest in STEM careers among girls | Lack of diverse representation among program facilitators and mentors |
“A key indicator of success is not just the initial impact but also the lasting change in mindset and opportunities for women in STEM.”
Challenges and Obstacles to Overcome
Breaking down the barriers to women’s participation in STEM fields requires a multifaceted approach. Simply raising awareness isn’t enough; we must identify and address the deeply ingrained societal factors and biases that contribute to this disparity. Understanding these obstacles is crucial for developing effective strategies to foster inclusivity and create pathways for women to thrive in these fields.
Common Barriers to Women’s Participation in STEM
Societal expectations and stereotypes often steer women away from STEM careers. From early childhood, girls may be subtly discouraged from pursuing science, technology, engineering, and mathematics. This can manifest in limited access to resources, fewer role models, and a lack of encouragement to pursue STEM-related subjects and professions. Implicit biases, often unconscious, can also play a significant role in shaping career paths and opportunities.
This can lead to women facing challenges in recruitment, promotion, and recognition within STEM organizations.
Societal Factors Contributing to Obstacles
Traditional gender roles often place women in the domestic sphere, limiting their time and resources to dedicate to pursuing STEM careers. These roles often include significant childcare responsibilities, which can create barriers to balancing work and family life. Cultural norms and societal pressures can also influence women’s choices and perceptions of STEM fields. A lack of visible female role models and mentors in STEM can contribute to a sense of isolation and uncertainty.
These factors often combine to create an environment where women may feel less encouraged, supported, and confident in their abilities within STEM fields.
Organizations are doing great work raising awareness of women in STEM fields, highlighting the importance of inclusivity. Meanwhile, the Stevens Points Breast Care Center has received a redesignation, a significant achievement that underscores the crucial role of quality healthcare facilities like this Stevens Points Breast Care Center receives redesignation. This kind of progress in healthcare, in turn, inspires future generations of women to pursue STEM careers.
The Role of Unconscious Bias in Hindering Progress
Unconscious biases are deeply ingrained, often subtle prejudices that can affect decision-making processes. These biases can lead to women being overlooked for opportunities, facing unfair evaluations, or experiencing microaggressions. For example, hiring managers might unconsciously favor candidates with perceived “traditional” characteristics or associate women with less technical expertise. This can lead to a cycle of disadvantage, hindering women’s advancement in STEM careers.
Furthermore, these biases can manifest in subtle, everyday interactions and behaviours, impacting women’s experiences in the workplace.
Potential Solutions to Challenges
Addressing these challenges requires a multi-pronged approach, incorporating changes at various levels of society.
| Challenge | Potential Solution |
|---|---|
| Societal Expectations and Stereotypes | Promote gender equality in early education, highlighting positive female role models in STEM. Encourage early exposure to STEM concepts and activities for girls. Support initiatives that foster a sense of belonging and reduce societal pressures on women. |
| Work-Life Balance | Implement flexible work arrangements, parental leave policies, and childcare support systems to help women balance work and family responsibilities. Advocate for policies that promote family-friendly environments. |
| Unconscious Bias | Implement unconscious bias training for hiring managers and mentors to help them identify and address their own biases. Establish clear and objective criteria for evaluations and promotions. Encourage mentorship programs that pair women with successful female role models. |
| Limited Access to Resources | Increase funding for STEM education and programs targeted at women and girls. Develop initiatives to provide access to high-quality STEM resources and mentorship programs. Support scholarship programs specifically designed to help women pursue STEM degrees. |
Analyzing the Role of Mentorship and Role Models
Mentorship and role models play a critical role in shaping career paths and fostering inclusivity in STEM fields. Effective mentorship programs can provide invaluable guidance and support, helping women navigate the unique challenges they may face in their professional journeys. Similarly, visible role models can inspire young women to pursue STEM careers, demonstrating that success in these fields is attainable.
This section delves into the importance of these crucial elements for women in STEM.Mentorship relationships are not just about career advice; they are about fostering a supportive network and building confidence. Strong mentorship can provide a safe space for women to discuss challenges, learn from experience, and gain a broader understanding of the industry. Role models, in turn, offer a tangible representation of success in STEM, demonstrating the potential and possibilities that exist for women within these fields.
Importance of Mentorship Programs
Mentorship programs offer structured guidance and support, helping women navigate the complexities of a STEM career. These programs provide a unique opportunity for women to learn from experienced professionals, gain insights into industry best practices, and develop essential professional skills. They can address specific challenges faced by women in STEM, such as navigating the workplace culture, balancing work and family, or overcoming implicit biases.
Examples of Successful Mentorship Models
Numerous organizations have implemented successful mentorship programs that benefit both mentors and mentees. One example is the program offered by the Society of Women Engineers (SWE), which pairs experienced female engineers with undergraduate and graduate students. This program facilitates knowledge transfer, career development, and professional networking. Another example is Google’s internal mentorship program, which fosters diverse and inclusive leadership within the company.
These programs often incorporate regular meetings, workshops, and networking opportunities to enhance the mentorship experience.
How Role Models Influence Career Choices and Aspirations
Visible role models significantly impact career choices and aspirations, particularly for young women. Exposure to successful female figures in STEM fields can help dispel stereotypes and demonstrate the possibility of achieving professional success. When young women see women excelling in STEM roles, they are more likely to consider these careers as viable options and pursue their own passions in these fields.
For instance, prominent female scientists like Marie Curie or Rosalind Franklin have inspired generations of women to pursue careers in science.
Types of Mentorship Programs and Effectiveness
| Type of Mentorship Program | Description | Effectiveness Factors |
|---|---|---|
| One-on-One Mentorship | Direct pairing of a mentor and mentee for regular interaction. | Strong personal connection, tailored guidance, immediate feedback. |
| Group Mentorship | Mentorship in a small group setting. | Networking opportunities, peer support, diverse perspectives. |
| Online Mentorship Platforms | Mentorship facilitated through digital tools. | Accessibility, broader reach, flexible scheduling. |
| Mentorship with Career Exploration | Focuses on career exploration and decision-making. | Gaining knowledge about various roles, identifying interests, setting goals. |
“Mentorship is not just about giving advice; it’s about building a relationship of trust and support.” – Unknown
Organizations are doing a fantastic job raising awareness of women in STEM fields, highlighting inspiring role models and encouraging girls to pursue these careers. This kind of initiative is crucial, but we also need to think about the broader environmental impact of our choices. For example, initiatives like sustaining our waters the fox wolf watershed alliance are vital for ensuring healthy ecosystems.
Ultimately, both environmental conservation and supporting women in STEM are crucial for a sustainable future.
The effectiveness of these programs often depends on factors such as the mentor’s experience, the mentee’s commitment, and the program’s structure. Continuous evaluation and feedback mechanisms are crucial for optimizing program outcomes.
Exploring Educational Initiatives and Outreach Programs: Organizations Raise Awareness Of Women In Stem
Igniting passion for STEM fields in young women requires targeted educational initiatives and outreach programs. These programs are crucial for fostering a diverse and inclusive STEM workforce. By creating engaging learning environments and providing accessible resources, we can cultivate a pipeline of future female innovators. This involves more than just awareness; it necessitates practical steps that connect with students on a personal level.Effective programs often combine hands-on activities, mentorship opportunities, and exposure to role models, fostering a sense of belonging and demonstrating the potential within STEM.
Organizations are doing a fantastic job raising awareness of women in STEM fields, and it’s inspiring to see the progress. This kind of initiative is crucial, especially when considering how local developments like Oshkosh’s new project near the Fox River here will need a diverse workforce. Hopefully, these efforts to spotlight women in STEM will continue to resonate and attract more talented individuals to these crucial roles.
This approach not only attracts girls but also empowers them to pursue STEM careers with confidence.
Examples of Educational Programs Designed to Attract Women to STEM
Various programs effectively engage girls in STEM, ranging from interactive workshops to summer camps. Many initiatives emphasize hands-on experimentation and problem-solving, providing a practical understanding of scientific concepts. For example, programs like the Girl Scouts’ STEM initiatives provide opportunities for girls to explore robotics, coding, and engineering through fun, engaging activities. Another example includes organizations like the Society of Women Engineers, which offer workshops, competitions, and mentoring to encourage female students to pursue STEM careers.
Outreach Programs Targeting Underrepresented Groups
Recognizing the importance of diversity, outreach programs should specifically target underrepresented groups. These programs should be designed to address specific barriers faced by these communities, such as cultural biases or lack of access to resources. Programs might include workshops in underserved communities, scholarships for students from low-income backgrounds, or mentorship opportunities tailored to their needs. Effective outreach programs often leverage community leaders and trusted figures to build trust and encourage participation.
Educational Materials Adapted to Engage Different Learners
Educational materials should be adaptable to cater to diverse learning styles and needs. This involves utilizing various mediums, such as visual aids, interactive simulations, and hands-on projects, to ensure that students connect with the material in a way that resonates with them. Recognizing that students learn in different ways is crucial. Consider offering options for students to express their understanding through creative projects, presentations, or discussions.
This approach can cater to different learning styles and encourage a more holistic learning experience.
Table of Educational Resources and Target Audiences
| Educational Resource | Target Audience | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Girl Scouts STEM Programs | Girls in elementary and middle school | Hands-on workshops and projects focusing on robotics, coding, and engineering |
| Society of Women Engineers (SWE) | High school and college students, and young professionals | Mentorship programs, competitions, and networking opportunities for women in STEM |
| STEM Summer Camps | Middle school and high school students | Immersive programs focused on specific STEM disciplines, with hands-on activities and project-based learning |
| Workshops in Underserved Communities | Girls and young women from underrepresented backgrounds | Accessible STEM workshops in local community centers or schools, often focused on topics relevant to the local community |
Highlighting Success Stories and Achievements
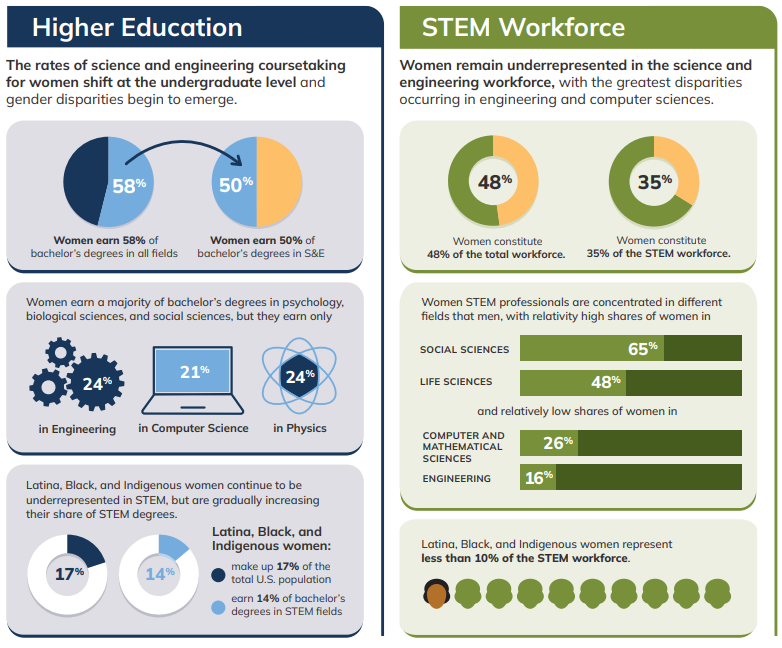
Inspiring narratives of women who have excelled in STEM fields are crucial to motivating the next generation of female scientists, engineers, and technologists. Sharing their journeys, highlighting the factors that contributed to their success, and demonstrating the impact of their achievements can create a powerful ripple effect, encouraging young women to pursue STEM careers. This section will delve into specific examples, showcasing the impact of these stories and the elements that paved the way for their success.
Illustrative Examples of Women in STEM
Numerous women have made significant contributions to various STEM fields. Their stories serve as powerful role models, demonstrating the potential for success and inspiring others to pursue their own ambitions. These stories go beyond simply recounting accomplishments; they illustrate the dedication, perseverance, and often, the unique challenges overcome to achieve their goals.
Factors Contributing to Success
Several key factors often contribute to the success of women in STEM. Strong support systems, both personal and professional, can be crucial. Access to quality education and mentorship programs can provide essential guidance and encouragement. Furthermore, a supportive and inclusive work environment that values diverse perspectives is critical to fostering innovation and achievement.
Impact on Younger Generations
The stories of successful women in STEM have a profound impact on younger generations, particularly girls. Seeing women in leadership roles and achieving significant milestones in STEM fields can significantly influence their aspirations and career choices. These stories can help break down stereotypes and demonstrate that women are capable of excelling in traditionally male-dominated fields.
Case Studies: Women in STEM
| Name | Field | Key Achievements | Factors Contributing to Success |
|---|---|---|---|
| Katherine Johnson | Mathematics | Calculated trajectories for NASA’s space missions, including the Apollo program. | Exceptional mathematical talent, perseverance, and dedication. Strong support system and recognition of her expertise. |
| Marie Curie | Physics and Chemistry | Pioneering research on radioactivity, the first woman to win a Nobel Prize, and the only person to win Nobel Prizes in two different scientific fields. | Exceptional intellect, independent drive, and determination in the face of societal barriers. |
| Ada Lovelace | Mathematics and Computing | Recognized as the first computer programmer for her work on Charles Babbage’s Analytical Engine. | Early understanding of the potential of computers, insightful analysis, and innovative thinking. |
Visualizing the Impact of Awareness Campaigns

Raising awareness for women in STEM requires more than just words; it demands a compelling visual narrative. A well-crafted visual representation can resonate deeply with audiences, sparking interest and fostering a deeper understanding of the challenges and triumphs of women in STEM throughout history. This approach not only increases visibility but also inspires the next generation of female scientists, engineers, mathematicians, and technologists.Visual communication is particularly powerful in the realm of STEM.
Complex scientific concepts and historical trends can be simplified and made accessible through visuals, making abstract ideas tangible and engaging for a wider audience. This visual storytelling approach can be highly effective in advocating for increased female representation in STEM fields, fostering a sense of belonging and encouraging continued participation.
Importance of Visual Representation in Promoting STEM
Visual representations, like images and infographics, are crucial in STEM outreach campaigns. They can communicate complex ideas in a concise and memorable way. Pictures and graphics can convey information and emotions more effectively than text alone, capturing attention and fostering engagement. Furthermore, visual narratives can help personalize the STEM journey, showcasing the human stories behind scientific achievements and fostering a sense of relatability.
Visual Representation of Women in STEM Throughout History
A timeline depicting women in STEM throughout history would be a powerful tool for awareness campaigns. The timeline should showcase prominent figures, highlighting their contributions to various scientific fields, including but not limited to, astronomy, medicine, computer science, and engineering. Each entry could include a brief description of their work, along with a visual representation (e.g., a portrait or an image related to their field).
This would create a compelling narrative of the evolution of women in STEM, emphasizing their crucial role in shaping scientific progress. This visual narrative should also include a variety of women, reflecting the diversity within the STEM community. Examples of such figures include Ada Lovelace, Marie Curie, and Katherine Johnson.
Use of Infographics and Other Visual Aids in Campaigns
Infographics are particularly effective in conveying data and statistics related to women in STEM. For instance, an infographic comparing the representation of women in different STEM fields (computer science, engineering, mathematics, etc.) could highlight the disparity and the need for change. Other visual aids like videos, animations, and interactive websites can also engage audiences, making the information more memorable and accessible.
Using diverse visuals, including different skin tones, ages, and ethnicities, can create a more inclusive and relatable message.
Table Illustrating How Visuals Can Communicate Complex Ideas Effectively
| Visual Element | Description | How it Communicates Complex Ideas |
|---|---|---|
| Image of a female scientist in a lab | A photo of a woman conducting an experiment in a laboratory setting. | Provides a relatable image of women in STEM, demonstrating the practical application of scientific knowledge. |
| Timeline of women in STEM | A visual representation of historical milestones and contributions of women in STEM, including portraits of notable figures. | Illustrates the evolution of women in STEM, showcasing their impact across different periods. |
| Infographic comparing gender representation in STEM fields | A visually appealing graphic comparing the percentage of women in different STEM disciplines (e.g., computer science, engineering, mathematics). | Quickly and effectively communicates quantitative data, highlighting disparities and promoting a deeper understanding of the problem. |
| Animated video explaining a scientific concept | A video with animated graphics that illustrate a complex scientific process or concept. | Makes complex scientific concepts more easily understood by using visual aids, including animation and illustrations. |
Strategies for Sustainable Change
Building a truly equitable STEM landscape requires more than just awareness campaigns. It demands a fundamental shift in how organizations approach diversity, inclusion, and gender equality, fostering a sustainable change that benefits both individuals and the field as a whole. This requires long-term strategies, ingrained cultural shifts, and a commitment to continuous improvement. Only through these sustained efforts can we ensure that women have the opportunities they deserve to thrive in STEM.Sustaining progress in promoting gender equality within STEM necessitates a multi-faceted approach.
This involves implementing proactive measures within organizations, from hiring practices to mentorship programs, while consistently evaluating the effectiveness of these initiatives. A commitment to continuous learning and adaptation is crucial to ensuring long-term impact.
Long-Term Strategies for Promoting Gender Equality in STEM
A long-term strategy is vital for achieving meaningful change. It’s not a one-time event but a continuous process of policy implementation, program development, and evaluation. This involves embedding diversity and inclusion into every facet of the organization’s operations, from recruitment to promotion to leadership development.
Integrating Diversity and Inclusion into Organizational Culture, Organizations raise awareness of women in stem
Diversity and inclusion are not just buzzwords; they are integral to fostering an environment where everyone feels valued and respected. This involves reviewing recruitment processes to ensure they are unbiased and attract a diverse pool of candidates. Mentorship programs, designed to support women in their careers, are also critical components. Additionally, the creation of employee resource groups and inclusive leadership training can play a significant role in fostering a sense of belonging and empowering women in leadership positions.
- Bias-free recruitment: Implementing strategies to eliminate unconscious bias in hiring processes, including diverse interview panels and blind resume reviews, can greatly improve the representation of women in STEM fields.
- Mentorship programs: Structured mentorship programs, pairing women with experienced mentors, provide guidance and support throughout their careers. Mentors can offer insights into navigating the professional landscape, providing crucial networking opportunities.
- Inclusive leadership training: Leadership training programs should emphasize inclusive leadership styles, focusing on communication, collaboration, and decision-making strategies that empower all employees.
- Employee resource groups (ERGs): Establishing ERGs dedicated to women in STEM creates a safe space for networking, sharing experiences, and advocating for their needs within the organization.
Continuous Evaluation and Improvement
A sustainable initiative demands ongoing evaluation and improvement. This is not a one-and-done approach. Regular assessments of the effectiveness of implemented programs, tracking key metrics like representation in different roles and levels, are crucial. Collecting feedback from women in STEM is vital for understanding their experiences and tailoring interventions for better outcomes. Data analysis and reporting should be transparent and readily accessible.
Key Elements of a Sustainable STEM Initiative
A successful and sustainable STEM initiative requires a coordinated effort that addresses multiple facets of the organization.
| Category | Key Elements |
|---|---|
| Recruitment & Selection | Bias-free policies, diverse interview panels, blind resume reviews |
| Mentorship & Support | Structured programs, access to experienced mentors, networking opportunities |
| Leadership Development | Inclusive leadership training, sponsorship programs, promotion policies |
| Work Environment | Flexible work arrangements, supportive culture, respectful communication channels |
| Evaluation & Improvement | Regular assessments, data analysis, feedback mechanisms, continuous learning |
Closing Summary
In conclusion, organizations raising awareness of women in STEM are crucial for fostering a more inclusive and equitable future in these fields. The initiatives discussed, from targeted campaigns to mentorship programs, demonstrate a commitment to increasing representation and overcoming systemic barriers. Success stories and the importance of continuous evaluation and improvement underscore the path towards a more diverse and successful STEM community.

