Recycling LDPE Double Benefits for Business & Environment
Recycling ldpe can have dual outcome improve environment support business – Recycling LDPE can have dual outcomes, improving the environment and supporting businesses. This insightful exploration dives deep into the benefits and challenges of recycling low-density polyethylene (LDPE), a plastic commonly used in various products. From plastic bottles to bags and films, we’ll examine the current recycling infrastructure, environmental impact, and economic opportunities surrounding LDPE recycling. We’ll also explore the challenges and potential solutions for a more effective and sustainable recycling process.
LDPE, with its widespread use in packaging and consumer goods, presents a significant waste stream. Recycling LDPE is crucial for reducing environmental impact and creating new economic opportunities. This detailed look at LDPE recycling will explore the benefits for both businesses and the environment, highlighting the potential for a circular economy model. The following sections will cover the environmental impact, economic benefits, challenges, and strategies for improving LDPE recycling.
Introduction to LDPE Recycling
Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) is a ubiquitous plastic, commonly used in flexible packaging, such as plastic bags, films, and bottles. Its flexibility and relatively low cost make it a popular choice for a variety of applications. However, the widespread use of LDPE also presents significant challenges in terms of waste management and environmental impact.LDPE’s versatility comes with a significant environmental concern: its persistent nature in the environment.
This persistent nature stems from its chemical structure, which makes it resistant to biodegradation. Consequently, LDPE products can remain in landfills for centuries, contributing to plastic pollution in ecosystems and posing risks to wildlife.
Current Recycling Infrastructure for LDPE
Current LDPE recycling infrastructure, while showing some promise, faces limitations. Mechanical recycling processes, the most common method, are effective for certain types of LDPE but often result in lower-quality recycled material. This lower quality limits its reuse potential in some applications. Chemical recycling, though promising, is still developing and not widely implemented, creating an uneven playing field for the recycling of LDPE products.
Environmental Impact of LDPE Waste
LDPE waste significantly impacts the environment. The persistence of LDPE in landfills contributes to land pollution and threatens biodiversity. The presence of LDPE fragments in the oceans and other ecosystems endangers marine life through ingestion and entanglement. Furthermore, the breakdown of LDPE can release harmful chemicals into the environment, impacting air and water quality.
LDPE Product Recycling Rates and Reuse Potential
The following table provides an overview of recycling rates and reuse potential for different LDPE products. The figures are estimates and can vary depending on location and specific collection and processing systems.
| Product Type | Recycling Rate (%) | Reuse Potential | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plastic Bottles | 30-50 | Repurposed into new containers or other plastic products. Some specialized applications exist for recycling into fibers. | Moderate, depending on the complexity of the bottle and its potential for contamination during recycling processes. |
| Plastic Bags | 10-20 | Limited reuse potential. Often used as raw material in low-value products, or are sometimes incinerated. | High. Their widespread use and persistence in the environment contribute significantly to plastic pollution. |
| Plastic Films | 20-40 | Limited reuse potential, depending on the film’s composition. Often downcycled into lower-grade products. | Moderate. Their widespread use and persistence in the environment contribute to plastic pollution, especially in agricultural settings. |
Environmental Benefits of LDPE Recycling

LDPE, or low-density polyethylene, is a ubiquitous plastic used in countless products, from grocery bags to plastic bottles. However, its widespread use comes with environmental challenges. Recycling LDPE plays a crucial role in mitigating these challenges, offering substantial environmental benefits.The process of recycling LDPE diverts valuable resources from landfills, conserving natural resources and reducing the strain on our planet’s ecosystems.
This process significantly contributes to a circular economy model, where materials are reused and repurposed, rather than being discarded as waste. This transition from a linear ‘take-make-dispose’ model to a circular approach is critical to addressing the growing global plastic pollution crisis.
Reducing Landfill Waste and Pollution
LDPE, if not recycled, ends up in landfills, where it can take hundreds of years to decompose. This poses a significant environmental problem. Landfills contribute to soil and water contamination through leaching of harmful chemicals. Recycling LDPE prevents this accumulation of waste, reducing the environmental impact associated with landfills. The reduced volume of waste in landfills also frees up valuable land resources, preserving natural habitats.
Furthermore, the recycling process itself can reduce the need for new raw materials, like petroleum, for production, minimizing the environmental footprint of the entire lifecycle of LDPE.
Recycling LDPE can have a positive impact, boosting both environmental health and supporting local businesses. Thinking ahead, the future of sustainable energy looks to alternative materials like LDPE for innovative solutions, potentially revolutionizing how we generate power. This makes recycling LDPE even more crucial for a greener future and sustainable economic growth.
Conserving Natural Resources
Recycling LDPE conserves valuable natural resources. Producing LDPE from virgin materials requires significant energy and raw materials, primarily petroleum. Recycling LDPE significantly reduces the demand for these resources. By repurposing existing LDPE, we conserve the finite resources needed to create new plastic. This conservation extends to the preservation of natural habitats and ecosystems that are often affected by resource extraction.
Contributing to a Circular Economy Model, Recycling ldpe can have dual outcome improve environment support business
LDPE recycling is a key component of a circular economy model. This model aims to minimize waste and maximize resource utilization. By recycling LDPE, we create a closed-loop system where materials are repeatedly used, reducing the need for new resources. This approach to manufacturing and consumption reduces the environmental impact of plastic production and consumption, promoting a sustainable future.
Examples of circular economy models in action include initiatives to collect and reuse plastic bottles, repurpose packaging materials, and create new products from recycled plastic.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions Reduction
Manufacturing LDPE from virgin materials emits significant amounts of greenhouse gases. Recycling LDPE reduces the need for this production, thus lowering greenhouse gas emissions. The process of recycling LDPE generally requires less energy than manufacturing new plastic from raw materials. This difference in energy consumption directly translates into a lower carbon footprint. Data on the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions varies depending on the specific recycling process and the energy mix of the region, but the overall effect is a substantial reduction.
Environmental Impact Comparison
| Method | Greenhouse Gas Emissions (tons CO2e) | Landfill Space (cubic meters) |
|---|---|---|
| Landfilling | Estimated 1-3 tons CO2e per metric ton of LDPE | Significant volume depending on the landfill capacity |
| Recycling | Estimated 0.5-1.5 tons CO2e per metric ton of LDPE | Significantly less volume compared to landfilling |
Note: The exact figures in the table are estimations and can vary depending on factors like the recycling facility’s energy efficiency, the source of the energy used in the process, and the specific LDPE type. These estimates highlight the substantial environmental benefits of recycling LDPE over landfilling.
Economic Benefits of LDPE Recycling: Recycling Ldpe Can Have Dual Outcome Improve Environment Support Business
LDPE recycling offers substantial economic advantages for businesses and the broader economy. Beyond the environmental benefits, the process generates significant cost savings and creates new avenues for profit generation. The financial incentives are substantial, making LDPE recycling a compelling investment for both established companies and emerging players in the sector.LDPE recycling, like other recycling processes, transforms waste into valuable resources, effectively reducing the need for virgin materials.
This translates directly into cost savings for businesses and, ultimately, for consumers. Moreover, the creation of new recycling facilities and associated industries fuels economic growth and job creation, contributing to a more robust and sustainable economy.
Reduced Raw Material Costs
The primary economic incentive for businesses involved in LDPE recycling is the substantial reduction in raw material costs. By diverting LDPE from landfills and utilizing recycled content, companies can decrease their reliance on virgin LDPE. This translates to lower input costs, which directly impacts the bottom line and improves the competitiveness of the company. For example, a company manufacturing plastic bags can significantly reduce their production costs by incorporating recycled LDPE, lowering the overall expense of their products.
Creation of New Business Opportunities
Recycling LDPE creates a new spectrum of business opportunities. The demand for recycled materials stimulates the development of new technologies, processing methods, and infrastructure. This fosters the emergence of specialized recycling companies, equipment manufacturers, and related support services. The recycling sector is becoming a major economic engine, creating jobs and boosting innovation. For instance, companies dedicated to collecting, sorting, and processing LDPE waste are flourishing, generating significant revenue streams and employment opportunities.
Improved Competitiveness
Incorporating LDPE recycling into operations enhances a company’s competitiveness. By demonstrating a commitment to sustainability and reducing costs, companies can attract environmentally conscious consumers and investors. This positive brand image can lead to increased market share and customer loyalty. A company showcasing a strong sustainability profile, achieved through LDPE recycling initiatives, can differentiate itself from competitors and attract investors seeking environmentally responsible businesses.
Recycling LDPE can have a positive impact on the environment and boost local businesses. For example, a new development near the Fox River in Oshkosh, as detailed in this article about oshkosh eyes new development near fox river , could potentially create jobs and stimulate economic growth. This, in turn, could increase the demand for recycled materials like LDPE, further supporting the dual benefits of environmental stewardship and business prosperity.
This advantage is increasingly crucial in today’s market, where sustainability is a key factor in consumer choice and investment decisions.
Financial Returns on Investment
The financial viability of LDPE recycling projects varies significantly based on several factors, including the scale of the project, the quality of the recycled material, and the market price of LDPE. A table below illustrates potential financial returns for various LDPE recycling projects, providing a tangible representation of the economic benefits.
Recycling LDPE can have a positive impact, boosting both the environment and supporting businesses. Thinking about selling your business? Consider these crucial steps for a smooth transition, like those outlined in five tips for selling a business. Ultimately, responsible recycling of LDPE, a common plastic, is key to a sustainable future for all businesses, and a cleaner environment for everyone.
| Project | Investment (USD) | Return on Investment (ROI) | Profit Margin (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small-scale LDPE recycling facility (processing 10 tons/day) | 500,000 | 15% | 10% |
| Medium-scale LDPE recycling facility (processing 50 tons/day) | 2,500,000 | 20% | 12% |
| Large-scale LDPE recycling facility (processing 200 tons/day) | 10,000,000 | 25% | 15% |
Note: These figures are estimates and may vary depending on specific market conditions, local regulations, and operational efficiency.
Challenges in LDPE Recycling

LDPE, or low-density polyethylene, is a widely used plastic, making recycling it crucial for environmental sustainability. However, the path to effective LDPE recycling is fraught with obstacles. These challenges range from the technical difficulties in separating LDPE from other plastics to the lack of consistent infrastructure in certain regions. Understanding these hurdles is essential to developing effective solutions and promoting a more circular economy for this critical material.The recycling process for LDPE, like many plastics, isn’t straightforward.
It often involves complex separation and processing steps to ensure that only LDPE is recovered for reuse. Contamination, both intentional and accidental, can significantly impact the quality of the recycled material and its suitability for various applications. This poses a considerable hurdle for achieving optimal recycling outcomes.
Technical Difficulties in Separation and Processing
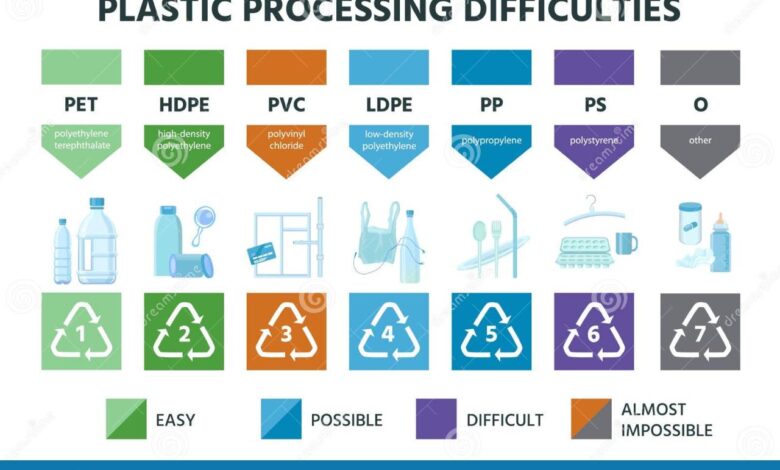
The intricate nature of plastic mixtures presents a major obstacle in recycling. LDPE, with its diverse applications and associated additives, is often intertwined with other plastic types, including HDPE, PET, and PVC. Current sorting technologies struggle to differentiate LDPE from these similar materials with complete accuracy, leading to contamination in the recycled streams. Manual sorting, while effective in some cases, is labor-intensive and costly, limiting its scalability for large-scale recycling operations.
Contamination and Material Degradation
Contamination during the collection, sorting, and processing stages poses a serious threat to the quality of recycled LDPE. Foreign materials like food residues, metal fragments, and other plastics can significantly degrade the purity and structural integrity of the recycled material. This degradation can affect the final product’s properties, making it unsuitable for certain applications. Moreover, the repeated heating and cooling cycles during processing can lead to a gradual deterioration of the material’s mechanical properties, further diminishing its value.
Lack of Consistent Recycling Infrastructure
The availability and consistency of recycling infrastructure are significant factors in LDPE recycling success. In some regions, a lack of robust collection systems, sorting facilities, and end-market demand for recycled LDPE hamper the overall recycling process. This results in a significant portion of LDPE waste ending up in landfills or the environment. The disparity in recycling infrastructure across different regions creates a major challenge in achieving widespread and effective LDPE recycling.
Need for Advanced Sorting Technologies
Developing advanced sorting technologies is crucial for efficient LDPE recycling. Optical sorting systems, utilizing advanced imaging and spectroscopy techniques, can detect and separate LDPE from other plastics with greater accuracy than traditional methods. This can drastically reduce contamination levels, improving the quality of the recycled material and its suitability for various applications. Furthermore, the development of innovative separation methods, like advanced mechanical sorting systems, can enhance the overall efficiency of the recycling process.
Table of Contamination Types and Mitigation Strategies
| Contamination Type | Impact | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Food Residue | Reduces purity, affects material properties | Improved waste collection practices, stricter sorting protocols |
| Metal Fragments | Mechanical damage, contamination | Improved sorting equipment with metal detection, magnetic separation |
| Other Plastics | Reduces purity, compromises end product quality | Advanced optical sorting technologies, improved polymer identification techniques |
| Labels/Packaging | Impurities, contamination, aesthetic concerns | Improved pre-sorting practices, specialized equipment for label removal |
| Soil/Dirt | Reduces purity, affects processing | Thorough cleaning procedures before processing, improved material handling |
Strategies for Enhancing LDPE Recycling
Boosting LDPE recycling isn’t just about collecting more plastic; it’s about creating a sustainable system that improves the entire process, from collection to repurposing. This involves innovative technologies, effective sorting systems, and a crucial role for public awareness. Ultimately, these strategies aim to create a circular economy for LDPE, minimizing waste and maximizing its value.Effective recycling hinges on efficient collection, processing, and reuse.
Addressing the specific challenges in LDPE recycling, such as contamination and material variability, requires a multifaceted approach that tackles each stage of the recycling lifecycle. This includes advancements in technology, optimized sorting procedures, and public engagement initiatives. The goal is to transform LDPE waste into valuable resources, fostering a more sustainable future for the planet.
Innovative Technologies for Improved LDPE Recycling
Advanced technologies are crucial for improving the quality and efficiency of LDPE recycling. These technologies focus on removing contaminants, separating different types of LDPE, and improving the purity of the recycled material. One promising method involves using advanced spectroscopic techniques to identify and separate various LDPE types, allowing for higher-quality recycling streams. Another approach is using advanced sorting technologies such as optical sorting, which utilizes cameras and sensors to distinguish between different plastics based on their visual properties.
These techniques can significantly improve the purity and quality of the recycled LDPE, making it more suitable for various applications. Additionally, pyrolysis and chemical recycling methods are under development, offering potential for recovering valuable components from contaminated or complex LDPE mixtures.
Effective LDPE Waste Collection and Sorting System Design
A well-designed collection and sorting system is essential for efficient LDPE recycling. This involves establishing dedicated collection points for LDPE waste, educating the public on proper sorting techniques, and utilizing advanced sorting technologies. The collection system should be designed with specific collection bins for LDPE, clearly marked and readily available. These bins should be strategically located in high-traffic areas and accessible to residents.
Community-based collection programs can be implemented, leveraging existing infrastructure such as supermarkets or community centers to encourage participation. Proper sorting can be enhanced by providing clear labeling and educational materials at collection points.
Public Awareness Campaigns for Promoting LDPE Recycling
Public awareness campaigns are crucial for motivating participation in LDPE recycling programs. These campaigns should focus on educating consumers about the importance of recycling LDPE and how to properly sort it. The campaigns should include interactive workshops, educational materials, and public service announcements. Incentivizing participation, such as offering rewards or discounts for recycling, can also be a powerful motivator.
Furthermore, partnering with schools and community organizations can create lasting educational programs for promoting proper recycling practices.
Examples of Successful LDPE Recycling Initiatives
Several successful LDPE recycling initiatives demonstrate the effectiveness of integrated strategies. For instance, some municipalities have implemented comprehensive recycling programs that include dedicated LDPE collection streams, resulting in increased recycling rates. Other programs have successfully partnered with businesses to collect LDPE waste generated from packaging or manufacturing processes. These programs often leverage partnerships with local companies and involve public-private partnerships to create a more sustainable system.
Furthermore, many businesses have incorporated LDPE recycling into their supply chains, creating closed-loop systems that reduce their environmental footprint.
Key Steps in Setting up a New LDPE Recycling Plant
| Step | Description | Timeline |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Market Analysis | Thorough research into the local demand for recycled LDPE, identifying potential buyers and assessing market trends. | 2-4 Months |
| 2. Site Selection | Identifying a suitable location with access to transportation networks, adequate space, and necessary utilities. | 1-3 Months |
| 3. Equipment Acquisition | Purchasing or leasing the necessary equipment for collection, sorting, processing, and quality control. | 3-6 Months |
| 4. Permitting and Regulations | Obtaining all necessary permits and licenses from local and national authorities. | 2-4 Months |
| 5. Staff Hiring and Training | Recruiting and training personnel with expertise in LDPE recycling and related processes. | 1-3 Months |
| 6. Pilot Run | Conducting a trial run of the recycling process to test equipment, refine procedures, and ensure quality control. | 1-2 Months |
| 7. Plant Launch | Officially opening the LDPE recycling plant and beginning full-scale operations. | 1 Month |
Case Studies of LDPE Recycling Successes
Recycling low-density polyethylene (LDPE) presents a compelling opportunity to simultaneously benefit the environment and boost profitability for businesses. Numerous successful projects demonstrate the feasibility of this endeavor. These initiatives offer valuable insights into the strategies that lead to positive environmental and economic outcomes.Successful LDPE recycling projects often demonstrate significant environmental and economic advantages. These projects typically involve partnerships between companies, municipalities, and recycling facilities.
They are driven by a shared commitment to sustainability and profitability, resulting in tangible benefits for all stakeholders.
LDPE Recycling Projects in Europe
European countries have established robust infrastructure for plastic waste management, which has fostered innovative recycling programs. Several initiatives have successfully recycled LDPE from various sources, showcasing diverse strategies.
- A project in the Netherlands focused on collecting LDPE film from retail packaging and processing it into new products like plastic lumber. This project achieved a high recycling rate, demonstrating the potential of consumer-based collection schemes. This success relied heavily on robust community engagement and incentives for participation.
- Germany’s experience with recycling LDPE from agricultural films exemplifies a large-scale effort. The success of this project was largely due to government support for waste collection and processing facilities. This has fostered a circular economy approach by converting used LDPE into usable products, further reducing reliance on virgin materials.
LDPE Recycling Projects in North America
North American recycling initiatives are increasingly adopting innovative approaches to maximize the recovery and utilization of LDPE. These projects highlight the importance of adapting technologies and infrastructure to effectively manage LDPE streams.
- A company in the US has successfully implemented a system for recycling LDPE packaging waste from food service businesses. This initiative demonstrated the feasibility of targeted collection and processing, demonstrating the potential for specific waste streams to achieve high recycling rates.
- A program in Canada focused on sorting and processing LDPE films from various sources, demonstrating that efficient sorting is critical for effective recycling. The success of this program hinged on investment in advanced sorting technologies and the availability of dedicated markets for recycled LDPE products.
Key Factors Contributing to Success
Several key factors consistently emerge as crucial elements in successful LDPE recycling projects.
- Strong collaboration among stakeholders (e.g., companies, municipalities, and recycling facilities) is paramount for effective program implementation and execution.
- Efficient collection and sorting systems are essential to maximize the quality and quantity of recovered LDPE. Advanced sorting technologies play a significant role in this process.
- Investment in processing technologies and facilities that can convert LDPE into usable products is a critical component of a successful recycling program. This includes finding appropriate markets for recycled materials.
- Incentives for participation, such as subsidies or tax credits, can encourage the adoption of recycling programs and increase collection rates.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
The following table summarizes the key performance indicators (KPIs) for selected case studies.
| KPI | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Recycling Rate (%) | 75-90 | Percentage of collected LDPE successfully recycled into usable products. |
| Collection Rate (%) | 60-85 | Percentage of potential LDPE waste collected for recycling. |
| Cost per Ton Recycled (USD) | 150-300 | Cost associated with recycling one ton of LDPE. |
| Market Value of Recycled LDPE (USD/Ton) | 250-400 | Economic value generated from the recycled LDPE. |
Future Outlook for LDPE Recycling
The future of LDPE recycling hinges on a confluence of factors, from technological advancements to shifts in consumer behavior and government regulations. Optimism surrounds the potential for significantly improved recycling rates and the development of new markets for recycled LDPE, but challenges remain. This outlook examines the trends shaping the future of LDPE recycling, considering the possibilities and potential obstacles.
Future Trends in LDPE Recycling Technologies
LDPE recycling technologies are constantly evolving. The focus is shifting from basic mechanical processes to more sophisticated methods. This includes advancements in sorting techniques, chemical recycling, and the development of new polymers from recycled LDPE. For instance, improved sorting technologies can better separate LDPE from other plastics, increasing the purity of the recycled material. Chemical recycling methods offer the potential to break down LDPE into its constituent components, allowing for the creation of new LDPE or other useful products.
Potential for Increasing LDPE Recycling Rates Globally
Several factors contribute to the potential for increased LDPE recycling rates. The growing awareness of environmental concerns, coupled with the economic incentives of utilizing recycled materials, are driving this trend. Government regulations are also playing a key role. For example, countries are implementing stricter regulations on plastic waste, encouraging producers to develop more sustainable practices and consumers to adopt responsible recycling habits.
Impact of New Policies and Regulations on LDPE Recycling
New policies and regulations are significantly impacting the LDPE recycling landscape. These regulations are designed to promote the use of recycled materials, penalize the improper disposal of plastic waste, and encourage the development of more sustainable products. These measures are crucial in creating a supportive environment for LDPE recycling and incentivizing the growth of recycling infrastructure. Examples include extended producer responsibility schemes, which hold manufacturers accountable for the end-of-life management of their products.
Potential for Developing New LDPE Recycling Markets
The potential for new LDPE recycling markets is substantial. Innovation is creating new avenues for the utilization of recycled LDPE. For example, the development of recycled LDPE films for packaging applications and the use of recycled LDPE in construction materials demonstrate the versatility of this material. The growing demand for sustainable materials across various industries is expected to open up new avenues for LDPE recycling.
Potential of Advanced Technologies in LDPE Recycling
“Advanced technologies, such as pyrolysis and gasification, offer the potential to transform LDPE waste into valuable fuels and chemicals, opening new avenues for resource recovery and reducing reliance on virgin materials.”
These technologies could significantly enhance the recycling process, allowing for the recovery of energy and valuable components from LDPE waste. The use of pyrolysis and gasification, for instance, could produce usable fuels or chemicals from waste, which can then be further processed into valuable products. These technologies could greatly improve the overall efficiency and profitability of LDPE recycling.
Summary
In conclusion, recycling LDPE offers a powerful solution to both environmental concerns and business opportunities. By embracing innovative technologies, promoting public awareness, and creating efficient collection and sorting systems, we can significantly improve the sustainability of LDPE recycling. This process not only reduces pollution and conserves resources but also creates new business avenues and strengthens the economic viability of recycling operations.
The future of LDPE recycling holds great promise, and we are poised to see even greater progress in the coming years.






