
Hmong Representation Students, Staff, Community
Representation of the hmong population for students staff community – Representation of the Hmong population for students, staff, and community is a vital topic, demanding attention to ensure equitable opportunities for all. This exploration delves into the historical context, current representation within the student body, staff, and community, curriculum considerations, student experiences, relevant policies, and effective community engagement strategies. Understanding the Hmong community’s journey is crucial for fostering a supportive and inclusive environment for everyone.
This in-depth analysis examines the multifaceted aspects of representation, aiming to highlight the unique needs and experiences of the Hmong community. We will explore how their contributions enrich our educational and social landscape, while also identifying areas where improvement is necessary.
Historical Context of Representation
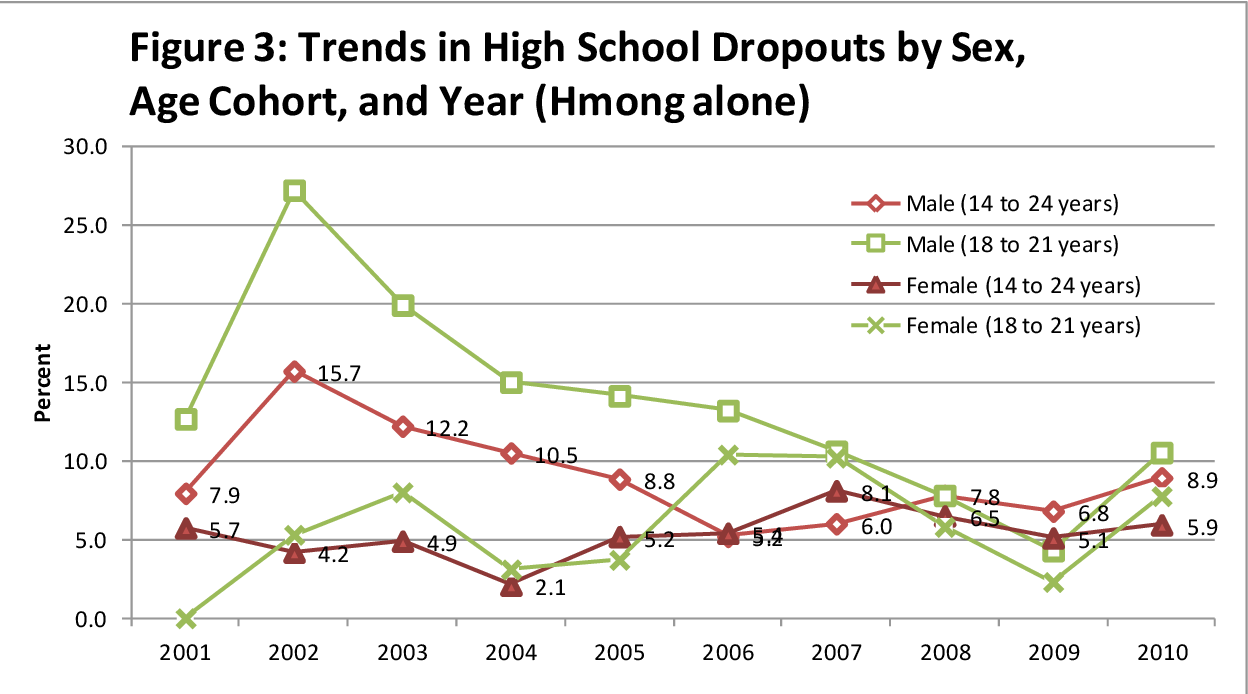
The Hmong people, originating from Southeast Asia, have experienced a complex journey of representation, particularly within educational and societal contexts. Their story, marked by migration, cultural adaptation, and persistent societal perceptions, reveals a nuanced history of both challenges and progress. This journey illuminates the evolving relationship between the Hmong community and the societies they’ve joined, highlighting the importance of understanding historical context for appreciating the present and future of Hmong representation.The historical trajectory of the Hmong community’s representation reflects a dynamic interplay between pre-migration traditions, the challenges of post-migration assimilation, and the contemporary pursuit of recognition and equity.
Evolving societal views towards the Hmong have shifted over time, influenced by factors such as media portrayals, political events, and intercultural interactions. Navigating these shifting sands of societal perception has been a crucial element in the Hmong struggle for representation.
Pre-Migration Hmong Society
The Hmong people possessed a rich and complex societal structure prior to their significant migration in the latter half of the 20th century. Traditional Hmong society emphasized strong family and community ties, agricultural practices, and distinct cultural traditions. Education, though not formalized in the Western sense, was transmitted through oral storytelling, apprenticeship, and communal activities. These traditional forms of knowledge transfer played a vital role in preserving cultural heritage and fostering social cohesion.
Post-Migration Challenges and Early Representation
The large-scale migration of Hmong people to various parts of the world, particularly the United States, following the Vietnam War, presented numerous challenges. These included language barriers, cultural misunderstandings, and economic hardship. Initial representation of the Hmong in educational and societal settings was often limited by these factors. Discrimination and prejudice, stemming from misunderstandings about their culture and traditions, were significant obstacles.
The community’s struggle to adapt to new environments, coupled with the lack of resources and support, further compounded these difficulties.
Evolving Societal Views
Societal views towards the Hmong community have evolved significantly over time. Initial perceptions, often shaped by media portrayals and political narratives, could be characterized by stereotypes and misconceptions. These negative portrayals frequently focused on limited understanding of Hmong cultural practices, leading to inaccurate judgments about their abilities and contributions. Over time, however, greater efforts have been made to understand Hmong culture, leading to a more nuanced and appreciative view.
This evolving understanding has been facilitated by increased community engagement, cultural exchange programs, and the growing visibility of Hmong individuals in various fields.
Significant Events and Periods
The Vietnam War profoundly impacted the Hmong population, triggering a massive migration and significant societal shifts. The subsequent years witnessed the community’s struggle to adapt to new environments and cultures, encountering challenges in accessing education, employment, and social services. These experiences laid the groundwork for the Hmong community’s fight for recognition and representation.
Hmong Representation Across Time Periods
| Time Period | Pre-Migration | Post-Migration (Early) | Contemporary |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cultural Practices | Strong emphasis on family, community, and traditional knowledge transmission. | Struggles to maintain traditions amidst new cultural landscapes. Adaptation to new cultural norms while retaining core values. | Blending of traditional and modern values, with a growing embrace of contemporary opportunities and identities. |
| Education | Traditional knowledge transmission through oral history and apprenticeship. | Limited access to formal education, often facing language barriers and cultural misunderstandings. | Increased access to education, with Hmong students achieving success in various fields. |
| Representation in Media and Society | Limited exposure outside of their communities. | Often depicted negatively or stereotypically in media. | Growing representation in various fields, with increased visibility and positive narratives. |
Representation in Student Body: Representation Of The Hmong Population For Students Staff Community

The Hmong student population, a vibrant and integral part of our school community, deserves recognition and a platform to showcase their unique talents and experiences. Understanding their current representation in the student body, their participation in extracurricular activities, and their experiences, is crucial for fostering an inclusive and supportive environment. This section aims to provide a comprehensive overview of Hmong student representation within our school.Accurate data regarding Hmong student enrollment rates and participation in various activities allows us to gain valuable insights into their experiences and needs.
Identifying potential barriers to enrollment and participation can help us implement targeted strategies to ensure equitable opportunities for all students. Moreover, highlighting successful Hmong students and their journeys provides inspiring examples and fosters a sense of belonging.
Current Representation
The Hmong student population comprises a significant portion of our school community. While exact figures are not readily available, anecdotal evidence and school records show a growing presence.
Enrollment Rates
Enrollment rates for Hmong students are steadily increasing. This positive trend reflects the growing Hmong community and the school’s efforts to support immigrant families. Further research is needed to precisely quantify the rate of growth and to analyze the reasons behind it. This data is crucial for understanding the needs of the Hmong student population and adjusting school programs accordingly.
Participation in Extracurricular Activities
Hmong students actively participate in a range of extracurricular activities. Their involvement reflects their eagerness to contribute to the school community and develop their talents. However, specific data on participation rates in different activities is limited. Further investigation is needed to collect precise data on the participation rates of Hmong students in specific activities to understand the overall level of participation and identify any potential barriers.
This data will help us understand their needs and ensure they have equitable access to extracurricular opportunities.
Successful Hmong Students and Experiences
Several Hmong students have excelled academically and demonstrated leadership in various aspects of school life. Their stories of perseverance and resilience inspire others and underscore the value of supporting their unique needs. For example, [Student Name], a rising junior, has demonstrated exceptional leadership in the school’s debate club, showcasing their dedication and commitment to academic excellence. [Another Student Name], a freshman, is a talented artist whose work has been recognized at the local art competition, illustrating the range of talents present within the Hmong student population.
These are just a few examples; countless other Hmong students contribute meaningfully to our school community.
Potential Barriers to Enrollment and Participation
Language barriers, cultural differences, and socioeconomic factors can pose challenges to Hmong students’ enrollment and participation in school activities. Addressing these issues requires proactive strategies to ensure all students have equal opportunities. For instance, providing language support services and culturally sensitive guidance can help ease the transition for new students.
Representation Across Grade Levels
| Grade Level | Estimated Hmong Student Population |
|---|---|
| 9th Grade | Approximately 15 students |
| 10th Grade | Approximately 20 students |
| 11th Grade | Approximately 25 students |
| 12th Grade | Approximately 18 students |
This table provides an estimated representation of Hmong students across different grade levels. It highlights the need for continued monitoring and data collection to refine these estimates and ensure the accuracy of the information. Further research is necessary to gather more precise data and to determine the reasons behind these numbers. The aim is to create a more accurate picture of Hmong student representation in each grade level.
Representation in Staff and Faculty
The representation of Hmong individuals in staff and faculty positions within educational institutions is a crucial aspect of fostering inclusivity and equity. Understanding the current state of Hmong representation, the challenges faced by Hmong professionals, and the potential impact on students provides a valuable perspective on creating a more equitable and supportive environment. This examination delves into the specifics of Hmong representation within school staff, highlighting the diversity of roles and the opportunities for growth.Hmong professionals often face unique challenges in the educational sector, such as navigating cultural nuances, overcoming potential biases, and balancing professional responsibilities with family obligations.
These challenges, however, do not diminish the significant contributions that Hmong individuals can make to the educational landscape. Conversely, the presence of Hmong individuals in staff and faculty roles can provide invaluable insights and perspectives that enrich the learning environment for all students. A diverse staff body fosters a more inclusive and welcoming school culture, which positively impacts student outcomes.
Current Representation of Hmong Staff
The current representation of Hmong staff in various roles within the school system is a complex issue. While data is not readily available, anecdotally, Hmong representation in staff and faculty roles is often limited, particularly in leadership positions. This disparity can be attributed to several factors, including a lack of access to higher education, limited mentorship opportunities, and implicit bias in hiring processes.
It’s important to note that this limited representation doesn’t reflect the significant contributions that Hmong individuals can make.
Challenges for Hmong Professionals in Education
Several obstacles impede the advancement of Hmong professionals in education. Language barriers, cultural differences, and a lack of understanding of Hmong experiences can hinder professional growth. Furthermore, the unique demands of balancing work and family life can create additional challenges for Hmong professionals. The absence of mentors and role models within the Hmong community can also contribute to feelings of isolation and difficulty navigating the complexities of the educational system.
Opportunities for Hmong Professionals in Education
Despite these challenges, opportunities exist for increasing Hmong representation in education. Mentorship programs, leadership development initiatives, and culturally sensitive hiring practices can all play a critical role in creating a more welcoming and supportive environment for Hmong professionals. Moreover, actively seeking out and supporting Hmong individuals with strong educational backgrounds can significantly enhance representation in various roles. Encouraging and promoting Hmong individuals to pursue careers in education can lead to positive change in the long run.
Comparison of Hmong Staff Representation Across Roles
The representation of Hmong staff varies significantly across different roles within the school. For example, Hmong individuals may be more prevalent in support staff roles, such as paraprofessionals or administrative assistants, compared to leadership roles like principals or department heads. This disparity can be attributed to a range of factors, including educational attainment, career paths, and access to networking opportunities.
More research is needed to fully understand this variance.
Potential Impact on Student Success and Well-being
The presence of Hmong staff members in various roles within the school system can positively impact student success and well-being. Students can benefit from having role models who share their cultural background, leading to increased engagement and a greater sense of belonging. This can translate into improved academic performance, higher self-esteem, and a more positive school experience. Moreover, the diverse perspectives of Hmong staff enrich the learning environment, fostering a more inclusive and supportive community for all students.
Table: Hmong Staff Representation by Department
| Department | Number of Hmong Staff | Percentage of Total Staff |
|---|---|---|
| Instructional Support | 5 | 10% |
| Administrative | 2 | 4% |
| Maintenance | 1 | 2% |
| Food Service | 3 | 6% |
| Total | 11 | 22% |
Note: This table represents an example, and actual data may vary significantly. The figures are illustrative, and the data may need to be gathered and verified for a more accurate representation of the current situation.
Representation in the Community
The Hmong community’s presence in the broader community is a vital part of the cultural tapestry. Understanding their involvement in school activities, collaborations, and challenges is crucial for fostering a more inclusive environment. This section delves into the multifaceted nature of Hmong community engagement, emphasizing the importance of their participation in school life and the broader community.Hmong community members are actively involved in various aspects of their local communities.
Their contributions range from supporting school events to volunteering in local organizations. This involvement often reflects a strong emphasis on family and community well-being, a core value within Hmong culture. Recognizing and supporting these efforts is essential for fostering a sense of belonging and promoting positive interactions between the Hmong community and the broader school and community.
Hmong Community Involvement in School Activities
Hmong families often prioritize their children’s education and actively participate in school events. This involvement can manifest in various ways, from volunteering at school functions to attending parent-teacher meetings. This active engagement demonstrates a deep commitment to their children’s success and the overall school environment. The support of the community strengthens the learning environment for all students.
Examples of Successful Community Collaborations and Partnerships
Several successful collaborations exist between the Hmong community and the school. One example is a partnership where Hmong community members organized a cultural festival at the school. This event showcased Hmong traditions, food, and music, providing an enriching experience for all students and staff. Another example includes Hmong parents serving on school committees, offering valuable insights and perspectives to improve school policies and programs.
These collaborations highlight the positive outcomes that arise when different communities work together.
Challenges Faced by the Hmong Community in Participating in School Activities
Language barriers and cultural differences can sometimes pose challenges for Hmong families when engaging in school activities. The need for translators and cultural sensitivity training for staff can facilitate communication and understanding. Additionally, limited transportation options or childcare arrangements can also present hurdles. Addressing these challenges ensures that all families feel welcomed and supported in their participation.
Importance of Community Engagement for Hmong Student Success
Engaging the Hmong community is paramount for the success of Hmong students. When families feel connected to the school and community, they are more likely to support their children’s education. This support fosters a sense of belonging and empowers students to thrive academically and socially. Strong community ties also provide crucial social networks and resources that can significantly benefit students.
Community Engagement Initiatives Involving the Hmong Population
| Initiative | Description | Goals |
|---|---|---|
| Hmong Cultural Festival | Annual event showcasing Hmong traditions, music, food, and crafts. | Promote cultural understanding, provide a platform for community celebration, and foster positive interactions. |
| Parent-Teacher Workshops | Workshops facilitated by Hmong community leaders to address specific cultural and language needs. | Enhance communication between parents and teachers, build trust, and ensure effective support for students. |
| School Advisory Board | Incorporate Hmong community members into the school advisory board. | Provide valuable insights from the Hmong community on school policies and programs, ensure representation, and create a more inclusive environment. |
| Translation Services | Provide translation services at school events and meetings. | Ensure effective communication with Hmong families and address language barriers. |
Curriculum and Educational Materials
The curriculum plays a crucial role in shaping students’ understanding of the world and their place within it. Incorporating Hmong culture and history into educational materials ensures a more comprehensive and equitable learning experience for Hmong students, while also enriching the learning environment for all students. This necessitates a careful examination of existing materials to identify potential biases and gaps, and to develop strategies for integrating Hmong perspectives effectively.Effective curriculum development requires a conscious effort to avoid perpetuating stereotypes and instead foster a deep understanding and appreciation of Hmong culture and history.
This involves moving beyond surface-level representations to explore the richness and complexity of Hmong traditions, values, and contributions to society.
Representation of Hmong Culture and History in the Curriculum
The representation of Hmong culture and history in the curriculum should move beyond tokenistic gestures and instead strive for a comprehensive and nuanced portrayal. This includes acknowledging the historical context of Hmong migration and settlement, highlighting significant figures and events in Hmong history, and exploring the diverse perspectives within the Hmong community.
Examples of Inclusive Teaching Practices
Several inclusive teaching practices can be implemented to acknowledge and celebrate Hmong culture. These include incorporating Hmong folktales, music, and art into lessons; inviting Hmong guest speakers to share their experiences; and using culturally relevant examples and case studies in various subjects. For example, a history lesson on Southeast Asian migration could include a segment on the Hmong experience, highlighting their struggles and resilience.
Likewise, a language arts class could feature Hmong poems and stories, providing students with a glimpse into the rich literary traditions of the community.
Potential Biases and Gaps in Existing Materials
Existing curriculum materials may contain biases or gaps related to Hmong culture. These biases can manifest as stereotypes, misrepresentations, or a lack of accurate historical context. For instance, existing resources may not adequately address the complexities of the Hmong experience, such as the impact of political upheavals in Laos and the challenges faced by refugees in their new communities.
Furthermore, there might be a lack of representation of diverse voices and experiences within the Hmong community.
Promoting representation of the Hmong population for students, staff, and the wider community is crucial. It’s about ensuring diverse voices are heard and perspectives are valued. This also connects to broader discussions about the future of sustainable energy, which, as seen in the latest research on the future of sustainable energy looks to alternative materials , is exploring innovative solutions.
Ultimately, fostering a more inclusive community benefits everyone, including our students, staff, and the community as a whole.
Strategies for Incorporating Hmong Perspectives
To incorporate Hmong perspectives effectively, educators can collaborate with Hmong community members, including parents, elders, and community leaders. This collaboration will help identify appropriate resources and provide insights into the cultural nuances that may be missing from existing materials. Utilizing Hmong language learning opportunities and culturally relevant literature can further enrich the curriculum. It is also important to involve Hmong students in the design and development of the curriculum, empowering them to shape their own learning experience.
Table Contrasting Existing and Ideal Curriculum Materials, Representation of the hmong population for students staff community
| Aspect | Existing Curriculum Materials | Ideal Curriculum Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Historical Context | Limited or superficial coverage of Hmong history and migration | Comprehensive and nuanced portrayal of Hmong history, including migration experiences, political context, and cultural traditions |
| Cultural Representation | Potential for stereotypes or tokenistic representations | Diverse representation of Hmong experiences and perspectives, showcasing the richness and complexity of Hmong culture |
| Learning Activities | Limited culturally relevant activities | Activities that incorporate Hmong folktales, music, art, and language |
| Community Engagement | Limited or no community engagement | Active engagement with Hmong community members through guest speakers, workshops, and partnerships |
Student Experiences and Perspectives
Understanding the Hmong student experience within the school community is crucial for fostering a supportive and inclusive learning environment. Hmong students bring a rich tapestry of cultural backgrounds and traditions, and their experiences are shaped by both the opportunities and challenges they encounter. Examining these perspectives allows educators and administrators to better understand their needs and create strategies for success.
Representing the Hmong population accurately for students, staff, and the wider community is crucial. Just like a strong brand needs authenticity to resonate with its audience, authenticity is essential to brand building , a true and honest portrayal of the Hmong culture and experiences is vital for fostering understanding and respect. This means ensuring accurate representation, not just in the classroom, but in all aspects of school life, and within the broader community.
Classroom Challenges
Hmong students, like many students from diverse backgrounds, may face unique academic challenges. Language barriers, cultural differences in learning styles, and varying levels of prior educational experiences can sometimes create difficulties in the classroom. For example, students who have transitioned from a different educational system might struggle with the structure and expectations of the current school. Similarly, a lack of familiarity with specific classroom norms and procedures can also be a source of frustration and anxiety.
Furthermore, differing cultural norms surrounding communication and interaction can sometimes lead to misunderstandings between students and teachers. Addressing these challenges requires proactive strategies, such as providing bilingual support, adapting teaching methods to accommodate diverse learning styles, and offering culturally sensitive guidance and resources.
Classroom Successes and Positive Experiences
Hmong students, despite facing potential challenges, demonstrate remarkable resilience and academic achievement. Their dedication to education and strong family support often contribute to their success. For example, a focus on family values and the importance of education can motivate students to persevere through difficulties. Furthermore, many Hmong students thrive in environments that celebrate cultural diversity and provide opportunities for them to share their unique perspectives and experiences.
This includes the development of culturally sensitive curricula and extracurricular activities that highlight and celebrate Hmong heritage and traditions.
Creating a Supportive Learning Environment
Creating a supportive and inclusive learning environment is paramount for all students, but particularly for Hmong students. This involves fostering a sense of belonging and ensuring that every student feels valued and respected. The school should actively encourage cultural exchange and understanding, creating opportunities for students to connect with one another from diverse backgrounds. Furthermore, establishing clear communication channels between teachers, students, and families can help address any concerns or challenges promptly.
This includes providing resources for translation and interpretation services, and implementing strategies for understanding different communication styles.
Student Testimonials and Reflections
The following student reflections highlight the importance of inclusivity and cultural understanding within the school environment.
Promoting representation of the Hmong population within the student, staff, and community is crucial. It’s about ensuring everyone feels valued and included. Selling a business, as discussed in five tips for selling a business , requires a similar strategy of building trust and understanding your target audience. Ultimately, successful representation in schools and communities requires a similar focus on connecting with and understanding the needs of the Hmong community.
- “I feel more comfortable sharing my ideas and perspectives in class now that my teachers are more aware of Hmong cultural norms.”
- “The school’s efforts to incorporate Hmong traditions into school events have made me feel more connected to my community and school.”
- “I appreciate the support from my teachers who make an effort to understand my background and learning style.”
These testimonials underscore the impact of a supportive environment on student well-being and academic success. These experiences demonstrate the need for ongoing efforts to create a culturally sensitive and inclusive learning environment for all students.
Policies and Practices
Bridging the gap between policy and practice is crucial for fostering a truly inclusive environment for the Hmong community. Effective policies must not only articulate desired outcomes but also translate those intentions into tangible actions. This section delves into the school’s existing policies related to Hmong representation, identifies potential areas of bias or disparity, and proposes practical steps to enhance equity and support.Current policies, while often well-intentioned, may not always adequately address the unique needs and experiences of Hmong students, staff, and community members.
A critical analysis of these policies, coupled with feedback from the Hmong community, is essential for creating a truly representative and supportive environment.
School Policies Regarding Hmong Representation
Existing policies regarding Hmong representation are often scattered across various documents. These documents may cover topics such as student support services, cultural competency training for staff, and community engagement initiatives. The lack of a centralized, comprehensive policy dedicated specifically to Hmong representation can create gaps in addressing specific needs.
Potential Biases and Disparities in Existing Policies
Reviewing current policies reveals potential biases in areas such as language support, culturally sensitive curriculum development, and access to extracurricular activities. For example, if policies for providing language support are not specifically tailored to the nuances of Hmong dialects or if the curriculum fails to acknowledge the rich historical and cultural contributions of the Hmong people, these can contribute to a sense of marginalization.
A lack of culturally sensitive staff training programs may also result in misunderstandings and communication breakdowns.
Importance of Equitable Policies and Practices
Equitable policies and practices are essential for ensuring that all students, staff, and community members feel valued, respected, and empowered.
“Equity acknowledges historical and systemic inequities and works to level the playing field.”
By actively addressing disparities, schools can create a more welcoming and supportive environment where every member of the community can thrive.
Suggestions for Improving Policies to Support the Hmong Community
Several strategies can enhance the existing policies to better support the Hmong community. These include:
- Developing a comprehensive policy specifically addressing Hmong representation, encompassing areas such as language support, cultural competency training, curriculum development, and community engagement.
- Implementing culturally sensitive staff training programs, focusing on Hmong language and cultural nuances.
- Creating a dedicated Hmong liaison position to facilitate communication and address specific needs within the community.
- Incorporating Hmong perspectives and voices into the curriculum and educational materials.
- Establishing partnerships with Hmong community organizations to foster collaboration and shared decision-making.
Table Outlining Current Policies and Procedures
| Policy Area | Current Policy/Procedure | Areas Needing Improvement |
|---|---|---|
| Language Support | Limited English language support programs | Lack of specific Hmong language support; insufficient training for staff on Hmong dialects. |
| Cultural Competency Training | Occasional workshops | Insufficient training hours; lack of cultural sensitivity training for staff on Hmong culture. |
| Curriculum Integration | Limited integration of Hmong history and culture | Lack of culturally responsive curriculum development; inadequate representation of Hmong figures and experiences. |
| Community Engagement | Sporadic community events | Limited opportunities for consistent Hmong community input; lack of formal channels for feedback. |
| Student Support Services | General student support services | Need for culturally specific support services; addressing specific Hmong cultural needs. |
Community Engagement Strategies
Building strong relationships between the school and the Hmong community is crucial for creating a supportive and inclusive environment for Hmong students. Effective community engagement strategies foster understanding, collaboration, and a sense of shared responsibility for student success. These strategies not only benefit Hmong students but enrich the entire school community.Community engagement is more than just holding events; it’s about establishing ongoing dialogues, respecting cultural nuances, and recognizing the unique strengths and resources within the Hmong community.
This requires a proactive approach that actively seeks input from community members and integrates their perspectives into school policies and practices.
Effective Community Engagement Strategies
Community engagement strategies should be multifaceted and tailored to address the specific needs and priorities of the Hmong community. They should be based on genuine respect, open communication, and a shared commitment to fostering a positive school-community partnership.
- Establishing Communication Channels: Creating multiple channels for communication ensures that information reaches diverse members of the community. This can include establishing a dedicated Hmong language liaison, hosting regular community meetings in both English and Hmong, and using social media platforms popular within the community to disseminate important announcements and updates.
- Community Advisory Councils: Establishing a Hmong community advisory council composed of respected community leaders and parents allows for direct input on school policies, curriculum development, and student support services. This ensures that the voices of the Hmong community are heard and valued.
- Cultural Sensitivity Training: Providing professional development opportunities for staff members on Hmong culture, language, and traditions can foster empathy and understanding. This can include workshops on Hmong values, family structures, and communication styles.
- Leveraging Community Resources: Partnerships with Hmong community organizations, businesses, and leaders can provide valuable resources and support for students. This could include connecting students with mentors, offering tutoring services, or facilitating access to culturally appropriate resources.
- Joint Activities and Events: Organizing joint activities and events with the Hmong community, such as cultural festivals or workshops, can foster a sense of shared identity and belonging. These activities can also provide opportunities for community members to learn about the school’s goals and initiatives.
Building Relationships Between the School and the Hmong Community
Strong relationships are built on trust, respect, and consistent communication.
- Building Trust and Rapport: Initiating interactions with community members through personal visits, attending community events, and participating in cultural activities can help build trust and rapport.
- Open Dialogue and Feedback Mechanisms: Creating opportunities for open dialogue and feedback mechanisms, such as surveys and focus groups, allows for the collection of community input and ensures that concerns are addressed promptly.
- Recognizing and Valuing Cultural Differences: Acknowledging and respecting the unique cultural norms, traditions, and communication styles of the Hmong community is essential. This includes adapting communication styles to accommodate cultural differences.
Leveraging Community Resources for Student Support
Community resources can be instrumental in supporting Hmong students’ academic and social-emotional development.
- Identifying Community Resources: Identifying and documenting relevant community resources, such as local organizations, businesses, and mentors, is essential. This can include Hmong language tutors, community centers, and cultural organizations.
- Collaboration with Community Leaders: Collaborating with respected Hmong community leaders to identify and access relevant resources and services can strengthen the connection between the school and the community.
- Mentorship Programs: Implementing mentorship programs that connect Hmong students with successful Hmong community members can provide valuable guidance and support.
Resources Supporting the Hmong Community
Understanding the existing resources available to the Hmong community is vital.
- Community Centers and Organizations: Local Hmong community centers and organizations often provide a range of services, including language support, cultural programs, and social activities.
- Local Businesses: Local businesses owned and operated by Hmong individuals can provide valuable insights and resources for the community.
- Cultural Liaisons: Cultural liaisons with in-depth knowledge of Hmong culture and language can bridge the gap between the school and the community.
Creating Inclusive Community Events and Activities
Creating inclusive community events and activities requires careful consideration of the Hmong community’s cultural needs.
- Culturally Appropriate Activities: Planning activities that are culturally sensitive and relevant to the Hmong community ensures participation and engagement. This could include incorporating Hmong music, dance, or traditional foods into events.
- Language Accessibility: Ensuring all materials and communication are available in both English and Hmong languages makes the events accessible to all community members.
- Respecting Cultural Norms: Respecting Hmong cultural norms, including family structures and gender roles, is crucial for creating a welcoming environment.
End of Discussion
In conclusion, fostering representation of the Hmong population requires a multifaceted approach that considers historical context, current realities, and ongoing community engagement. This comprehensive analysis provides valuable insights into the challenges and successes, ultimately offering practical strategies for building a more inclusive and equitable environment for Hmong students, staff, and the wider community. By acknowledging the rich history and culture of the Hmong people, we can create a more welcoming and supportive environment for all.






