Sustainable Business Strategies for Resource Savings
Sustainable business strategies to save resources and engage stakeholders lays out a roadmap for companies to operate responsibly. It delves into innovative resource-efficient technologies, optimizing supply chains, and measuring resource consumption. The strategies also cover engaging stakeholders, integrating sustainability into core business models, and measuring and reporting sustainability performance. This comprehensive approach offers a practical guide for businesses seeking to adopt environmentally conscious practices and build strong stakeholder relationships.
From optimizing energy use in manufacturing to building transparent communication channels with stakeholders, this Artikel provides a framework for achieving a greener, more sustainable future for businesses. The core concept revolves around balancing profitability with environmental stewardship and fostering engagement with diverse stakeholders. This is not just about ‘doing good,’ but also about creating a more resilient and prosperous business model for the long term.
Resource Conservation Strategies
Embracing sustainable practices is no longer a choice but a necessity for businesses seeking long-term prosperity. Resource conservation is pivotal in this journey, extending far beyond minimizing waste to encompass innovative technologies and holistic supply chain optimization. A proactive approach to resource management ensures environmental responsibility and fosters stakeholder engagement, ultimately driving profitability and brand reputation.Efficient resource utilization is intrinsically linked to financial sustainability.
By reducing waste and optimizing consumption, companies can lower operational costs and enhance competitiveness. Furthermore, resource conservation strategies contribute to a healthier planet, aligning business practices with societal expectations and attracting environmentally conscious consumers.
Innovative Resource-Efficient Technologies
Advanced technologies are transforming various industries, offering significant potential for resource conservation. In manufacturing, 3D printing is revolutionizing production by enabling customized parts with minimal material waste. Additive manufacturing, for instance, allows for the precise creation of components, reducing the need for excess material and enabling design optimization for weight reduction. Similarly, in agriculture, precision agriculture techniques utilizing sensors and data analytics are optimizing fertilizer and water application, minimizing environmental impact while maximizing yields.
Smart irrigation systems and drought-resistant crops further enhance water efficiency. Transportation benefits from electric vehicles and fuel-efficient engines, leading to a reduced carbon footprint and reliance on fossil fuels.
Optimizing Resource Utilization Across Supply Chains
Effective resource optimization extends beyond individual operations. A holistic approach across the entire supply chain is crucial. Companies can implement strategies like collaborative forecasting and inventory management to reduce material waste and ensure efficient delivery routes. Implementing circular economy principles, as discussed later, can also significantly impact supply chain resource utilization. For instance, companies can explore closed-loop systems where materials are reused or recycled throughout the production cycle, minimizing the need for virgin resources.
This circularity extends to packaging, with initiatives like compostable or reusable packaging options reducing landfill waste.
Framework for Measuring and Monitoring Resource Consumption
A comprehensive framework is essential for tracking resource consumption and evaluating the effectiveness of conservation strategies. This framework should encompass key metrics like water usage, energy consumption, waste generation, and material input. Companies should establish baselines for these metrics and track progress against targets. Regular reporting and analysis can identify areas for improvement and ensure that conservation efforts remain aligned with strategic objectives.
Utilizing real-time data dashboards allows for proactive adjustments and informed decision-making, minimizing potential resource-related risks.
Sustainable business strategies are crucial for saving resources and engaging stakeholders. Innovative solutions are needed to ensure the long-term health of our planet, and this means considering alternative energy sources. For example, the future of sustainable energy looks to alternative materials, like those explored in this insightful piece the future of sustainable energy looks to alternative materials.
Ultimately, these advancements in sustainable energy production will benefit companies committed to resource conservation and stakeholder engagement.
Circular Economy Principles in Sustainable Business Practices
The circular economy model offers a powerful framework for sustainable resource management. This model emphasizes reuse, repair, and recycling of materials, creating a closed-loop system where resources are kept in use for as long as possible. By incorporating circular economy principles, companies can significantly reduce their environmental impact. The key concept lies in shifting from a “take-make-dispose” linear model to a cyclical one where materials are recovered, reused, and repurposed.
This approach minimizes waste and reliance on finite resources.
Sustainable business strategies are crucial for resource conservation and stakeholder engagement. A great example of innovative thinking is highlighted in the recent post “Hello world!” Hello world! , showcasing how businesses can proactively address environmental concerns and build trust with their communities. Ultimately, these strategies are essential for long-term success and a positive impact on the world.
Case Studies of Successful Resource Conservation Measures, Sustainable business strategies to save resources and engage stakeholders
Numerous companies have successfully implemented resource conservation measures. For example, Interface, a flooring manufacturer, has implemented a groundbreaking cradle-to-cradle approach to their production process, emphasizing material reuse and minimizing waste. Similarly, Patagonia, a clothing company, prioritizes recycled materials and emphasizes the durability of their products, extending the lifespan of garments. These examples showcase how sustainable practices can be integrated into core business strategies and contribute to both environmental and financial success.
Comparison of Resource Conservation Techniques
| Technique | Description | Benefits | Implementation Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water Recycling | Treating and reusing wastewater for industrial processes or irrigation. | Reduced water consumption, cost savings, and environmental protection. | High initial investment for treatment plants, potential regulatory hurdles, and operational complexities. |
| Energy Efficiency | Implementing technologies and practices to reduce energy consumption. | Lower energy bills, reduced carbon footprint, and improved operational efficiency. | High upfront costs for new equipment, potential disruption to existing processes, and ongoing maintenance requirements. |
| Waste Reduction | Minimizing waste generation through process optimization, material selection, and product design. | Reduced landfill waste, lower disposal costs, and resource conservation. | Requires significant changes in processes, materials, and product designs, potentially affecting production costs initially. |
Stakeholder Engagement Strategies: Sustainable Business Strategies To Save Resources And Engage Stakeholders
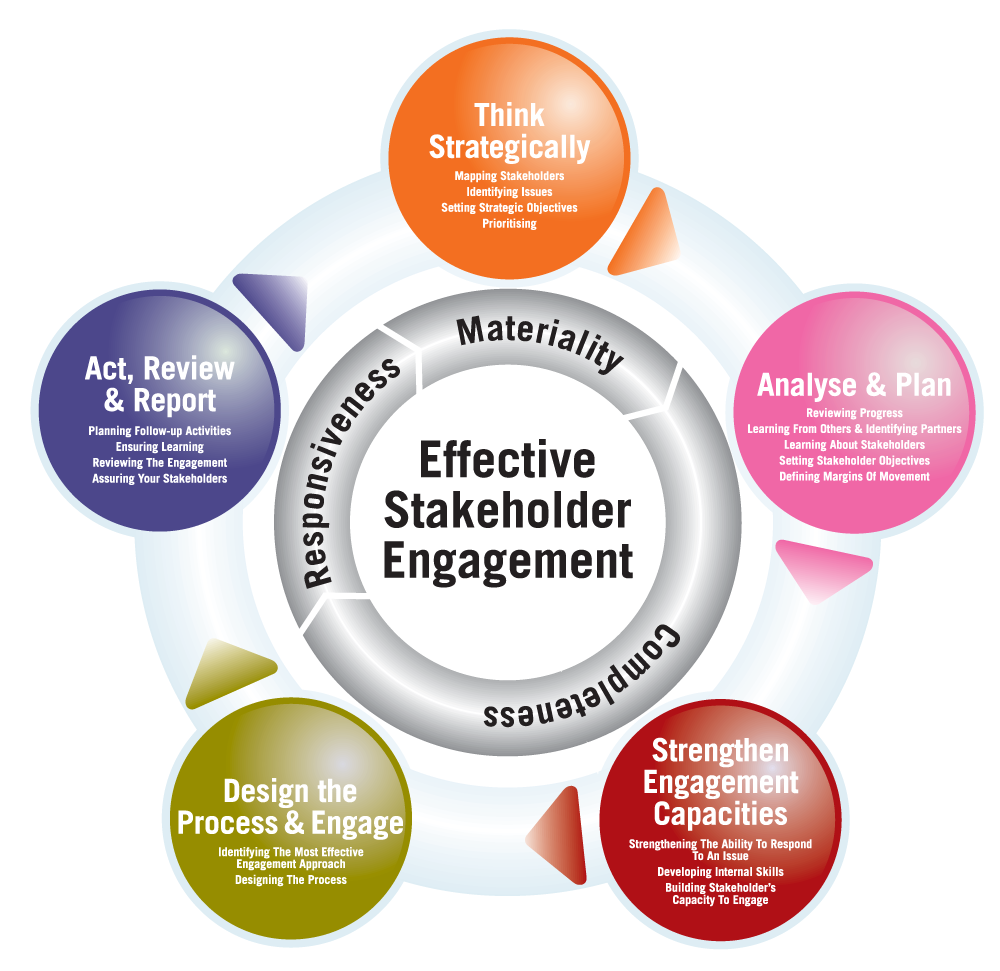
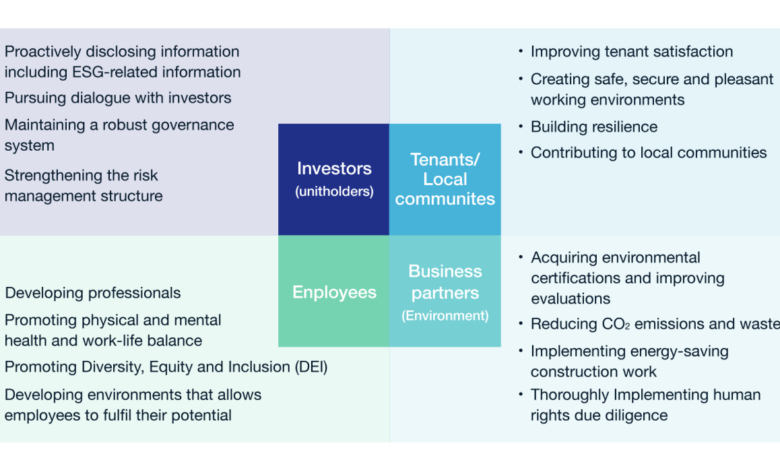
Engaging stakeholders effectively is crucial for the success of any sustainability initiative. A company’s ability to understand and address the concerns of its various stakeholders directly impacts its long-term viability and positive social and environmental impact. This includes employees, customers, investors, communities, and other groups affected by the company’s operations. Successful engagement fosters trust, transparency, and ultimately, a shared vision for a sustainable future.A holistic approach to stakeholder engagement recognizes the diverse perspectives and needs of different groups.
Understanding these perspectives is vital for tailoring communication and action plans that resonate with each stakeholder group. This allows businesses to identify potential conflicts early on and mitigate risks, leading to more effective and sustainable strategies.
Importance of Diverse Stakeholder Perspectives
Understanding the perspectives of different stakeholders is fundamental to creating impactful and sustainable strategies. Diverse perspectives bring a wealth of knowledge and experience that can uncover potential blind spots and enhance problem-solving. Consideration of diverse viewpoints ensures that the strategies reflect a broader range of needs and concerns, leading to more comprehensive and effective solutions.
Methods for Effective Communication
Effective communication is essential for engaging various stakeholder groups. Different methods are required to communicate with different stakeholders. For employees, internal communication channels like newsletters, intranets, and town hall meetings are effective. For customers, clear messaging on product packaging, social media campaigns, and dedicated sustainability websites are crucial. Investors appreciate detailed sustainability reports, presentations, and engagement in investor forums.
Communicating with communities often involves local events, partnerships with community organizations, and transparency about the company’s impact on the local environment.
Strategies for Building Trust and Transparency
Building trust with stakeholders requires transparency and accountability. Regular updates on sustainability progress, clear reporting mechanisms, and open dialogue are essential. Actively seeking feedback from stakeholders and responding to their concerns demonstrates a commitment to transparency. A transparent approach fosters trust, allowing stakeholders to feel heard and valued. Companies should be proactive in addressing any concerns raised, and demonstrating that their actions align with their stated commitments.
Tools and Platforms for Stakeholder Engagement
Various tools and platforms can facilitate stakeholder engagement. Online surveys, feedback forms, and social media platforms are useful for gathering input. Collaboration tools like Slack or Microsoft Teams can create dedicated spaces for stakeholder discussions. Dedicated sustainability portals can provide a centralized platform for information sharing, updates, and engagement. Using these tools, companies can foster a sense of shared responsibility and ownership in achieving sustainability goals.
Comparison of Stakeholder Engagement Models
Different stakeholder engagement models exist, each with its strengths and weaknesses. The “stakeholder dialogue” model emphasizes direct communication and collaboration, while the “materiality assessment” model focuses on identifying issues of most concern to stakeholders. The “multi-stakeholder platform” model creates a forum for different groups to interact and share knowledge. Selecting the appropriate model depends on the specific context and goals of the sustainability initiative.
Communication Channels and Effectiveness
| Stakeholder Group | Communication Channel | Example Message |
|---|---|---|
| Employees | Intranet, newsletters, town hall meetings | “Our new recycling program is helping reduce waste and improve our environmental footprint.” |
| Customers | Product packaging, social media, dedicated website | “Our new product line is made with sustainable materials, reducing our environmental impact.” |
| Investors | Sustainability reports, investor forums, presentations | “Our sustainability initiatives have resulted in significant cost savings and improved operational efficiency.” |
| Communities | Local events, partnerships, community forums | “We are committed to supporting local initiatives and creating positive impacts on the community.” |
Integrating Sustainability into Business Models
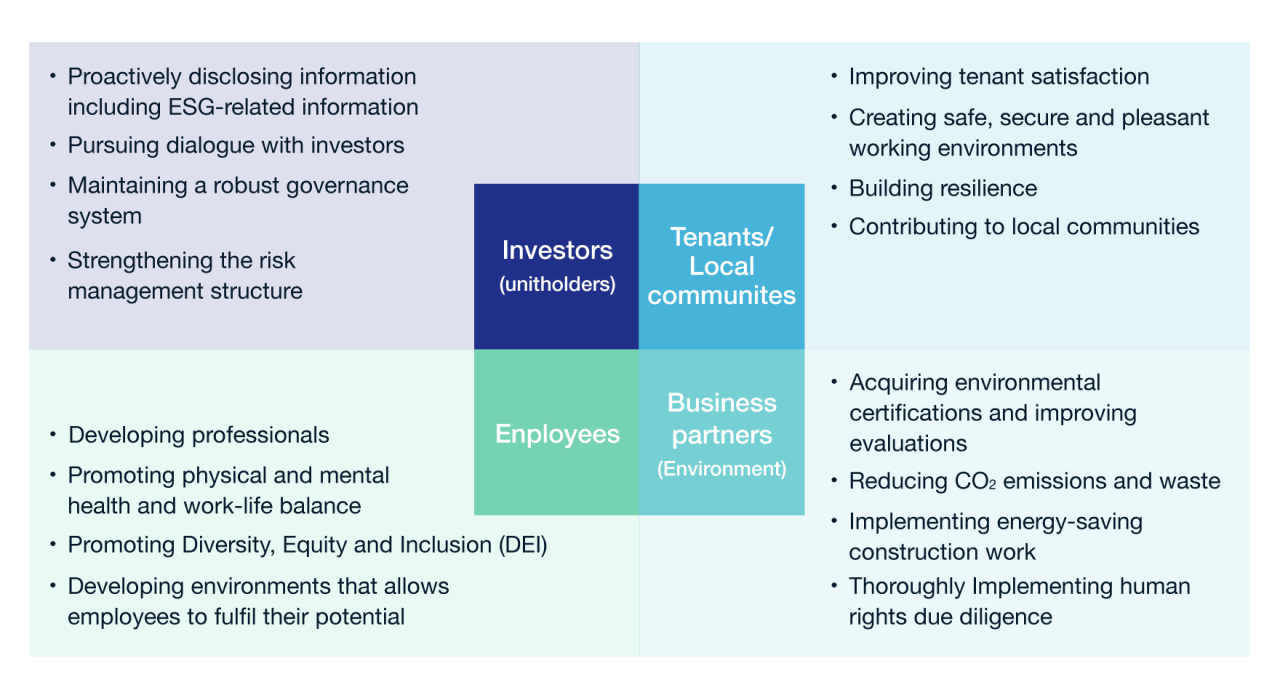
Embracing sustainability is no longer a trend; it’s a necessity for long-term success. Integrating sustainable practices into the core of a business model isn’t just about doing good; it’s about creating a more resilient and profitable future. Companies are increasingly recognizing the potential of sustainability to drive innovation, enhance brand reputation, and unlock new market opportunities.Businesses that successfully integrate sustainability are not only mitigating their environmental footprint but also enhancing their financial performance.
This approach often fosters a culture of innovation, attracting environmentally conscious customers and investors. Sustainable practices can lead to cost savings through resource efficiency, reduced waste, and optimized processes. Ultimately, these practices create a win-win situation, benefiting both the planet and the bottom line.
Examples of Businesses with Successful Sustainability Integration
Several companies have demonstrated that sustainable practices can be profitable and impactful. Patagonia, known for its outdoor apparel, has built a brand around environmental responsibility, from sourcing sustainable materials to minimizing their environmental impact throughout their supply chain. Similarly, Unilever, a large consumer goods company, has set ambitious goals for sustainability across its product portfolio, including reducing their environmental footprint and promoting ethical sourcing.
These examples highlight the potential for businesses to create significant positive change while also enhancing their financial performance.
How Sustainable Business Practices Drive Innovation
Sustainable business practices frequently spur innovation. Companies often discover new, more efficient ways to use resources when they prioritize environmental protection. For example, by reducing their reliance on fossil fuels, businesses can explore alternative energy sources, leading to technological advancements and new revenue streams. This focus on resource efficiency can also lead to the development of innovative products and services that cater to growing consumer demand for sustainable options.
Financial and Non-Financial Benefits of Sustainable Business Models
Sustainable business models offer a range of benefits, extending beyond the financial. Reduced operational costs from resource efficiency, improved brand reputation, and increased customer loyalty are just a few examples of non-financial advantages. Financially, companies often experience increased profitability due to cost savings, access to new markets, and enhanced investor relations. These advantages are increasingly influencing investment decisions, as investors prioritize companies with robust sustainability strategies.
Quantifying the Environmental Impact of Products and Services
Accurate quantification of a product’s or service’s environmental impact is crucial for effective sustainability management. Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) is a powerful tool for evaluating the environmental effects of a product throughout its entire lifecycle, from raw material extraction to disposal. By analyzing the different stages of a product’s journey, businesses can identify areas for improvement and develop strategies to minimize their environmental footprint.
LCA considers factors like energy consumption, water usage, and waste generation.
Metrics for Tracking Sustainability Progress
Tracking the progress of sustainability initiatives is essential for measuring success and identifying areas for improvement. A comprehensive set of metrics should be established to monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) related to resource consumption, waste generation, emissions, and stakeholder engagement. These metrics can include energy consumption per unit of production, water usage per unit of output, and the percentage of waste recycled or reused.
Creating a Sustainability Report
A sustainability report is a crucial communication tool that showcases progress and impacts. The report should clearly articulate the company’s sustainability goals, strategies, and performance metrics. Transparency and clarity are paramount, ensuring that stakeholders understand the company’s commitment to sustainability. The report should highlight both quantitative and qualitative achievements, illustrating the positive environmental and social impact of the company’s actions.
Furthermore, the report should demonstrate how sustainability initiatives are integrated into the core business strategy, thereby creating long-term value for the company and its stakeholders.
Measuring and Reporting Sustainability Performance
Tracking and reporting on sustainability performance is crucial for demonstrating progress, identifying areas for improvement, and ultimately driving positive change. A robust system for measuring and reporting allows businesses to understand their environmental and social impact, set realistic targets, and communicate their efforts to stakeholders, including investors, customers, and employees. This transparent approach fosters trust and encourages accountability.Effective measurement and reporting are not just about meeting regulatory requirements but also about creating a culture of sustainability within the organization.
By systematically tracking key performance indicators (KPIs), businesses can gain a deeper understanding of their environmental footprint and social responsibility initiatives. This insight can then be used to refine strategies, optimize resource use, and create more sustainable business models.
Developing Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Defining meaningful KPIs is essential for accurately reflecting a company’s sustainability performance. KPIs should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). For example, a company focused on reducing its carbon footprint might track energy consumption per unit of production, water usage per product, or waste generation per employee. Other potential KPIs include the percentage of renewable energy used, the number of recycled materials, and the number of employees participating in sustainability training programs.
Importance of Transparent and Verifiable Reporting Mechanisms
Transparent and verifiable reporting is paramount for building trust and credibility with stakeholders. This involves disclosing data accurately and consistently, providing evidence of its authenticity, and making it readily available. Stakeholders need to have confidence in the information presented to ensure the sustainability initiatives are genuine and impactful. Transparency also facilitates constructive feedback and continuous improvement.
Sustainable business strategies are crucial for resource conservation and stakeholder engagement. A great example of this is the Stevens Points Breast Care Center, which recently received redesignation, showcasing how prioritizing community health can be a win-win for both the organization and the environment. By focusing on efficient resource use and transparent communication, businesses can achieve similar positive outcomes, ultimately fostering a more sustainable future for all.
stevens points breast care center receives redesignation demonstrates how proactive steps towards better health care can also contribute to these sustainable practices.
Using Sustainability Standards and Certifications
Adhering to recognized sustainability standards and certifications provides a framework for measuring and reporting performance. Standards like ISO 14001, focusing on environmental management systems, and B Corp certification, assessing a company’s social and environmental performance, offer a structured approach. These frameworks provide benchmarks and best practices that can enhance the reliability and comparability of sustainability data.
Analyzing Data from Various Sources
Sustainability performance assessments require consolidating data from diverse sources. These might include energy consumption records, waste management reports, employee surveys, and third-party audits. Integrating data from different systems can create a comprehensive picture of a company’s sustainability footprint. Data visualization tools can help in presenting complex data in a user-friendly format.
Available Reporting Templates for Sustainability Data
Several organizations provide templates for reporting sustainability data. The Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) Standards offer a comprehensive framework, while the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) standards provide industry-specific guidance. These templates can assist in structuring reports and ensure comparability across companies. Examples include GRI’s Sustainability Reporting Guidelines, SASB’s Materiality Maps, and CDP (formerly Carbon Disclosure Project) reporting frameworks.
Hypothetical Business Sustainability Dashboard
This dashboard tracks key sustainability metrics for “GreenTech Solutions,” a company specializing in eco-friendly technologies.
| Metric | Target | Actual | Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Consumption (kWh) | 100,000 | 95,000 | -5,000 (5% reduction) |
| Water Usage (gallons) | 50,000 | 48,000 | -2,000 (4% reduction) |
| Waste Recycled (%) | 80% | 85% | +5% (Exceeded Target) |
| Employee Sustainability Training | 100% | 98% | -2% (Near Target) |
This simplified dashboard illustrates how to track progress toward sustainability goals. Real-world dashboards would incorporate more metrics, graphs, and visualizations for a more detailed analysis.
Case Studies of Sustainable Business Practices
Diving deep into the real-world applications of sustainable business strategies is crucial for understanding their impact and potential. This section explores successful case studies across various industries, highlighting the challenges overcome, solutions adopted, and factors contributing to their success. By analyzing these examples, we can glean valuable insights and inspiration for developing our own sustainable initiatives.
Case Studies by Industry Sector
Analyzing successful sustainability implementations across different sectors reveals diverse approaches and outcomes. Understanding these variations provides valuable insights into the interplay between specific industry contexts and the effectiveness of sustainable strategies.
Consumer Goods
The consumer goods sector presents a significant opportunity for resource conservation and sustainable practices. Companies are actively seeking ways to reduce their environmental footprint, often focusing on packaging reduction, waste management, and sourcing sustainable materials.
- Patagonia: Renowned for its commitment to environmental activism and sustainable practices, Patagonia prioritizes reducing its environmental impact throughout its entire supply chain. This includes using recycled materials, minimizing waste, and promoting fair labor practices. Their transparent approach to sustainability resonates with consumers, fostering brand loyalty and attracting environmentally conscious customers. Challenges faced included balancing cost-effectiveness with sustainability goals, but their innovative solutions have positioned them as a leader in the industry.
Key factors contributing to their success include a strong commitment to sustainability, transparency with consumers, and a focus on continuous improvement.
- Unilever: Unilever has made substantial strides in sustainability, particularly focusing on reducing its environmental impact throughout its value chain. Their commitment extends to reducing water usage in their manufacturing processes, promoting sustainable agriculture practices, and minimizing waste. Challenges encountered include the complexity of managing a global supply chain, and integrating sustainability into diverse product lines. However, they’ve successfully implemented solutions through partnerships, investments in sustainable technologies, and stringent supply chain audits.
Key success factors include strong leadership support, strategic partnerships, and transparent reporting.
Technology
The technology sector, while often perceived as environmentally intensive, can also be a driver of sustainable solutions. Companies in this sector are actively exploring ways to reduce energy consumption, promote circularity, and utilize renewable energy sources.
- Apple: Apple has been increasingly focused on reducing its environmental impact, from manufacturing processes to product design. They’ve committed to using renewable energy in their facilities, promoting circularity through product repair and recycling programs, and implementing sustainable supply chain practices. Challenges include balancing innovation with sustainability, especially with the need for ever-evolving technology. Solutions include investment in renewable energy sources, collaborations with suppliers to improve their environmental performance, and the development of sustainable materials.
Key success factors include their substantial financial resources, commitment to innovation, and global reach.
- Tesla: Tesla’s core business model is centered around electric vehicles and renewable energy. This direct approach to sustainability makes them a leader in the industry. Challenges faced include the need for large-scale infrastructure development for charging stations and the need for sustainable raw material sourcing. Their solutions include investing heavily in battery technology research and development, and developing sustainable sourcing strategies for materials.
Key success factors include a clear vision, innovative technology, and a strong commitment to renewable energy.
Renewable Energy
The renewable energy sector is experiencing rapid growth, driven by the need for sustainable energy sources. Companies in this sector are actively developing and implementing technologies to generate clean energy.
- SolarCity: SolarCity, now part of Tesla, has been a pioneer in the solar energy industry, promoting residential and commercial solar installations. Challenges included cost-effectiveness of solar energy, and the need for public acceptance. Solutions included developing innovative financing models and engaging communities in the benefits of solar energy. Key success factors include a strong focus on consumer education and the development of innovative business models.
Comparison Table
| Company | Industry | Key Strategy | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patagonia | Consumer Goods | Sustainable materials, waste reduction, fair labor | Increased brand loyalty, environmental leadership |
| Unilever | Consumer Goods | Water reduction, sustainable agriculture, waste minimization | Improved environmental performance, consumer appeal |
| Apple | Technology | Renewable energy, circularity, sustainable supply chain | Reduced environmental footprint, positive brand image |
| Tesla | Technology | Electric vehicles, renewable energy | Market leadership in electric vehicles, renewable energy adoption |
| SolarCity (Tesla) | Renewable Energy | Solar installations, financing models | Increased solar adoption, innovative business models |
Conclusion
In conclusion, implementing sustainable business strategies isn’t just a trend; it’s a crucial step toward a more sustainable future. The strategies discussed, from resource conservation to stakeholder engagement, highlight the importance of integrating environmental considerations into core business operations. By adopting these strategies, companies can not only reduce their environmental footprint but also enhance their brand reputation, attract investors, and create a positive impact on the communities they serve.
Ultimately, this journey toward sustainability fosters a more resilient and profitable future for all.

