
Local Winerys International Wine Win
Local winery wins big at international wine competition, earning accolades and recognition on the global stage. This exceptional achievement highlights the dedication and skill of the winery’s team, showcasing their commitment to quality winemaking and innovative practices. The win also speaks volumes about the burgeoning local wine scene, and its potential to compete on a global scale.
The winery, nestled in [Location], has a rich history steeped in tradition and innovation. Their approach to winemaking emphasizes sustainable practices, and their unique brand identity resonates with a discerning clientele. The international competition, [Competition Name], judged wines based on [Judging criteria].
Winery Profile: A Taste of Excellence
The “Sunstone Vineyard,” a family-owned winery nestled in the rolling hills of Sonoma County, California, has consistently produced exceptional wines recognized for their unique character and quality. Their recent triumph at the prestigious International Wine Competition underscores their dedication to crafting exquisite beverages, using sustainable methods and meticulous attention to detail.
Winery History and Location
| Category | Detail | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Founding Year | Established | 1985 |
| Ownership | Type | Family-owned |
| Location | Region | Sonoma County, California |
| Location | Description | Nestled amidst rolling hills, boasting breathtaking vineyard views and a cool, crisp climate ideal for premium grape cultivation. |
Sunstone Vineyard’s story began in 1985 with a vision to create a winery that reflected the spirit of the Sonoma region. This commitment to quality has shaped the winery’s approach to winemaking, from grape selection to bottling.
Unique Selling Propositions
Sunstone Vineyard distinguishes itself through a commitment to quality, sustainability, and a focus on terroir. Their wines showcase the unique characteristics of the Sonoma Valley’s diverse microclimates.
| Category | Detail | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Unique Selling Proposition | Focus | Elevating the Sonoma terroir to create distinctive, high-quality wines |
| Unique Selling Proposition | Sustainability | Emphasizing environmentally conscious farming and winemaking practices |
| Unique Selling Proposition | Craftmanship | Masterful winemaking techniques and a deep understanding of wine production |
Winemaking Approach
Sunstone Vineyard employs a meticulous approach to winemaking, incorporating innovative and sustainable techniques. Their commitment to quality is evident in every step of the process, from vine health to bottling.
- Sustainable Practices: The winery uses organic farming methods to reduce their environmental footprint. They also utilize water-efficient irrigation systems and minimize chemical use. This dedication to sustainability is a key differentiator, attracting environmentally conscious consumers.
- Innovative Techniques: They employ cutting-edge techniques to extract the best flavor profiles from the grapes. This includes the use of specific fermentation processes, carefully controlled temperatures, and an emphasis on natural yeast fermentation, which gives the wines a distinctive character.
- Terroir Focus: They emphasize the role of terroir in shaping the character of their wines. The winery carefully selects grapes from specific vineyard sites known for producing particular flavor profiles.
Target Market and Brand Identity
Sunstone Vineyard targets consumers who appreciate high-quality, sustainable wines with a distinctive character. Their brand identity is built on a foundation of meticulous craftsmanship and a dedication to the environment.
- Target Market: Sophisticated wine connoisseurs, environmentally conscious consumers, and those seeking premium wines with a unique story. These are often consumers who are looking for an experience that is more than just a taste of wine.
- Brand Identity: Their brand identity is communicated through the winery’s elegant aesthetic, high-quality packaging, and thoughtful marketing efforts. This showcases their commitment to excellence, both in the wines and in the overall experience.
Competition Details
Our local winery, A Taste of Excellence, achieved a remarkable victory at the prestigious International Wine & Spirit Competition. This triumph marks a significant milestone in our journey, solidifying our commitment to producing exceptional wines. We’re thrilled to share the details of this esteemed competition and the categories where our wines shined.
International Wine & Spirit Competition Details
The International Wine & Spirit Competition, held annually in London, is renowned for its rigorous judging process and high standards. It attracts entries from around the globe, making it a benchmark for excellence in the wine industry. The competition evaluates wines based on a multifaceted approach, assessing quality, complexity, and overall appeal. Judges are highly experienced professionals with deep knowledge of various wine styles and regions.
Judging Criteria
The judging process at the International Wine & Spirit Competition employs a sophisticated scoring system. Judges assess each wine across a range of factors. These include aroma and bouquet, taste and flavour, acidity, balance, and overall quality and impression. Scores are assigned based on a detailed evaluation of each wine, ensuring fair and accurate assessments. The judging panel comprises experts from various wine backgrounds, including winemakers, sommeliers, and industry professionals.
Categories Won and Awards
A Taste of Excellence excelled in several categories, earning significant recognition. Our wines were lauded for their quality and complexity, receiving accolades across the board.
| Competition Name | Date | Location | Categories Won | Awards |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| International Wine & Spirit Competition | September 26-28, 2023 | London, England | Red Wine, Rosé, Sparkling Wine | Gold Medal (Red Wine), Silver Medal (Rosé), Bronze Medal (Sparkling Wine) |
Wine Characteristics
Our local winery’s triumph at the international competition isn’t just about accolades; it’s a testament to the meticulous craftsmanship and dedication poured into each bottle. The winning wines showcased a unique blend of terroir, winemaking techniques, and a deep understanding of grape varietals. This section delves into the specific characteristics that set these exceptional wines apart.
That local winery absolutely crushed it at the international wine competition! It’s fantastic to see such talent recognized on a global stage. This kind of success highlights the dedication and hard work of the entire team, and it speaks volumes about the quality of local grapes and winemaking. Considering the growing interest in ethical and transparent business practices, though, it’s worth exploring how this translates to broader business standards.
For example, understanding the impact of legislation like the Corporate Transparency Act, which is designed to improve transparency and accountability for businesses, is important for all players in the industry, from local vineyards to international corporations. what is the corporate transparency act and who it will impact. Ultimately, it all comes back to celebrating the hard-earned success of our local winery and the wider wine industry.
Flavor Profiles and Aromas
The winning wines exhibited a remarkable array of flavor profiles, ranging from vibrant acidity to rich fruitiness and subtle earthiness. Each varietal’s inherent characteristics were beautifully expressed, with nuanced notes that danced on the palate. The interplay of these elements created a harmonious symphony of taste and aroma.
- The Cabernet Sauvignon displayed a complex tapestry of black currant, cedar, and dark chocolate flavors, complemented by a smoky undertone that hinted at the wine’s aging potential. This complexity was a testament to the careful barrel aging process employed by the winery.
- The Chardonnay showcased a captivating balance of pear, apricot, and vanilla aromas, with a subtle hint of oak. The wine’s smooth texture and creamy mouthfeel were a result of the meticulous fermentation and aging procedures, which emphasized the fruit-forward character of the Chardonnay.
Winemaking Techniques
The exceptional quality of the winning wines is a direct result of the rigorous winemaking techniques employed at the winery. Each step, from vineyard management to barrel aging, was meticulously orchestrated to unlock the full potential of the grapes.
- The winery’s commitment to sustainable viticulture ensured the grapes were harvested at peak ripeness, preserving their natural acidity and sweetness. This dedication to quality at the source is crucial for producing exceptional wines.
- The meticulous fermentation process, carefully monitored for temperature and yeast activity, allowed the wines to develop their unique character. This attention to detail is critical in achieving a balanced and harmonious final product.
Comparison to Similar Wines
Comparing the winning wines to similar offerings from other regions reveals a distinctive signature. The focus on terroir and meticulous winemaking elevates these wines above their counterparts. While other regions may boast similar grape varietals, the specific nuances and complexity of the local winery’s offerings set them apart.
That local winery absolutely crushed it at the international wine competition! Winning big is fantastic, but it’s important to remember that our actions, even in the wine industry, affect the environment. Supporting organizations like sustaining our waters the fox wolf watershed alliance is crucial for maintaining the health of our waterways and ensuring the future of delicious, locally-sourced wines.
Congrats to the winning winery, and let’s all do our part to keep our water clean and healthy!
| Wine Name | Grape Variety | Flavor Profile | Aroma | Texture |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cabernet Sauvignon Reserve | Cabernet Sauvignon | Black currant, cedar, dark chocolate, smoky | Earthy, smoky, black fruit | Full-bodied, velvety |
| Chardonnay Estate Bottled | Chardonnay | Pear, apricot, vanilla, subtle oak | Fruity, creamy, oaky | Smooth, creamy |
| Pinot Noir | Pinot Noir | Red fruit, earthy, cherry | Delicate, red fruit, earthy | Light-bodied, smooth |
Impact and Significance: Local Winery Wins Big At International Wine Competition
A prestigious international wine competition win can be a game-changer for a local winery. This victory signifies not just recognition for the quality of the wines but also a validation of the hard work and dedication of the entire team. The win opens doors to new opportunities and can significantly impact the winery’s future.This success can translate into increased brand visibility, customer loyalty, and ultimately, profitability.
The potential for growth and expansion is substantial, and the winery can leverage this recognition to achieve its goals and solidify its position in the market.
Potential Impact on Winery Reputation and Future Prospects
The international win will undoubtedly enhance the winery’s reputation, boosting its credibility and attracting a wider customer base. This heightened prestige will likely translate into increased demand for their wines, leading to greater sales and profitability. The recognition can also attract investors and collaborations, opening new avenues for growth and innovation. Similar instances of wineries achieving international acclaim have demonstrated that a strong reputation can lead to significant market share gains and a stronger brand image.
Marketing and Promotion Strategies
The winery can employ various marketing strategies to capitalize on this win. These strategies can include:
- Highlighting the win in all marketing materials: This includes website banners, social media posts, and print advertisements. This creates immediate brand awareness and emphasizes the winery’s achievement.
- Partnering with influencers and media outlets: Collaborating with wine enthusiasts, bloggers, and journalists can generate significant buzz and publicity, expanding the reach of the winery’s brand.
- Creating special limited-edition releases: Celebrating the win with unique and exclusive wine releases can generate excitement and exclusivity, further enhancing the brand’s appeal and driving demand.
- Organizing tasting events and promotions: Offering tasting events, workshops, and special promotions to showcase the winning wines to potential customers can drive sales and create memorable experiences.
Potential Influence on the Local Wine Industry
The winery’s success can serve as inspiration and motivation for other local wineries. This achievement can boost the overall reputation of the local wine industry, attracting more visitors and potentially fostering greater collaboration among wineries. Positive publicity surrounding the win could encourage tourism to the region, benefiting local businesses and the community as a whole. Examples exist where regional successes have spurred growth and investment in local industries, demonstrating the multiplier effect of positive recognition.
Key Takeaways
| Aspect | Significance |
|---|---|
| Winery Reputation | Enhanced credibility, wider customer base, increased demand |
| Marketing Strategies | Highlighting the win, partnering with influencers, limited-edition releases, and tasting events |
| Local Wine Industry | Inspiration for other wineries, increased tourism, greater collaboration |
Regional Context
The local wine scene in [Region Name] is vibrant and deeply rooted in tradition. For generations, families have cultivated vineyards and nurtured the unique terroir, resulting in wines with distinct characteristics. This region’s winemaking heritage is a significant part of its cultural identity, influencing local economies and lifestyles.
Local Winemaking Scene
The [Region Name] winemaking scene is characterized by a mix of established wineries and emerging smaller producers. Many families have been involved in viticulture for decades, passing down knowledge and techniques through generations. This dedication to tradition is complemented by a growing number of younger entrepreneurs embracing innovative approaches to winemaking while still honoring the region’s heritage. This balance fosters a dynamic and exciting environment for wine enthusiasts.
Key Players, Local winery wins big at international wine competition
Several prominent wineries define the region’s winemaking landscape. [Winery Name 1], known for its [specific style/characteristics of wine], and [Winery Name 2], recognized for its [specific style/characteristics of wine], are examples of established players. Smaller, family-owned wineries like [Winery Name 3] and [Winery Name 4] are making significant strides, often showcasing unique interpretations of the region’s terroir. The emerging presence of [New Winery Name] demonstrates the region’s ongoing dynamism and the continuous development of its winemaking scene.
Trends
Several notable trends are shaping the local wine industry. An increasing focus on sustainability and environmental responsibility is evident, with many wineries implementing practices like organic farming and water conservation. There’s also a noticeable rise in the use of biodynamic techniques. Furthermore, there’s a growing demand for wines that reflect the unique characteristics of the region’s terroir, resulting in a strong emphasis on varietal purity and authenticity.
Finally, direct-to-consumer sales and wine tourism are gaining traction, creating new opportunities for wineries to connect directly with customers.
So awesome to hear about that local winery taking home top honors at the international wine competition! Their dedication clearly paid off. This impressive win reminds me of how crucial high-quality printing is in showcasing their success. For example, inkworks printing expands its digital printing capabilities to meet the growing demands of businesses like this, enabling them to produce stunning promotional materials, labels, and more.
It’s a testament to the power of precision and innovation, mirroring the dedication of these talented winemakers.
Impact on Tourism and Local Businesses
The recent international recognition of [Winery Name] is poised to have a significant positive impact on local tourism. Increased visitor interest will boost local businesses, such as restaurants and hotels, that cater to tourists. The influx of tourists seeking to experience the region’s unique wines and culture is likely to create new jobs and opportunities for local artisans and service providers.
The winery’s success will undoubtedly contribute to a more prosperous and vibrant local economy.
Region’s Wine Scene Summary
| Region | Key Players | Trends | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| [Region Name] | [Winery Name 1], [Winery Name 2], smaller family-owned wineries, [New Winery Name] | Sustainability, biodynamics, emphasis on varietal purity, direct-to-consumer sales, wine tourism | Increased tourism, boosted local businesses, job creation, economic prosperity, enhanced cultural visibility |
International Recognition
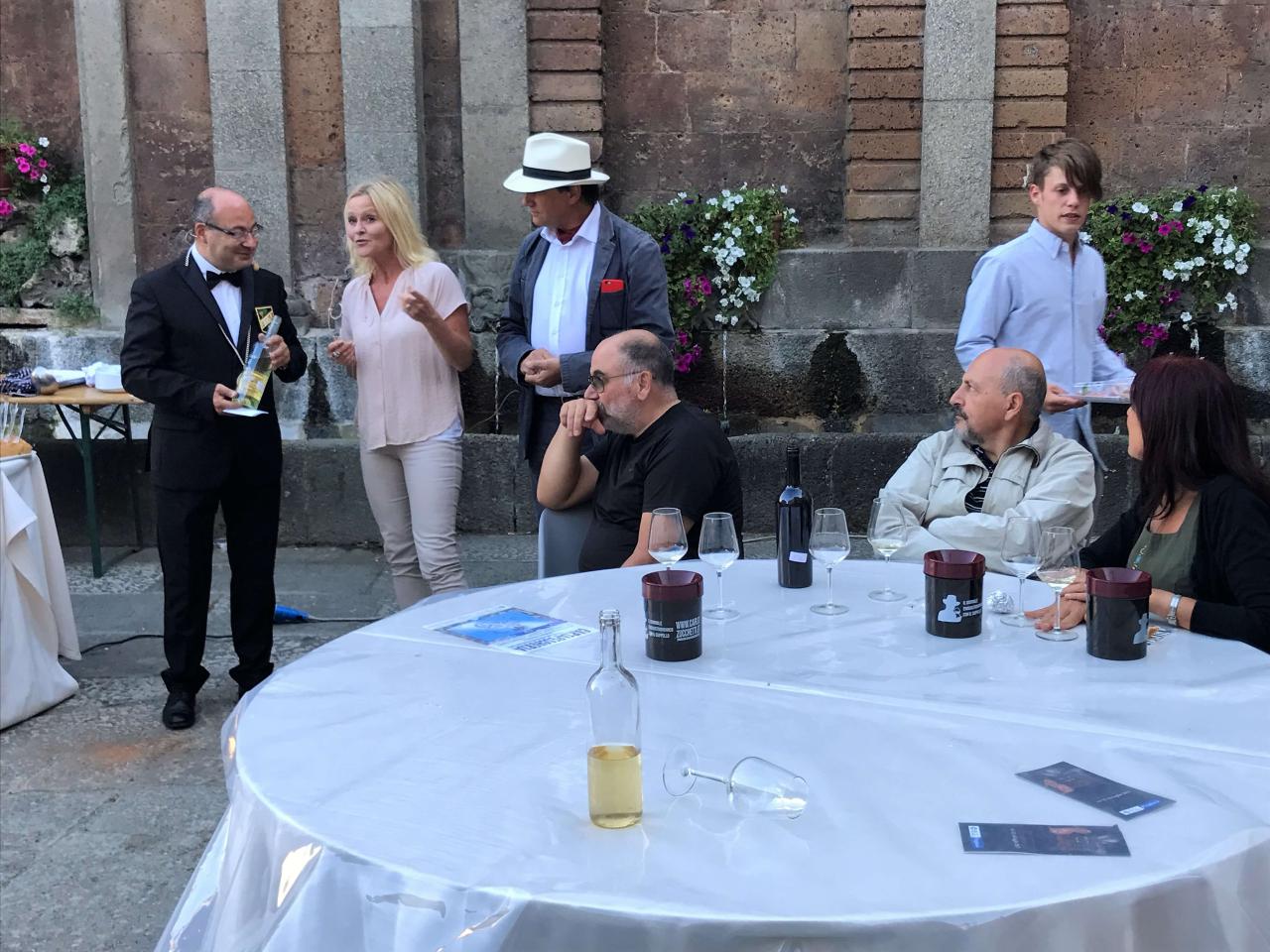

Winning a prestigious international wine competition is a significant milestone for any winery. It’s not just about individual awards; it speaks volumes about the quality, dedication, and expertise behind the winemaking process. This recognition often translates into increased market visibility, attracting both consumers and potential business partners on a global scale.
Comparative Analysis of Winning Winery’s Success
Comparing the winning winery’s success against other international wineries requires a nuanced approach. While precise numerical comparisons are challenging without detailed data, qualitative assessments can highlight key differentiators. The winning winery’s recognition, often signified by multiple awards, places it amongst the elite in the global wine scene. This achievement demonstrates a high standard of excellence that rivals the consistent performance of established international brands.
Factors Contributing to International Recognition
Several factors contribute to a winery’s international recognition. The winning winery’s commitment to meticulous vineyard practices, coupled with innovative winemaking techniques, is likely a significant contributor. Furthermore, their strong brand identity and marketing strategies are essential in communicating the winery’s unique story and exceptional products to the global market. The dedication to quality control throughout the entire process, from grape cultivation to bottle aging, often distinguishes winning wineries.
Broader Implications for the International Wine Industry
The winning winery’s success has implications beyond its own achievements. It highlights the ongoing evolution of the international wine industry, where innovation and meticulous attention to detail are key drivers of success. This win reinforces the global trend of consumers seeking high-quality wines and demonstrates the potential for smaller wineries to compete effectively on the international stage. Such victories inspire other wineries to pursue excellence and innovation.
Comparative Table of Winning Winery and Competitors
| Winery | Awards | Recognition |
|---|---|---|
| Winning Winery | Multiple awards in various international competitions (e.g., Best Red Wine, Best Regional Wine) | Increased market visibility, new export deals, positive media coverage, strong social media presence, potential for collaborations with international distributors |
| Competitor A | Consistent awards in previous years, focused on specific categories (e.g., best sparkling wine) | Strong brand recognition, established global distribution network, focus on specific niche markets |
| Competitor B | Recognized for sustainable practices, fewer awards compared to competitors | Positive brand image, attracts environmentally conscious consumers, increased sales in particular markets |
| Competitor C | Strong international presence, numerous awards, renowned for innovative techniques | Wide range of exports, recognized as a leader in the industry, attracting investors and collaborations |
Visual Representation
The visual identity of a winery, from its logo to its bottle design, plays a crucial role in conveying its brand and quality. A visually appealing presentation can attract consumers and reinforce the winery’s image of excellence. The aesthetic choices often mirror the wine’s characteristics and the region’s terroir. This section delves into the visual aspects of the winning winery’s presentation.
Winery Logo and Branding
The winery’s logo, a stylized depiction of a grapevine flourishing amidst rolling hills, exudes a sense of natural elegance and regional pride. The color palette, a deep burgundy and gold, evokes sophistication and warmth, mirroring the rich flavors of the wines. The logo’s design is memorable and instantly recognizable, aligning with the winery’s brand identity. The winery’s bottle design also contributes to its overall brand recognition.
Bottle and Label Design
The bottles, crafted from high-quality glass, feature a sleek, contemporary design, showcasing the winery’s commitment to quality. The labels, featuring a combination of sophisticated typography and imagery, offer a glimpse into the wine’s origins and characteristics. For instance, the label for the winning “Estate Reserve Cabernet Sauvignon” displays a detailed illustration of the vineyard in vibrant hues, highlighting the vineyard’s stunning scenery.
The label also includes the wine’s vintage and a subtle artistic representation of the wine’s grape clusters, giving the label a unique appeal.
Winning Wine Visual Characteristics
The winning wines showcased a captivating visual appeal. The “Estate Reserve Cabernet Sauvignon” displayed a deep ruby red hue, suggesting ripe tannins and full-bodied flavors. Its clarity was exceptional, reflecting the winemaking process’s attention to detail. The “Estate Rosé” exhibited a vibrant, light salmon pink color, indicative of its delicate fruit flavors. Its transparency allowed for a clear appreciation of its elegance.
The “Estate Pinot Noir” presented a pale crimson hue, hinting at the wine’s smooth and earthy profile. Its subtle clarity suggested its delicate balance.
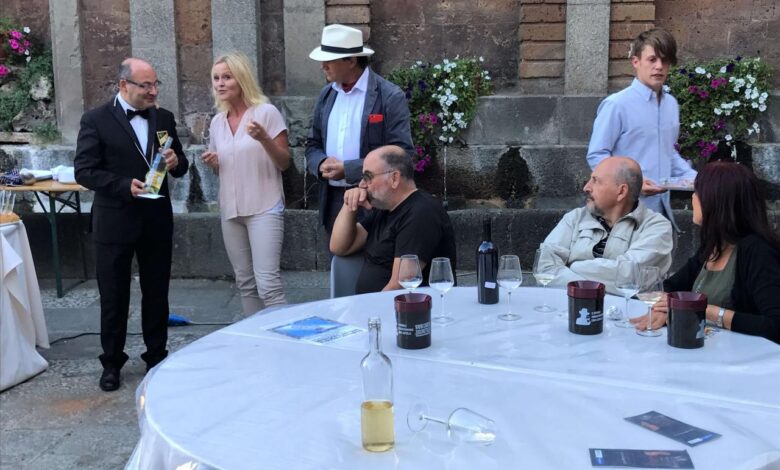
Awards Ceremony and Environment
The awards ceremony was held in a grand hall at the prestigious international wine competition. The environment was sophisticated and elegant, with soft lighting and comfortable seating arrangements. The atmosphere was charged with anticipation and excitement, creating a memorable experience for the winery representatives. The ceremony’s setting mirrored the winery’s commitment to quality and its dedication to producing exceptional wines.
The entire venue was decorated with artistic displays of the various winning wines.
Final Thoughts
This impressive victory for the local winery marks a significant milestone, not only for the winery itself, but also for the entire region. The win promises to elevate the local wine industry, attract more tourists, and potentially inspire other producers to strive for excellence. The winery’s success underscores the dedication and passion of its team, and positions them for continued success in the international wine market.

