
Why Do We Prioritize Strategy Over Talent?
Why do we create a strategic vision but not a talent vision? This question delves into a crucial organizational blind spot, exploring the often overlooked importance of talent development in achieving strategic goals. Many companies meticulously craft their strategic visions, outlining ambitious targets and market positions. However, the human element, the very people who will execute those strategies, often gets short shrift.
This post examines the reasons behind this imbalance and explores how integrating a talent vision can transform organizational success.
A strong strategic vision is essential, but it’s only as good as the people who carry it out. Without a complementary talent vision, a company risks losing valuable employees, hindering innovation, and ultimately falling short of its potential. This exploration delves into the reasons behind this imbalance, identifying the underlying assumptions, cultural factors, and resource allocation challenges that contribute to this disconnect.
We’ll also uncover strategies for bridging this gap and creating a more holistic approach to organizational success.
Defining the Distinction
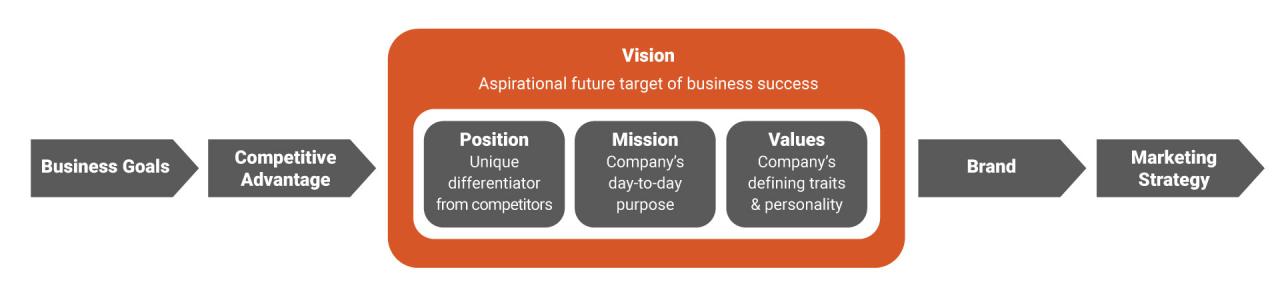
A strategic vision paints a picture of the future direction of an organization, outlining its goals and aspirations. It’s about where the company wants to be, what markets it will target, and how it will achieve its objectives. However, a talent vision focuses on the human capital needed to make that strategic vision a reality. It defines the qualities, skills, and capabilities of the employees required to execute the strategy effectively.
While often intertwined, these two visions are distinct entities requiring different approaches to development and implementation.The strategic vision lays out the “what” and “where,” while the talent vision Artikels the “who” and “how.” A successful organization recognizes that the human element is crucial for translating strategic goals into tangible outcomes. Therefore, a strong talent vision serves as a critical underpinning for realizing the strategic vision.
We often meticulously craft strategic visions, outlining where we want the company to go. But why do we so rarely create a talent vision, a roadmap for developing the people who will get us there? It’s almost like we’re planning the destination without considering the drivers. This lack of talent vision is a missed opportunity, especially when considering selling a business.
To ensure a smooth transition and maximize value, you need a strong team. Understanding the crucial elements of how to sell a business effectively, like these five tips for selling a business , will reveal the need for a detailed talent vision. Ultimately, a clear talent vision is as vital to a successful business as a robust strategic one.
The Core Elements of Strategic Vision
Strategic vision encompasses the organization’s future direction, its desired market position, and the long-term objectives it seeks to achieve. It includes a clear articulation of the company’s values, mission, and core competencies. The process typically involves extensive market analysis, competitor benchmarking, and internal assessment of strengths and weaknesses. A well-defined strategic vision provides a roadmap for decision-making, resource allocation, and innovation across all departments.
Examples include a tech company aiming to become the global leader in AI solutions, or a retail giant striving for sustainable growth through e-commerce expansion.
The Core Elements of Talent Vision
A talent vision defines the ideal employee profile for executing the strategic vision. It Artikels the specific skills, knowledge, and behaviors required to support the organization’s future goals. This vision encompasses the recruitment, development, and retention strategies needed to build a workforce capable of achieving ambitious targets. The process involves identifying critical roles, defining required skill sets, and developing training programs aligned with the strategic objectives.
Examples include a software company focusing on hiring data scientists and machine learning engineers to drive AI innovation, or a financial institution emphasizing adaptability and problem-solving skills in its workforce to navigate the changing financial landscape.
Comparison of Development Processes
Developing a strategic vision often involves a top-down approach, with executive leadership and strategic planning teams driving the process. This frequently involves market research, competitor analysis, and internal discussions to establish long-term goals and strategies. The process usually involves extensive data analysis and external consultations.In contrast, the talent vision often involves a more bottom-up approach. Discussions with department heads, HR teams, and individual employees are vital for understanding the specific skill gaps and needs.
This process is typically more iterative, with continuous feedback loops to ensure alignment with the strategic vision. It often incorporates training and development programs tailored to specific roles and future demands.
Timelines and Resource Allocation
Strategic visions typically have longer timelines, often spanning several years, with a phased approach for implementation. Resource allocation is substantial, involving significant investments in research, development, and infrastructure.Talent visions, while important, often have shorter timelines for implementation, particularly in terms of recruitment and development programs. Resources allocated are frequently focused on training, technology, and HR initiatives that directly support the workforce.
Connection in Successful Organizations
In highly successful organizations, strategic and talent visions are inextricably linked. A well-articulated talent vision ensures that the workforce has the necessary capabilities to execute the strategic plan. This is not just about recruiting the “right” people, but also about providing the training, development, and support to nurture and empower employees to achieve the organization’s goals. A disconnect between these two visions can lead to wasted resources, missed opportunities, and ultimately, a failure to realize the strategic objectives.
For instance, a company might have a compelling vision for global expansion, but lack the skilled international sales teams to execute it effectively. Conversely, a company might have a strong sales team but lack the strategic vision to identify new market opportunities. Successful organizations demonstrate a clear and consistent connection between their strategic and talent visions.
Identifying Underlying Reasons
Prioritizing strategic vision over talent vision in organizations is a pervasive issue, often rooted in misconceptions about talent’s role in achieving strategic goals. This lack of a dedicated talent vision often leads to a disconnect between the organization’s desired future and its ability to create the necessary workforce to achieve it. Understanding the reasons behind this disparity is crucial to fostering a more holistic and effective approach to organizational development.This disparity arises from a variety of factors, ranging from ingrained organizational structures to a fundamental misunderstanding of the interconnectedness between talent and strategy.
Many companies mistakenly believe that a strong strategic vision inherently guarantees the talent to execute it. This narrow perspective ignores the vital role of talent in shaping, adapting, and ultimately, realizing the strategic vision.
Potential Reasons for Prioritizing Strategic Vision Over Talent Vision
Many organizations prioritize strategic vision over talent vision due to a combination of factors. A lack of skilled HR professionals or a limited understanding of talent management best practices can lead to the strategic vision overshadowing the critical needs of the workforce. Further, the complexity and ambiguity of the future talent landscape, with rapid technological advancements and evolving skill requirements, often make it challenging to develop and implement a robust talent vision.
- Focus on External Factors: Many organizations are more focused on external market trends and competitive pressures. This can lead to a lack of attention being paid to the internal capabilities and skill sets necessary to execute the strategic vision effectively. For example, a company might be intensely focused on developing new products based on projected market demand but neglect the need to develop the skills of its engineers to innovate in these new areas.
- Short-Term vs. Long-Term Perspectives: Short-term financial goals and immediate performance targets can often overshadow the importance of building a future-ready workforce. Investing in talent development and acquiring the skills necessary for the long-term strategic vision is often viewed as a less immediate return on investment compared to short-term gains. A good example is a company prioritizing immediate sales targets and potentially compromising employee training and development programs to maximize profits in the short-term.
- Misconceptions about Talent Vision: There are misconceptions about the importance of talent vision, such as the belief that talent vision is simply an HR function and not a strategic imperative. This separation of talent from strategy leads to ineffective integration of the two, potentially hindering overall organizational success.
Common Misconceptions about the Importance of Talent Vision
Often, the significance of a talent vision is underestimated, leading to its neglect. A talent vision is not merely a recruitment strategy; it’s a holistic approach to aligning the organization’s future workforce with its strategic objectives. A common misconception is that talent management is a purely reactive process, responding to immediate workforce needs instead of proactively shaping the talent pipeline for the future.
We often meticulously craft strategic visions for our businesses, outlining ambitious goals and pathways to success. But why do we so often neglect a talent vision? Perhaps it’s because the future of sustainable energy looks to alternative materials, like those explored in this fascinating article the future of sustainable energy looks to alternative materials , demanding a shift in our skillsets and approach.
If we’re serious about adapting to these changes, a talent vision—identifying and developing the right people for the future—is just as critical as a strategic vision. It’s a missing link in many businesses today.
- Talent as a Cost Center: A common misconception is that talent development is a cost center rather than a strategic investment. A well-defined talent vision allows organizations to identify and cultivate talent who are aligned with the organization’s long-term goals. This leads to increased productivity, innovation, and overall organizational success.
- Reactive Workforce Planning: Many companies treat talent planning as a reactive process, addressing immediate staffing needs rather than developing a proactive strategy for the future workforce. This short-sighted approach can result in a gap between the skills needed and the skills available, hindering the execution of the strategic vision.
Examples of Companies Successfully Integrating Talent Vision, Why do we create a strategic vision but not a talent vision
Several companies have successfully integrated talent vision into their strategic planning, achieving significant results. For example, Google’s emphasis on fostering a culture of innovation and continuous learning has cultivated a highly skilled and adaptable workforce, enabling them to remain at the forefront of technological advancements.
- Google: Google’s focus on continuous learning and development, including initiatives like internal training programs and mentorship opportunities, has created a culture of adaptability and innovation within its workforce. This has allowed Google to respond effectively to rapid technological advancements and maintain its leadership in the tech industry.
- Microsoft: Microsoft invests heavily in talent development programs that equip employees with the skills needed to support the company’s strategic goals. This proactive approach has ensured that Microsoft maintains a highly skilled workforce that can meet the evolving demands of the industry.
Potential Risks and Drawbacks of Neglecting Talent Vision
Neglecting a talent vision carries significant risks and drawbacks, impacting both the short-term and long-term success of the organization. This can result in a lack of qualified candidates for crucial roles, leading to project delays and diminished performance.
- Talent Shortages: Organizations that neglect talent vision risk facing critical talent shortages as the demands of the strategic vision increase. The workforce may not have the necessary skills or expertise to execute the strategic plan effectively, potentially resulting in project delays or failure.
- Diminished Innovation: A lack of investment in talent development can stifle innovation and creativity within the organization. A workforce lacking the skills and knowledge to adapt to evolving market demands will struggle to contribute to the company’s innovation pipeline.
Consequences of Focusing Solely on Strategic Vision
Focusing solely on strategic vision without a corresponding talent vision can have serious consequences for an organization. This narrow focus often leads to unrealistic expectations, potentially hindering the ability to achieve strategic goals. The lack of a talent pipeline for future leadership and innovation can lead to long-term organizational decline.
- Unrealistic Expectations: Without a talent vision, organizations may set unrealistic expectations about their ability to execute their strategic vision. This can lead to frustration and disappointment when the necessary talent is not available or possesses the required skills.
- Slowed Growth and Development: Organizations that solely focus on strategic vision may experience a decline in growth and development. Without the right talent, the organization may struggle to innovate, adapt, and compete effectively in the marketplace.
Examining Organizational Culture
Organizational culture plays a pivotal role in shaping an organization’s approach to both strategic and talent visions. It dictates the values, beliefs, and norms that permeate decision-making processes, influencing how resources are allocated and priorities are set. A strong culture that prioritizes talent development fosters a different environment compared to one that primarily focuses on achieving strategic goals. Understanding these cultural nuances is crucial for creating a holistic vision that encompasses both the organization’s long-term objectives and the human capital needed to achieve them.Organizational culture is a complex tapestry woven from shared values, beliefs, and behaviors.
It profoundly impacts the development and implementation of any vision, whether it’s strategic or focused on talent. A culture that deeply values employee growth and development is likely to actively support a talent vision, whereas one primarily focused on short-term gains might overlook the importance of nurturing internal talent. This difference in emphasis often stems from differing leadership styles and communication practices, further shaping the organizational environment.
Impact of Organizational Culture on Talent Vision
A culture that prioritizes talent development fosters an environment where employees feel valued and empowered to contribute their best work. Such cultures typically include opportunities for skill development, mentorship programs, and clear career paths. These elements create a sense of purpose and belonging, which are critical for employee engagement and retention.
We often meticulously craft strategic visions, outlining where we want to be in the future. But why do we neglect a talent vision? Take a look at Oshkosh, for example, where they’re planning a new development near the Fox River oshkosh eyes new development near fox river. This expansion highlights the need for a talent strategy to support the growth.
Without a clear talent vision, how can we ensure we have the right people in place to execute our strategic ambitions? It’s a critical link often overlooked.
Examples of Cultures Prioritizing Talent Development
Several companies are renowned for their commitment to talent development. For instance, Google’s emphasis on continuous learning and development, coupled with its supportive environment, has been cited as a key factor in its success. Similarly, companies like Patagonia, known for their strong environmental values, often integrate these values into employee development programs. These examples demonstrate how a culture that invests in its people can lead to a virtuous cycle of growth and innovation.
Comparing Cultures Supporting Strategic Vision vs. Talent Vision
Organizations prioritizing a strategic vision often emphasize efficiency, productivity, and achieving quantifiable results. These cultures may place less emphasis on individual development and focus more on achieving specific milestones. In contrast, cultures that support a talent vision recognize the long-term value of investing in their human capital. These cultures view employee development as a strategic asset, recognizing the importance of nurturing skills and knowledge for future growth.
The difference lies in the timeframe considered and the resources allocated accordingly.
Leadership Styles and Emphasis on Each Vision
Transformational leadership styles, characterized by inspiring vision and empowerment, are often associated with cultures that prioritize talent development. Such leaders recognize the importance of employee growth and create opportunities for development. Conversely, transactional leadership styles, focused on clear objectives and rewards, may not prioritize talent development as a primary focus. These styles tend to emphasize achieving short-term goals.
The style of leadership significantly shapes the direction and emphasis of the overall organizational vision.
Communication Practices and Vision Integration
Open communication channels are essential for effectively integrating both strategic and talent visions. Regular feedback mechanisms, transparent performance reviews, and clear communication about career development opportunities contribute to a shared understanding of both visions. Conversely, a lack of transparency or inconsistent communication can lead to confusion and disengagement, hindering the integration of both visions. A well-structured communication plan that addresses both strategic goals and talent development is vital.
Analyzing Resource Allocation: Why Do We Create A Strategic Vision But Not A Talent Vision
Strategic visions often receive significant attention and resources, while talent visions are frequently overlooked. This disparity stems from a variety of factors, including differing perceptions of urgency and the complexities of talent management. Understanding how resources are allocated to each reveals crucial insights into the underlying priorities of an organization.
Resource Allocation for Strategic Vision
Resource allocation for strategic vision development typically involves a dedicated budget for market research, competitive analysis, and the hiring of consultants. Time is often allocated to brainstorming sessions, workshops, and executive retreats focused on the vision’s development and implementation. Personnel, such as analysts, strategists, and senior management, are dedicated to these tasks, representing a significant investment of human capital.
| Resource Type | Typical Allocation | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Financial | Significant budget for market research, competitor analysis, and potential acquisition strategies. | $500,000-$2,000,000 for a comprehensive market analysis. |
| Time | Dedicated time for strategy sessions, workshops, and executive retreats. | Multiple days or weeks of dedicated time for senior leadership teams. |
| Personnel | Assignment of dedicated analysts, strategists, and senior management to the vision’s development and implementation. | A dedicated team of 5-10 people, potentially including external consultants. |
Resource Allocation for Talent Vision
In contrast, talent vision development often receives significantly less dedicated funding, time, and personnel. The intangible nature of talent and the difficulty in quantifying its impact contribute to this disparity.
| Resource Type | Typical Allocation | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Financial | Limited budget for training programs, employee surveys, and succession planning. | $50,000-$100,000 for an employee engagement survey and focus groups. |
| Time | Sporadic allocation of time for talent discussions or during team meetings. | A few hours per quarter for a leadership development workshop. |
| Personnel | Limited or no dedicated personnel; talent initiatives are often integrated into existing roles. | A few members of HR or existing managers tasked with talent development. |
Metrics for Measuring Vision Success
Strategic vision success is typically measured through quantifiable metrics such as market share growth, revenue increases, and profitability. Talent vision success is more challenging to measure, often relying on qualitative indicators like employee satisfaction, retention rates, and the development of high-potential talent.
Impact of Resource Allocation on Perceived Importance
The disparity in resource allocation directly impacts the perceived importance of each vision. Strategic visions, backed by substantial resources, are often viewed as crucial to the organization’s future. Conversely, talent visions, often lacking dedicated resources, are sometimes seen as secondary priorities.
Reallocating Resources for a Talent Vision
Reallocating a portion of resources from strategic initiatives to talent development can yield significant returns. By investing in employee training, development programs, and leadership coaching, organizations can build a stronger, more engaged workforce. This investment can translate into improved productivity, reduced turnover, and enhanced innovation. A company that prioritizes talent development will see a more motivated workforce capable of achieving more ambitious goals.
Exploring Potential Solutions
Bridging the gap between strategic vision and talent vision requires proactive steps. Simply acknowledging the gap isn’t enough; we need concrete strategies to integrate talent considerations into existing organizational frameworks. This involves more than just lip service; it demands a shift in mindset and a commitment to action. The successful integration of talent vision fosters a dynamic and adaptable workforce capable of achieving strategic goals.Effective talent management is no longer a supplementary function but a crucial driver of organizational success.
By weaving talent vision into the fabric of strategic planning, companies can unlock untapped potential and achieve sustainable growth. This involves a multifaceted approach, encompassing communication, planning, implementation, and ongoing evaluation.
Successful Strategies for Integrating Talent Vision
Companies successfully integrating talent vision into strategic plans often start by clearly defining the specific skills and capabilities needed to execute their strategic initiatives. This involves a thorough analysis of current talent gaps and future skill requirements. For example, a company aiming for increased market share in a rapidly evolving technological sector might identify the need for data scientists and software engineers.
This, in turn, shapes recruitment strategies and training programs to acquire and develop these critical competencies.
Methods for Communicating the Value of Talent Vision
Effective communication is paramount. Stakeholders must understand how a robust talent vision supports the overall strategic objectives. This can be achieved through presentations, workshops, and internal communications emphasizing how talent development directly contributes to profitability, innovation, and long-term success. For instance, linking specific talent development initiatives to measurable business outcomes—such as reduced project completion times or increased customer satisfaction—provides concrete evidence of the talent vision’s value.
Creating a Roadmap for Developing a Talent Vision
Developing a roadmap requires a structured approach. This involves setting clear goals, outlining actionable steps, and establishing timelines for talent development programs. The roadmap should include a detailed assessment of current talent capabilities, identification of critical skill gaps, and the development of targeted training programs. Furthermore, it should address the need for leadership development to foster a culture of continuous learning and improvement.
A well-defined roadmap ensures that talent development efforts align with the strategic goals and provide measurable results.
Evaluating Current Talent Practices Against the Talent Vision
A structured process for evaluating current talent practices is essential. This involves a comparative analysis of current talent practices against the talent vision. For example, companies can analyze current hiring processes, training programs, performance management systems, and succession planning to ensure they align with the talent vision. This analysis reveals areas requiring improvement, facilitating a targeted approach to talent development.
Embedding Talent Vision into Performance Management and Succession Planning
Integrating talent vision into performance management and succession planning is crucial. Performance management systems should be designed to measure and reward behaviors and skills aligned with the talent vision. Succession planning processes should proactively identify and develop high-potential employees for future leadership roles. For instance, a company aiming to foster innovation might reward employees for creative problem-solving and initiative.
This fosters a culture where talent development is prioritized and recognized.
Illustrating the Impact of Neglect
A strategic vision, outlining the desired future direction, is crucial for organizational success. However, often overlooked is the equally vital aspect of a talent vision, which focuses on the human capital needed to achieve that strategic vision. Ignoring this critical link can have profound and detrimental effects on an organization’s performance and long-term viability.Neglecting a talent vision leads to a disconnect between the organization’s aspirations and its ability to execute them.
This disconnect manifests in various ways, impacting everything from attracting top talent to adapting to market shifts. The consequences can be severe, as illustrated by the struggles faced by companies that prioritize strategy without adequately considering their workforce.
Examples of Organizational Decline Due to Talent Vision Neglect
Several organizations have experienced significant setbacks due to a lack of foresight in talent acquisition and development. One notable example is the decline of a once-dominant retail chain. Their focus on short-term profit maximization led to a lack of investment in employee training and development. This, in turn, resulted in a decline in employee morale, high turnover rates, and ultimately, a loss of market share.
The chain struggled to adapt to evolving customer preferences and lost its competitive edge. Another example includes a technology firm that focused solely on product innovation. They neglected to invest in the development of a skilled engineering workforce, hindering their ability to effectively deliver and support their cutting-edge products. This ultimately led to a decline in market share and customer satisfaction.
Correlation Between Talent Acquisition, Retention, and Organizational Success
A well-defined talent vision directly correlates with a company’s success in attracting, retaining, and developing the right talent. By clearly outlining the skills and competencies needed, companies can proactively seek out individuals who align with their values and long-term goals. This strategic approach to talent acquisition leads to a higher quality workforce, fostering a culture of collaboration and innovation.
Moreover, a strong talent vision is crucial for employee retention. Employees who feel valued and recognized for their contributions are more likely to stay with the organization. This reduced turnover translates into significant cost savings and a more stable, productive workforce. Companies with a robust talent vision are more likely to adapt to changes in the market, allowing them to maintain a competitive advantage.
Strong Talent Vision Fosters Innovation and Adaptability
A well-defined talent vision cultivates an environment conducive to innovation and adaptability. By attracting individuals with diverse perspectives and skill sets, organizations are better positioned to address emerging challenges and opportunities. A strong talent vision also promotes a culture of continuous learning and development, enabling employees to adapt to changing market conditions and embrace new technologies. This continuous learning translates to a more adaptable and innovative workforce, allowing organizations to maintain a competitive advantage in the long run.
Link Between Talent Vision and Organizational Response to Market Changes
A clear talent vision allows an organization to anticipate and respond to market changes effectively. By identifying the skills and competencies needed to navigate future trends, companies can proactively develop and implement strategies to stay ahead of the curve. This proactive approach to talent management enables a smoother transition during periods of market volatility, ensuring a more resilient and adaptable organization.
Detailed Description of a Company’s Decline Due to Lack of Talent Vision
Consider a manufacturing company that initially experienced rapid growth but eventually stagnated and declined. They focused primarily on production efficiency and cost reduction, overlooking the importance of a skilled workforce. Over time, the company struggled to attract and retain skilled engineers and technicians, leading to a decline in the quality of their products and a loss of competitive advantage.
As competitors adopted more advanced technologies, the company struggled to keep up, ultimately facing decreased profitability and market share. The lack of a comprehensive talent vision ultimately contributed to the company’s decline.
Structuring the Content
Defining a clear strategic vision is crucial for organizational success, outlining the desired future state. However, often overlooked is the equally important need for a talent vision, which details the necessary skills and capabilities to achieve that strategic objective. This section will delve into the practical aspects of structuring a comprehensive approach to understanding and addressing the critical gap between strategic and talent visions.
Key Differences Between Strategic and Talent Vision
Understanding the distinctions between strategic and talent visions is paramount to creating a holistic framework for organizational development. A strategic vision focuses on the external environment and future market positioning, outlining the desired trajectory of the organization. In contrast, a talent vision is an internal focus, describing the essential human capital needed to execute the strategic vision. The following table illustrates the core differences:
| Characteristic | Strategic Vision | Talent Vision | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Focus | External environment, market position, future state | Internal capabilities, skills, competencies | Strategic: Becoming a leader in sustainable energy; Talent: Building a team of expert engineers and sustainability specialists |
| Scope | Broad, encompassing the entire organization | Specific, focusing on required talent pool | Strategic: Expanding into new markets; Talent: Developing international sales and marketing teams |
| Timeframe | Long-term, often decades | Medium-term, aligning with strategic goals | Strategic: Becoming a global leader in 10 years; Talent: Developing global expertise in 5 years |
| Measurement | Market share, revenue, brand recognition | Employee skills, engagement, retention rates | Strategic: Increased market share by 20%; Talent: 90% of employees having the necessary skills |
Evaluating Talent Against Vision
Developing methods for evaluating talent against a vision is essential for ensuring alignment and identifying gaps. Effective evaluation methods will provide actionable insights into the workforce’s preparedness to achieve the envisioned future. This table Artikels different evaluation approaches:
| Evaluation Method | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Skill Assessments | Formal testing, skill inventories, or performance reviews to measure current talent skillsets against desired competency levels. | Assessing engineers’ proficiency in renewable energy technologies against desired expertise. |
| Competency Frameworks | Using a structured set of competencies to evaluate talent against the vision. | Employing a framework to assess leadership skills in a team poised for international expansion. |
| Gap Analysis | Identifying the difference between current talent capabilities and those required to meet the vision. | Identifying the skills gaps between current marketing team skills and those required for a new product launch. |
| 360-degree Feedback | Gathering feedback from various stakeholders (superiors, peers, subordinates) to gain a comprehensive understanding of employee strengths and weaknesses. | Collecting feedback on the sales team’s adaptability and collaboration skills. |
Roles in Vision Creation
Identifying the appropriate roles involved in creating both strategic and talent visions is critical for successful implementation. This process requires collaboration across various departments and levels within the organization.
| Vision | Key Roles | Responsibilities |
|---|---|---|
| Strategic Vision | Executive leadership, strategic planning team, market research analysts | Defining the organization’s long-term goals, conducting market analysis, and aligning the vision with external factors. |
| Talent Vision | HR leadership, talent acquisition managers, L&D specialists, departmental heads | Identifying talent needs, designing development programs, and ensuring workforce alignment with strategic goals. |
Creating a Talent Vision Document
A well-structured talent vision document is essential for clear communication and actionable steps. The following process Artikels the key steps:
- Define the Strategic Vision: Clearly articulate the organization’s long-term objectives.
- Identify Talent Needs: Analyze the specific skills, competencies, and experience required to achieve the strategic vision.
- Develop Talent Profiles: Create detailed profiles of ideal talent, outlining required skills and experience.
- Design Development Plans: Artikel training and development initiatives to equip current employees with the necessary skills.
- Establish Performance Metrics: Define key performance indicators to track talent development and progress.
Factors Affecting Vision Creation
Various internal and external factors influence the creation of both strategic and talent visions. Understanding these factors is essential for effective planning and execution.
| Factor | Strategic Vision | Talent Vision |
|---|---|---|
| Market Trends | Influence strategic direction, product development, and expansion plans. | Impacts the skills and competencies required for success. |
| Economic Conditions | Affect resource allocation, investment decisions, and expansion strategies. | Impacts employee compensation, training budgets, and hiring priorities. |
| Technological Advancements | Drive innovation, necessitate adaptation, and shape future opportunities. | Creates new skill requirements and demands upskilling/reskilling. |
| Organizational Culture | Shapes decision-making processes and acceptance of change. | Influences employee engagement, retention, and development opportunities. |
Epilogue
In conclusion, the disconnect between strategic and talent visions highlights a critical gap in many organizations. By understanding the reasons behind this disparity, organizations can begin to address the underlying issues and develop a more holistic approach to talent management. Ultimately, prioritizing talent development isn’t just good HR practice; it’s a strategic imperative for long-term success and sustained growth.
A well-defined talent vision can act as a powerful catalyst for innovation, adaptability, and a stronger overall organizational performance. By integrating talent vision into existing strategic plans, organizations can build a more resilient and successful future.

